Maven remains one of the most widely used build automation tools in Java development, offering a standardized approach to project structure, dependency management, and lifecycle control. Yet, many developers underutilize its capabilities or run into performance bottlenecks due to inefficient configurations. Whether you're building a small utility or a large enterprise application, optimizing how you run your Maven project can save time, reduce errors, and improve team collaboration.
This guide walks through practical strategies to run Maven projects efficiently—from initial setup to advanced optimizations—so you can build faster, deploy reliably, and maintain consistency across environments.
1. Understand Maven’s Build Lifecycle
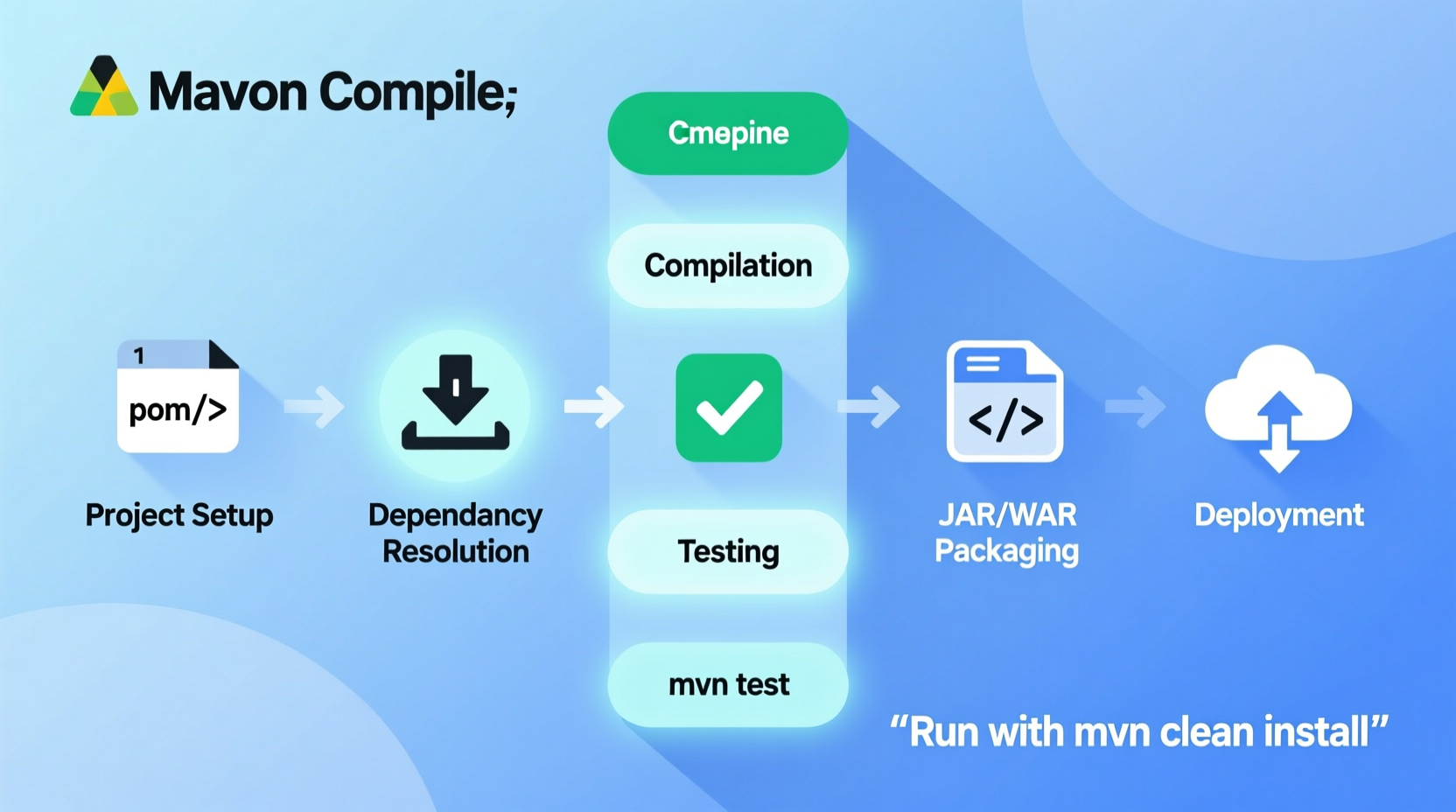
Maven operates on a well-defined build lifecycle composed of phases such as validate, compile, test, package, verify, install, and deploy. Each phase executes in sequence and triggers associated goals from plugins.
Knowing which phase you need helps avoid unnecessary work. For example:
- To compile only:
mvn compile - To package without tests:
mvn package -DskipTests - To install locally for another module:
mvn install
Running mvn clean install is common, but if tests are slow, consider skipping them temporarily during development using -DskipTests or -Dmaven.test.skip=true (the latter skips test compilation too).
mvn help:effective-pom to see the final POM after inheritance and profiles are applied—useful for debugging configuration issues.
2. Optimize Dependency Management
Efficient dependency handling reduces build time and avoids version conflicts. Start by organizing dependencies logically in your pom.xml.
Use the <dependencyManagement> section in parent POMs to centralize versions. This ensures consistency across modules without repeating version numbers.
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
Additionally, remove unused dependencies regularly. Tools like Maven Dependency Analyzer can identify unused or undeclared artifacts.
“Dependency sprawl is one of the top causes of slow builds and security debt.” — Sarah Thompson, DevOps Architect at Redshift Systems
3. Speed Up Builds with Parallel Execution and Caching
Modern multi-core machines can leverage parallel builds. Maven 3+ supports this via the -T flag:
mvn -T 4 clean install– Run with 4 threadsmvn -T 1C clean install– Allocate one thread per CPU core
This can significantly reduce build times in multi-module projects.
Also, take advantage of local repository caching. Once dependencies are downloaded to ~/.m2/repository, they don’t need re-fetching unless versions change. For CI environments, cache this directory between runs to avoid redownloading jars.
-o (offline mode) once dependencies are cached to prevent network calls.
4. Use Profiles for Environment-Specific Builds
Maven profiles allow conditional configuration based on environment (dev, test, prod). Define them in pom.xml or settings.xml.
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>development</id>
<properties>
<env>dev</env>
</properties>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
</profile>
<profile>
<id>production</id>
<properties>
<env>prod</env>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
Activate profiles via command line:
mvn clean install -PproductionThis enables tailored resource filtering, plugin settings, or dependency inclusion per environment—without duplicating code.
5. Streamline Multi-Module Projects
In large applications, modularization improves maintainability. However, inefficient execution can lead to long feedback cycles.
Use the following techniques:
- Selectively build modules:
mvn --projects module-a,module-b clean install - Resume from a specific module:
mvn -rf module-c clean install - Build only changed modules: Enable incremental builds with tools like Takari’s incremental compiler
| Scenario | Command | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Full rebuild | mvn clean install |
Ensures consistency |
| Skip tests | mvn install -DskipTests |
Faster iteration |
| Parallel build | mvn -T 1C install |
Reduced wall-clock time |
| Offline build | mvn -o install |
No network dependency |
Mini Case Study: Reducing CI Pipeline Time
A fintech startup was experiencing 18-minute Maven builds in their CI pipeline for a 12-module application. By analyzing the process, they implemented three changes:
- Enabled parallel builds with
-T 1C - Cached the
~/.m2directory in GitHub Actions - Used selective builds in pull request jobs (
--projects affected-module)
Result: Average build time dropped to 6 minutes—a 67% improvement—without sacrificing reliability.
Essential Checklist for Efficient Maven Execution
Follow this checklist before running any major build:
- ✅ Verify that
pom.xmluses consistent, minimal dependency versions - ✅ Remove unused dependencies with
dependency:analyze - ✅ Enable parallel execution in multi-module projects
- ✅ Cache local repository in CI/CD pipelines
- ✅ Use profiles for environment-specific configurations
- ✅ Skip tests only when appropriate (
-DskipTests) - ✅ Clean selectively—not every build requires
clean
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Even experienced developers fall into traps that degrade performance or introduce instability.
Here are common mistakes:
- Overusing
clean: While safe, it forces recompilation. Reservecleanfor releases or when issues arise. - Hardcoding paths: Makes builds non-portable. Use Maven properties instead.
- Ignoring plugin versions: Always specify versions to avoid unexpected behavior from transitive plugin dependencies.
- Large monolithic POMs: Break into modules with clear ownership and dependencies.
FAQ
How do I reduce Maven build time?
Enable parallel builds with -T, cache dependencies in CI, skip tests when appropriate, and use selective module builds. Also, ensure your hardware has sufficient RAM and fast disk I/O.
What’s the difference between -DskipTests and -Dmaven.test.skip=true?
-DskipTests compiles but doesn't run tests. -Dmaven.test.skip=true skips both compilation and execution of tests—faster but less safe.
Can I run integration tests separately?
Yes. Use the maven-failsafe-plugin bound to the integration-test phase. Run them selectively with mvn verify -DskipITs=false or disable with -DskipITs.
Final Steps: From Development to Deployment
An efficient Maven workflow extends beyond compilation. Automate packaging and deployment using plugins:
maven-compiler-plugin: Set source/target compatibilitymaven-jar-pluginormaven-war-plugin: Package outputmaven-deploy-plugin: Push artifacts to Nexus/Artifactoryexec-maven-plugin: Run apps locally during dev
Example: Run a Spring Boot app directly from Maven:
mvn spring-boot:runThis avoids exporting JARs manually and integrates seamlessly with IDEs.
Conclusion
Running a Maven project efficiently isn’t about memorizing commands—it’s about applying smart practices consistently. From understanding the build lifecycle to leveraging parallelism and caching, each optimization compounds over time, especially in team and CI environments.
Start by auditing your current pom.xml, eliminating bloat, and introducing parallel execution. Then, refine your workflow with profiles and selective builds. Small changes yield measurable gains in speed, reliability, and developer satisfaction.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?