As the search for natural anti-aging solutions grows, collagen has emerged as a key player in maintaining youthful, elastic skin. With visible signs of aging—like fine lines, dryness, and sagging—many turn to dietary interventions to support skin health from within. Two popular options dominate the conversation: hydrolyzed collagen supplements and homemade or store-bought bone broth. But when it comes to boosting skin elasticity, which one delivers better results?
The answer isn’t as straightforward as choosing one over the other. It depends on bioavailability, consistency, nutrient profile, and individual digestive efficiency. This article breaks down the science behind both approaches, compares their effectiveness, and offers practical guidance to help you make an informed decision.
The Science of Collagen and Skin Elasticity
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body, making up about 75% of the skin’s dry weight. It forms a fibrous network in the dermis that provides structure, firmness, and resilience. As we age, collagen production declines by approximately 1% per year after age 20. Environmental stressors like UV exposure, pollution, and poor diet accelerate this loss, leading to reduced skin elasticity and increased wrinkling.
Replenishing collagen through diet can help counteract this decline. When ingested, collagen is broken down into amino acids—particularly glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline—which are then used by the body to rebuild connective tissues, including the skin. However, not all sources deliver these building blocks with equal efficiency.
“Oral collagen peptides have been shown in multiple clinical trials to increase skin hydration, density, and elasticity within 8–12 weeks.” — Dr. Rebecca Tan, Dermatological Nutritionist
Collagen Supplements: Precision and Consistency
Hydrolyzed collagen supplements—also known as collagen peptides—are derived from animal sources (bovine, marine, or chicken) and processed into small, easily absorbed proteins. These peptides are pre-digested, meaning they bypass much of the breakdown required in digestion and enter the bloodstream quickly.
Most high-quality supplements contain Type I and III collagen, the primary types found in skin, hair, and nails. They are flavorless, mix easily into drinks, and offer a standardized dose—typically 10 grams per serving—with consistent amino acid profiles.
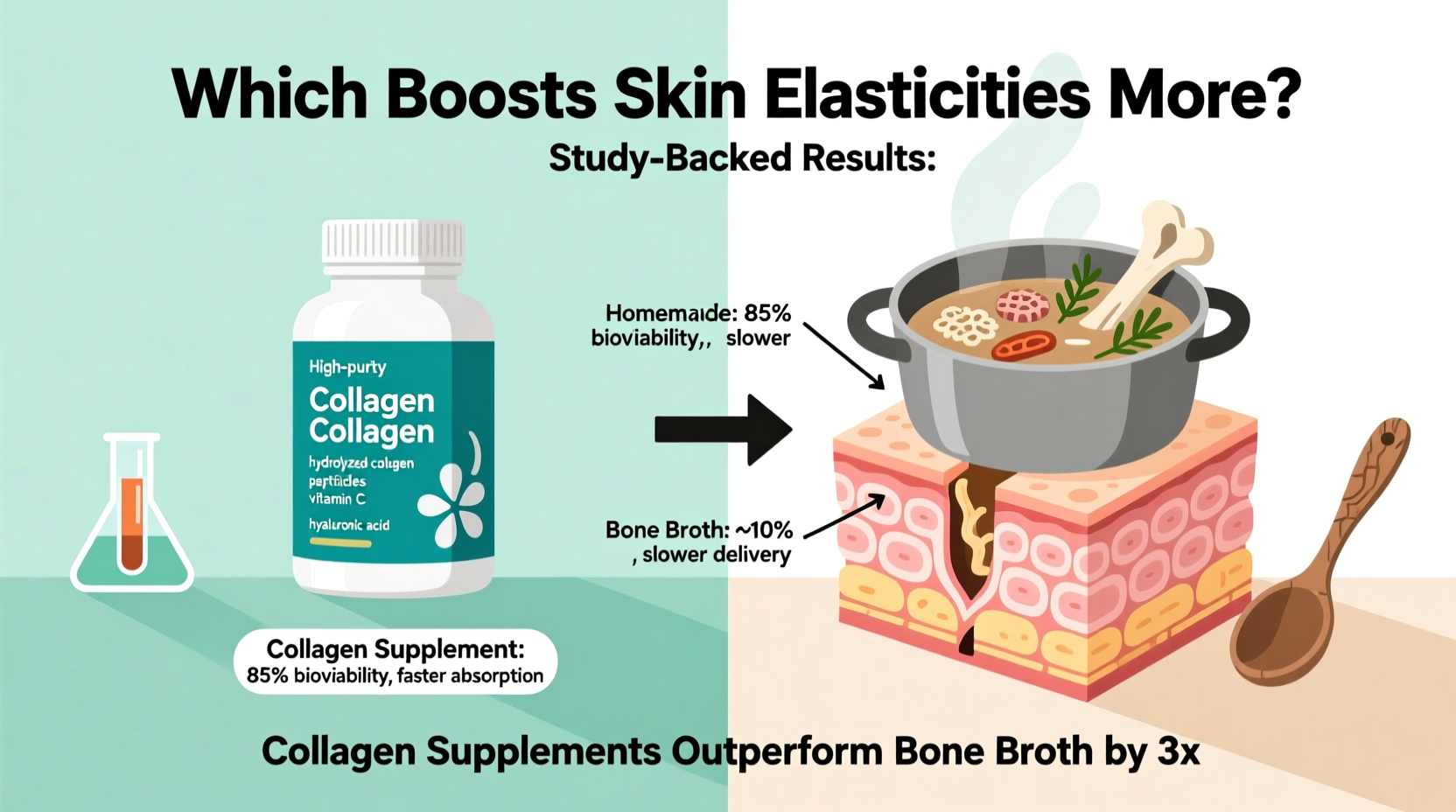
Clinical studies back their efficacy. A 2019 meta-analysis published in Clinics in Cosmetic and Laboratory Medicine reviewed 11 studies and concluded that daily intake of 2.5–10 grams of hydrolyzed collagen significantly improved skin elasticity and moisture levels after 8–12 weeks. Participants reported fewer wrinkles and a more even skin tone.
Advantages of Collagen Supplements
- Bioavailability: Peptides are rapidly absorbed in the gut and distributed to tissues, including the skin.
- Dosage control: Each scoop delivers a precise amount of collagen, ensuring consistent intake.
- Convenience: No preparation needed; easy to incorporate into morning routines.
- Purity: Free from excess fats, sodium, or contaminants when sourced responsibly.
Bone Broth: Tradition Meets Whole-Food Nutrition
Bone broth is made by simmering animal bones (often beef, chicken, or fish) for 12–48 hours, extracting collagen, gelatin, minerals, and other compounds like chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine. It has been used for centuries in traditional diets as a healing food for joints, digestion, and immunity.
When consumed regularly, bone broth provides a natural source of collagen. However, the actual collagen content varies widely depending on preparation methods, cooking time, and ingredients. A typical cup (240 ml) may contain anywhere from 1 to 10 grams of collagen, but rarely reaches the upper end without extended cooking and pressure techniques.
Unlike supplements, bone broth also contains supporting nutrients such as calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and amino acids like glutamine, which promote gut health—an indirect but important factor in skin clarity and inflammation reduction.
Limits of Bone Broth for Skin Elasticity
- Inconsistent dosing: Home-prepared broths vary in collagen concentration.
- Digestive conversion: The body must break down gelatin into usable peptides, which may be less efficient than pre-hydrolyzed forms.
- Time-consuming: Requires hours of simmering and storage planning.
- Sodium content: Store-bought versions often contain high levels of salt, which can dehydrate skin if consumed excessively.
“We see patients who drink bone broth daily but don’t notice skin changes. Meanwhile, those taking peptide supplements report visible tightening in under two months.” — Dr. Alan Zhou, Integrative Dermatologist
Direct Comparison: Supplements vs. Bone Broth
| Factor | Collagen Supplements | Bone Broth |
|---|---|---|
| Collagen Content | Standardized (8–10g per serving) | Variable (1–10g per cup) |
| Bioavailability | High (pre-hydrolyzed peptides) | Moderate (requires digestion into peptides) |
| Nutrient Diversity | Limited (mostly collagen + added vitamins) | High (minerals, gelatin, amino acids) |
| Convenience | Very high (powder or capsule) | Low to moderate (prep/storage needed) |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate ($30–$50/month) | Low to moderate (ingredients + energy cost) |
| Scientific Support for Skin Elasticity | Strong (multiple RCTs) | Anecdotal/limited clinical data |
While bone broth offers broader nutritional benefits, collagen supplements outperform it in delivering targeted, measurable improvements in skin elasticity due to their consistency and bioavailability.
Real-World Example: A 12-Week Skin Transformation
Sarah, a 42-year-old marketing executive, began noticing increased skin laxity around her jawline and under-eye area. She experimented with two approaches over six months. First, she drank 16 oz of homemade beef bone broth daily for eight weeks. While her digestion improved and joint stiffness decreased, she saw minimal change in skin firmness.
She then switched to a marine collagen peptide supplement (10g daily), taken with orange juice for vitamin C. After eight weeks, her dermatologist measured a 14% improvement in skin elasticity using a cutometer. Sarah reported tighter cheeks, reduced under-eye crepiness, and smoother texture overall.
This case illustrates a common trend: while bone broth supports general wellness, targeted supplementation tends to yield faster, more visible results for skin-specific goals.
How to Maximize Results: A Step-by-Step Guide
Whether you choose supplements, bone broth, or a combination, follow this timeline to optimize skin elasticity gains:
- Week 1–2: Choose Your Source
Select a reputable collagen supplement (look for third-party testing) or begin preparing bone broth using pasture-raised bones and vinegar to extract minerals. - Week 3–4: Establish Routine
Take 10g of collagen peptides every morning with 500mg vitamin C, or consume 1–2 cups of bone broth daily. Pair with a balanced diet rich in antioxidants. - Week 5–8: Monitor Early Changes
Look for improvements in skin hydration and reduced flakiness. Take weekly selfies in consistent lighting to track subtle shifts. - Week 9–12: Evaluate Elasticity
Pinch the skin on your cheek and observe how quickly it bounces back. Compare photos and consider professional assessment if possible. - Ongoing: Maintain & Adjust
Continue daily intake. If using bone broth alone and seeing no change, consider adding a supplement for enhanced effect.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I get enough collagen from food alone?
It’s challenging. While foods like bone broth, pork skin, and chicken feet contain collagen, the amounts are inconsistent and often come with high fat or sodium. Achieving the 5–10g daily dose used in studies would require consuming large volumes of specific foods daily—something most people find impractical.
Are there side effects to collagen supplements?
Collagen is generally safe. Some users report mild digestive discomfort, especially with higher doses. Marine collagen may pose allergy risks for shellfish-sensitive individuals. Always consult your doctor if you have kidney issues or autoimmune conditions.
Does it matter what type of collagen I take?
Yes. For skin health, prioritize supplements containing Type I collagen—the dominant type in human skin. Type III supports elasticity too, often found alongside Type I in bovine or marine sources. Avoid products where the type isn’t specified.
Expert Checklist: Choosing the Right Option for You
Use this checklist to decide whether collagen supplements or bone broth—or both—are right for your skin goals:
- ☐ I want visible improvements in skin tightness within 8–12 weeks → Choose supplements
- ☐ I prefer whole-food, traditional nutrition and enjoy cooking → Bone broth is a good fit
- ☐ I have digestive issues or leaky gut symptoms → Bone broth may offer additional gut benefits
- ☐ I value convenience and consistency → Supplements are superior
- ☐ I’m on a budget and can prepare broth at scale → Bone broth may be cost-effective
- ☐ I want maximum scientific backing for skin results → Go with hydrolyzed collagen peptides
Final Verdict: Which Boosts Skin Elasticity More?
The evidence points clearly toward collagen supplements as the more effective option for enhancing skin elasticity. Their standardized dosing, high bioavailability, and strong clinical validation make them a reliable choice for those seeking measurable, visible results.
Bone broth remains a valuable part of a holistic, nutrient-dense diet. It supports overall health—including gut integrity and joint function—which indirectly benefits the skin. However, its inconsistency and lower peptide availability limit its ability to deliver rapid or significant improvements in skin firmness compared to supplements.
For optimal outcomes, consider combining both: use collagen peptides as your primary tool for skin elasticity and include bone broth as a nourishing addition for systemic wellness. This dual approach leverages the precision of science and the wisdom of traditional nutrition.
Take Action Today for Healthier, Firmer Skin
Your skin reflects your internal health, and collagen is a foundational piece of the puzzle. Whether you start with a simple scoop of collagen in your morning coffee or simmer a batch of nutrient-rich broth on the weekend, the key is consistency. Real change happens over weeks, not days. Begin today, track your progress, and give your skin the building blocks it needs to stay resilient and radiant.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?