Understanding how much two values differ in percentage terms is essential across many fields—finance, science, education, and even everyday decision-making. Whether you're analyzing sales growth, comparing test scores, or assessing changes in temperature, percent difference provides a standardized way to express variation. Unlike percent change, which compares a new value to an old one, percent difference treats both numbers equally, making it ideal for symmetric comparisons. This guide walks you through the concept, formula, calculation steps, and real-world applications so you can compute percent difference accurately and confidently.
What Is Percent Difference?
Percent difference measures the relative difference between two values as a percentage of their average. It’s particularly useful when neither value is considered a “starting” or “ending” point. For example, if you’re comparing the weight of two different objects or the performance of two students on a test, percent difference gives a balanced perspective.
The key distinction between percent difference and percent change lies in symmetry:
- Percent change uses one value as a reference (usually the original), so the result depends on which value comes first.
- Percent difference uses the average of both values as the baseline, ensuring the result is the same regardless of order.
“Percent difference is indispensable when comparing two independent measurements where no clear baseline exists.” — Dr. Alan Reyes, Applied Mathematics Instructor
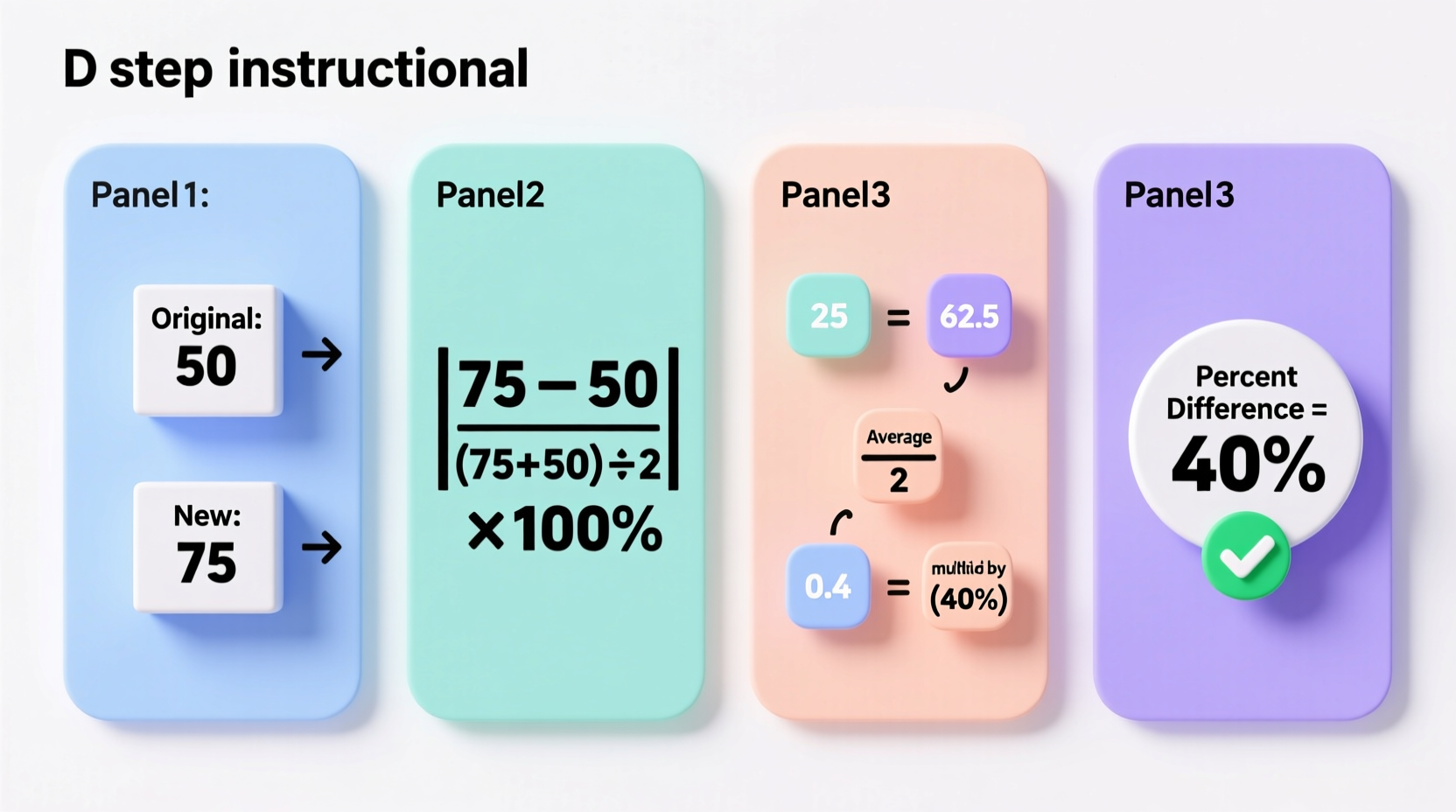
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Percent Difference
Follow these six clear steps to calculate the percent difference between any two numbers. We’ll use a real example throughout: comparing the prices of two smartphones—one priced at $650 and the other at $780.
- Identify the two values
Let’s call them Value A and Value B.
Example: A = 650, B = 780 - Find the absolute difference between the two values
Subtract one from the other and take the absolute value (ignore negative signs).
|A – B| = |650 – 780| = 130 - Calculate the average of the two values
Add the two numbers and divide by 2.
(A + B) / 2 = (650 + 780) / 2 = 1430 / 2 = 715 - Divide the absolute difference by the average
This gives you the relative difference as a decimal.
130 / 715 ≈ 0.1818 - Multiply by 100 to convert to a percentage
0.1818 × 100 = 18.18% - Round if necessary
Depending on context, round to a reasonable number of decimal places.
Final answer: 18.2% (rounded to one decimal place)
Using the Percent Difference Formula
The process above can be summarized into a single mathematical formula:
Percent Difference = ( |A – B| / ((A + B)/2) ) × 100
This formula ensures consistency and accuracy. Let's apply it again using our smartphone example:
| Step | Calculation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Values | A = 650, B = 780 | — |
| Absolute Difference | |650 – 780| | 130 |
| Average | (650 + 780) / 2 | 715 |
| Relative Difference | 130 / 715 | ≈ 0.1818 |
| Convert to Percentage | 0.1818 × 100 | 18.18% |
The result shows that the two phone prices differ by approximately 18.2% relative to their average price. This helps contextualize the gap beyond just the $130 difference.
Real-World Application: Comparing Test Scores
Consider a classroom scenario where two students scored differently on the same exam:
- Student A: 84 points
- Student B: 92 points
To assess how far apart these scores are in relative terms:
- Absolute difference: |84 – 92| = 8
- Average: (84 + 92) / 2 = 88
- Difference ÷ Average: 8 / 88 ≈ 0.0909
- Convert to percent: 0.0909 × 100 = 9.09%
The percent difference is about 9.1%. While the raw score difference is only 8 points, expressing it as a percentage of the average highlights that it represents a moderate gap in performance. Teachers might use this metric to evaluate variability in class outcomes or group students for tutoring based on relative performance spread.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even simple calculations can go wrong without attention to detail. Here are frequent errors and how to prevent them:
| Mistake | Why It’s Wrong | How to Fix It |
|---|---|---|
| Using percent change instead of percent difference | Leads to asymmetric results depending on which value is \"original\" | Use the average-based formula when no baseline is defined |
| Forgetting absolute value | Negative differences distort division and final percentages | Always use |A – B| to ensure positive difference |
| Dividing by one of the values instead of the average | Biases the result toward the smaller or larger number | Always divide by (A + B)/2 |
| Rounding too early | Introduces inaccuracies in final percentage | Keep decimals until the last step |
When to Use Percent Difference vs. Other Metrics
Choosing the right comparison tool matters. Here’s a quick checklist to help decide:
- ✅ Use percent difference when comparing two independent values of equal importance (e.g., two lab results, two product weights).
- ✅ Use percent change when tracking evolution over time (e.g., revenue increased from Q1 to Q2).
- ✅ Use percent error when comparing a measured value to a known or theoretical value (e.g., experimental density vs. accepted value).
Frequently Asked Questions
Can percent difference be more than 100%?
Yes. If one value is less than one-third of the other, the percent difference will exceed 100%. For example, comparing 10 and 90:
|10 – 90| = 80
Average = (10 + 90)/2 = 50
(80 / 50) × 100 = 160%
Is percent difference always positive?
Yes. Because it uses the absolute difference and averages both values, the result is always a non-negative percentage. This reflects magnitude of difference, not direction.
Can I use percent difference for negative numbers?
Proceed with caution. The formula still works mathematically, but interpretation becomes tricky. For instance, comparing -5 and +5 gives a percent difference of 200%, which may be misleading without context. In such cases, consider whether another metric better suits your needs.
Final Thoughts and Action Steps
Calculating percent difference is a straightforward yet powerful skill that brings clarity to comparisons. By focusing on the average of two values and using absolute difference, you gain a balanced view of how far apart they are in relative terms. Whether you're evaluating financial data, scientific measurements, or everyday choices, this method adds precision to your analysis.
To master this technique, practice with real examples from your work or life. Try comparing monthly utility bills, fitness progress metrics, or product prices. Over time, interpreting numerical differences in percentage terms will become second nature.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?