Sunburn is more than just a temporary discomfort—it’s a visible sign of UV damage that triggers the body’s natural healing process, often culminating in peeling skin. While peeling is a normal part of recovery, it can be itchy, unsightly, and increase the risk of infection if not managed properly. The good news is that with timely intervention and consistent care, you can significantly reduce irritation, speed up healing, and minimize long-term skin damage. This guide outlines proven methods to soothe inflamed skin and prevent excessive peeling after sun exposure.
Understanding Why Skin Peels After Sunburn
When UV radiation penetrates the skin, it damages the DNA in skin cells. In response, the body initiates an inflammatory reaction—what we recognize as redness, heat, and pain. As damaged cells begin to die, the top layer of skin starts to slough off, revealing newer, healthier skin underneath. This shedding process typically begins three to five days after the burn and may last up to a week or more depending on severity.
Peeling itself isn’t harmful, but aggressive removal or poor aftercare can lead to scarring, hyperpigmentation, or secondary infections. The goal isn’t to stop peeling entirely—it’s to support the skin’s natural regeneration while minimizing discomfort and preventing complications.
“Peeling is the body’s way of eliminating severely damaged cells. Forcing the process only increases inflammation.” — Dr. Lena Torres, Board-Certified Dermatologist
Immediate Care: First 48 Hours After Sunburn
The first two days are critical for reducing inflammation and setting the stage for healthy healing. Immediate post-sunburn actions determine how severe the peeling phase will be.
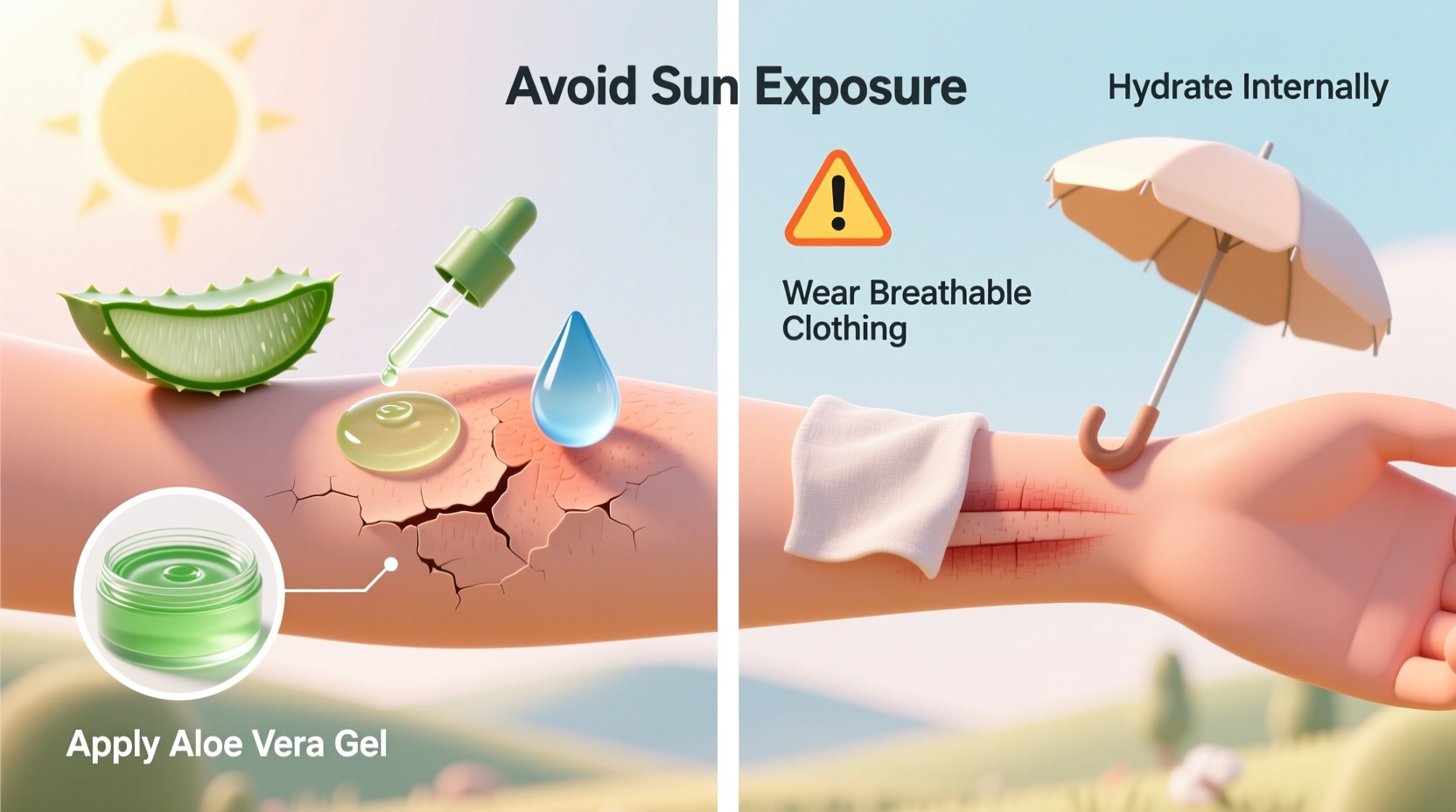
- Cool the skin: Use a cool compress or take a lukewarm bath (not cold) to lower skin temperature. Avoid ice directly on burned areas.
- Hydrate internally: Sunburn draws fluid to the skin’s surface, increasing dehydration risk. Drink plenty of water to support cellular repair.
- Apply aloe vera: Pure aloe gel has anti-inflammatory and moisturizing properties. Choose fragrance-free, medical-grade aloe for best results.
- Avoid irritants: Skip soaps, perfumes, and alcohol-based products that can further dry or sting the skin.
- Do not pop blisters: Blisters protect underlying tissue. Breaking them raises infection risk and delays healing.
Effective Remedies to Soothe Peeling Skin
Once peeling begins, focus shifts from cooling to gentle exfoliation and moisture retention. Harsh scrubbing or picking at loose skin should be avoided at all costs.
- Moisturize with ceramide-rich creams: Products containing ceramides, hyaluronic acid, or glycerin help rebuild the skin barrier and lock in moisture.
- Use oatmeal baths: Colloidal oatmeal reduces itching and calms irritated skin. Add one cup to lukewarm bathwater and soak for 15 minutes.
- Try a hydrating mask: Apply a sheet mask formulated for sensitive skin once daily to deliver intense hydration without friction.
- Wear soft, breathable clothing: Cotton minimizes friction against peeling areas, especially on shoulders, neck, and back.
What to Avoid During Peeling
| Action | Why It’s Harmful |
|---|---|
| Picking or peeling skin | Causes micro-tears, increases infection risk, and may lead to scarring |
| Using exfoliants (AHAs, scrubs) | Removes healthy new skin and worsens sensitivity |
| Hot showers or saunas | Dehydrates skin and intensifies irritation |
| Tight synthetic fabrics | Rubs against fragile skin, causing further damage |
Preventing Future Peeling: A Proactive Skincare Approach
Prevention is always more effective than treatment. Adopting a sun-smart routine reduces the likelihood of severe burns and subsequent peeling.
- Apply broad-spectrum SPF 30+ daily: Even on cloudy days, UV rays penetrate clouds. Reapply every two hours when outdoors.
- Seek shade during peak hours: Between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., UV intensity is highest.
- Wear protective clothing: UPF-rated garments, wide-brimmed hats, and UV-blocking sunglasses add physical protection.
- Check medication side effects: Some antibiotics, acne treatments, and diuretics increase photosensitivity.
- Hydrate skin year-round: Well-moisturized skin recovers faster from environmental stressors.
Real-Life Example: Recovering from a Beach Burn
Sarah, a 29-year-old teacher, spent a weekend at the coast without reapplying sunscreen. By Sunday evening, her shoulders and chest were bright red and painful. She immediately took a cool oatmeal bath, applied aloe vera every four hours, and increased her water intake. On day three, light flaking began. Instead of peeling the skin, she used a ceramide moisturizer twice daily and wore loose cotton shirts. By day seven, the peeling had resolved with no scarring. Her key takeaway? “Staying patient and avoiding temptation to pick made all the difference.”
Step-by-Step Healing Timeline (Days 1–7)
- Day 1–2: Cool skin, hydrate, apply aloe, avoid sun.
- Day 3–4: Begin gentle moisturizing; watch for early peeling.
- Day 5–6: Continue hydration; use non-comedogenic lotions.
- Day 7: Most peeling subsides; resume normal skincare gradually.
For moderate to severe burns with extensive blistering or fever, consult a healthcare provider. These symptoms may indicate second-degree burns requiring medical attention.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I still go in the sun while my skin is peeling?
No. Exposing healing skin to UV rays increases the risk of long-term damage and pigmentation issues. Stay out of direct sunlight until peeling stops and new skin fully matures.
Is it safe to use coconut oil on peeling skin?
Coconut oil can be comedogenic and may trap heat in already inflamed skin. While it has moisturizing properties, it's best avoided during active peeling. Opt for lighter, non-greasy alternatives like hyaluronic acid serums.
How long does peeling usually last?
Most cases resolve within 3 to 7 days. Larger or deeper burns may take up to two weeks. Consistent moisturizing shortens the duration.
Expert Insight: The Role of Nutrition in Skin Recovery
Diet plays a surprisingly significant role in skin repair. Antioxidant-rich foods combat oxidative stress caused by UV exposure.
“Patients who consume vitamin C, E, and omega-3 fatty acids recover faster from sun damage. Think citrus, nuts, spinach, and salmon.” — Dr. Raj Mehta, Nutritional Dermatology Researcher
Essential Post-Sunburn Care Checklist
- ✅ Cool the skin within the first hour
- ✅ Drink extra water for 48 hours
- ✅ Apply aloe vera or hydrocortisone cream (if needed)
- ✅ Moisturize with fragrance-free lotion twice daily
- ✅ Avoid picking or scrubbing peeling areas
- ✅ Wear loose, soft clothing
- ✅ Stay out of direct sunlight until healed
- ✅ Assess sunscreen habits for future prevention
Final Thoughts: Prioritize Long-Term Skin Health
Peeling skin after a sunburn is a clear signal that your body has endured UV stress. While the condition resolves on its own, how you respond determines both short-term comfort and long-term skin integrity. Gentle care, hydration, and patience are far more effective than quick fixes. More importantly, each sunburn increases the risk of premature aging and skin cancer. Protecting your skin isn’t just about avoiding a peel—it’s about safeguarding your health.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?