Mobile connectivity is essential for communication, navigation, work, and entertainment. When your phone displays a connection error—whether it's “No Internet Connection,” “LTE Not Available,” or a persistent spinning Wi-Fi icon—it disrupts daily routines. These errors can stem from hardware glitches, software bugs, carrier issues, or environmental factors. The good news: most problems are fixable without technical expertise. By following a structured approach, you can diagnose and resolve the issue quickly and efficiently.
1. Verify the Nature of the Connection Error
Before diving into fixes, identify the type of connection problem. Is it affecting Wi-Fi only? Cellular data? Or both? This distinction guides your next steps.
- Wi-Fi error: Phone connects to the router but shows no internet access.
- Cellular error: No signal bars, “Emergency Calls Only,” or slow/no data despite signal.
- Intermittent drops: Connection works briefly then fails repeatedly.
Determining the scope helps avoid unnecessary resets or repairs. For example, if only one app fails to load, the issue may lie with the app—not your network.
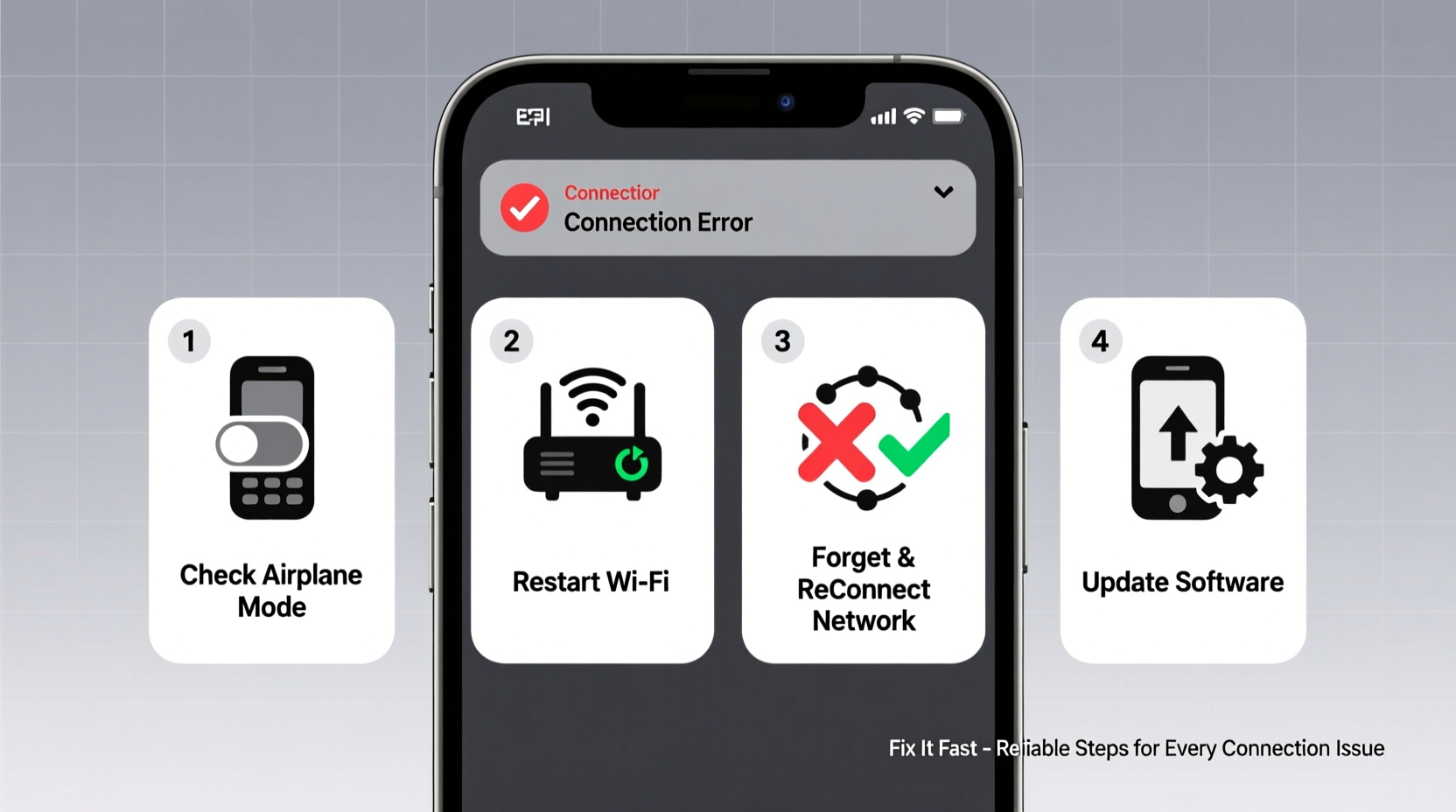
2. Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
Follow this logical sequence to isolate and fix the root cause:
- Toggle Airplane Mode – Turn on Airplane Mode for 15 seconds, then disable it. This forces the phone to re-establish network connections.
- Restart the Device – A reboot clears temporary software glitches affecting network services.
- Check Network Settings – Ensure Wi-Fi or Mobile Data is enabled. On iOS, go to Settings > Cellular; on Android, Settings > Network & Internet.
- Forget and Reconnect to Wi-Fi – In Wi-Fi settings, select your network, tap \"Forget,\" then reconnect by entering the password.
- Verify Date & Time Settings – Incorrect time can break secure connections (HTTPS). Enable “Set Automatically” in Date & Time settings.
- Reset Network Settings – This clears saved networks, Bluetooth pairings, and APN configurations. Use cautiously: Settings > General > Reset > Reset Network Settings (iOS) or Settings > System > Reset Options > Reset Wi-Fi, mobile & Bluetooth (Android).
This sequence resolves over 70% of common connection errors, according to mobile support technicians at major carriers.
3. Common Causes and Targeted Fixes
Different environments and usage patterns lead to different issues. Below is a breakdown of frequent culprits and their solutions:
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Connected to Wi-Fi but no internet | Router not passing traffic, IP conflict | Restart router, renew IP via DHCP, or assign static IP |
| No cellular signal indoors | Poor building penetration, weak tower coverage | Use Wi-Fi calling, install signal booster, or contact carrier for microcell |
| Phone shows full bars but slow speeds | Network congestion, throttling, or background apps | Limit background data, close bandwidth-heavy apps, test during off-peak hours |
| Connection drops after screen lock | Power-saving settings | Disable battery optimization for network services or Wi-Fi sleep policy |
“Over half the ‘no connection’ cases we see are due to misconfigured power settings that shut down radios too aggressively.” — David Lin, Senior Support Engineer at T-Mobile
4. Real-World Example: Resolving Persistent Wi-Fi Drops
A freelance graphic designer in Chicago reported her iPhone kept disconnecting from home Wi-Fi while uploading large files. She could browse emails but lost connection during file transfers. Initial troubleshooting failed: restarts, toggling Wi-Fi, and checking passwords didn’t help.
The solution emerged when she tested with another device. Her laptop stayed connected—indicating the router wasn’t at fault. Further inspection revealed her iPhone had an outdated DNS setting from a previous network. After resetting network settings and switching to Google’s public DNS (8.8.8.8), uploads completed without interruption.
This case underscores the importance of isolating variables: device vs. network, single-app vs. system-wide failure, and configuration history.
5. Expert Tips and Prevention Checklist
Preventing future errors is as important as fixing current ones. Follow this checklist to maintain reliable connectivity:
- ✅ Keep your phone’s OS updated to patch known network bugs.
- ✅ Avoid third-party Wi-Fi analyzers or boosters that may interfere with radio signals.
- ✅ Disable “Auto-Join” for unreliable public networks to prevent accidental connections.
- ✅ Use dual-SIM phones wisely—ensure correct SIM is set for data if both are active.
- ✅ Periodically reset your router (once a month) to clear memory leaks and refresh IP assignments.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does my phone show Wi-Fi connected but say “No Internet”?
This usually means your device has joined the local network but cannot reach the internet. Causes include router firmware issues, ISP outages, or captive portals (like hotel logins). Try opening a browser to trigger a login page or restart the router.
Can a faulty SIM card cause connection errors?
Yes. A damaged or improperly seated SIM can prevent cellular registration. Remove and reinsert the SIM, clean the tray, or request a replacement from your carrier. Test with another phone if possible.
Does clearing cache improve network performance?
Clearing app cache doesn’t directly fix network errors, but corrupted caches in system apps like Android’s Connectivity Services can interfere. Use “Clear Cache Partition” in recovery mode (Android) or reset settings (iOS) for broader effect.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Connection
Connection errors don’t have to mean downtime. With methodical testing and informed adjustments, most issues can be resolved in under 15 minutes. Start simple—restart and toggle settings—then progress to deeper diagnostics like network resets or DNS changes. Pay attention to patterns: if problems recur in specific locations, the issue may be environmental. Stay proactive with updates and maintenance to keep your mobile experience seamless.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?