Google Maps is an essential tool for navigation, local discovery, and route planning — even on a MacBook. But when it shows your location inaccurately, it can derail everything from finding nearby cafes to estimating commute times. Unlike smartphones with built-in GPS, MacBooks rely on Wi-Fi triangulation and browser-based geolocation services, making them more prone to errors. The good news? Most location inaccuracies are fixable with the right steps.
This guide walks through actionable, tested methods to correct Google Maps’ wrong location detection on your MacBook. Whether you're working remotely, traveling, or simply trying to locate a business near you, these solutions restore precision without requiring technical expertise.
Why Google Maps Shows the Wrong Location on MacBook
MacBooks don’t have dedicated GPS chips. Instead, they determine location using nearby Wi-Fi networks, IP address data, and browser permissions. This method works well in urban areas with dense network coverage but can falter in rural zones, multi-story buildings, or after network changes.
Common causes of incorrect location include:
- Outdated or cached geolocation data
- Incorrect Wi-Fi positioning due to router movement or ISP routing
- Browser permission issues blocking accurate access
- Firewall or privacy settings interfering with location services
- DNS or network configuration distorting IP-based location
Understanding these factors helps target the right fix — not just mask the symptom.
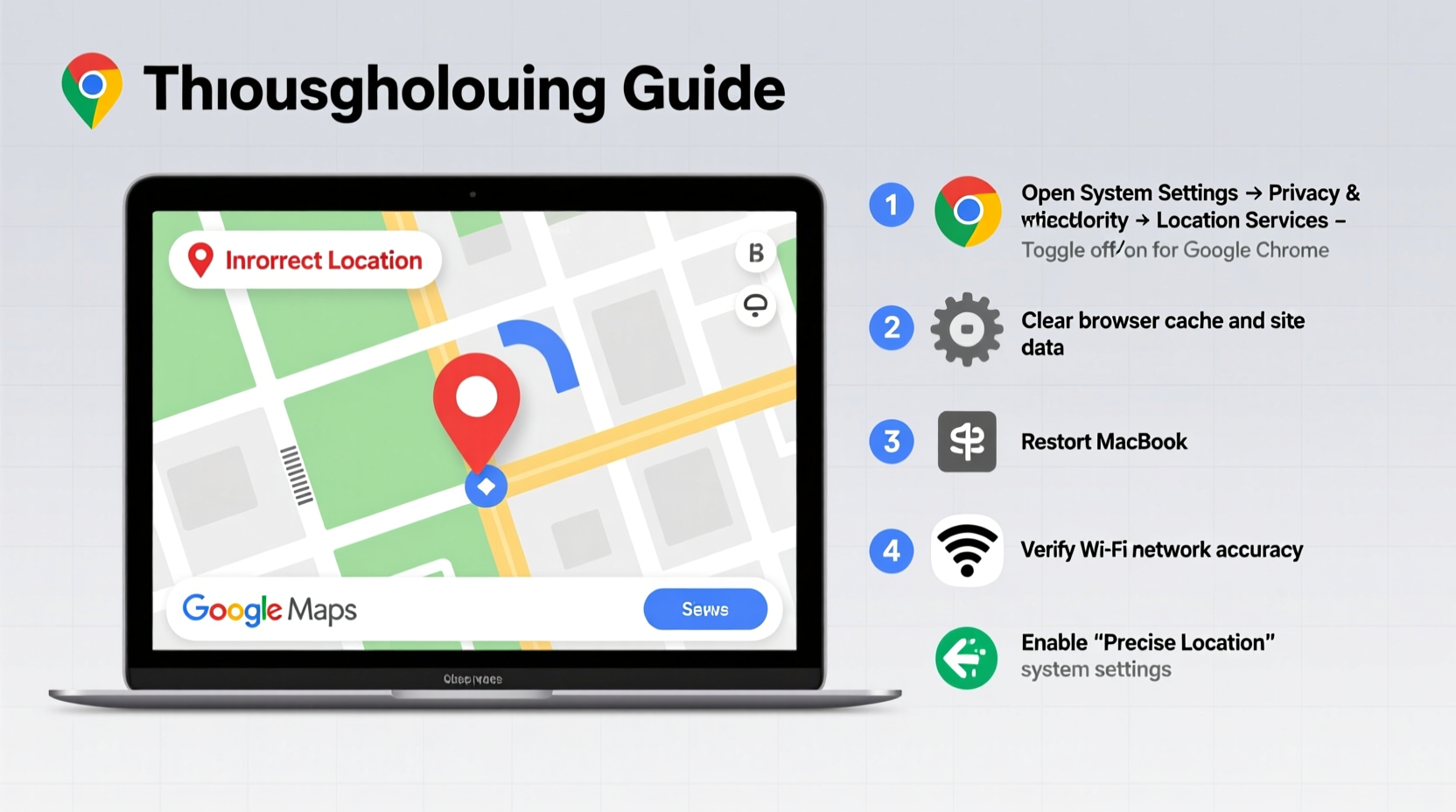
Step-by-Step Guide to Fix Location Accuracy
Follow this structured approach to systematically resolve location errors in Google Maps on your MacBook.
- Refresh Your Network Connection
Restart your Wi-Fi. Disconnect and reconnect to your network. If possible, switch to a different Wi-Fi network temporarily to test if location updates correctly. - Verify Browser Permissions
In Safari or Chrome, ensure Google Maps has permission to access your location:- Go to System Settings > Privacy & Security > Location Services.
- Ensure Location Services is turned on.
- Scroll down and confirm your browser (e.g., Safari, Chrome) is checked.
- Clear Browser Location Cache
Browsers store past geolocation decisions, sometimes reusing outdated positions.- In Chrome: Go to
chrome://settings/content/location, find maps.google.com, and click “Remove”. - In Safari: Safari doesn’t allow per-site location cache deletion, so reset by toggling Location Services off/on at the system level.
- In Chrome: Go to
- Force-Refresh Google Maps with Permission Reset
Visit Google Maps, click the lock icon in the address bar, and set location access to “Ask” or “Allow.” Reload the page and permit location sharing when prompted. - Use Incognito/Private Mode for Testing
Open an incognito window (Chrome) or private window (Safari), go to Google Maps, and check if the location is now accurate. This bypasses extensions and cached data. - Check Your IP Geolocation
Visit whatismyipaddress.com to see what location your public IP suggests. If it’s far from your actual city, your ISP may be routing traffic through distant servers — common with certain broadband providers or VPNs. - Disable VPN or Proxy Temporarily
Even inactive or background proxy tools can misroute geolocation signals. Turn off any active VPN and retry Google Maps.
Do’s and Don’ts: Maintaining Accurate Location
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Keep Wi-Fi enabled, even when using Ethernet — it aids location accuracy. | Ignore repeated “Location Not Available” warnings — they indicate deeper permission issues. |
| Regularly update macOS to ensure geolocation databases stay current. | Assume location errors are permanent — most are temporary and resolvable. |
| Use Google Maps in updated browsers like Chrome or Safari with JavaScript enabled. | Store sensitive location data in third-party extensions that override system settings. |
| Test location accuracy monthly if you travel or work across regions. | Disable Location Services entirely to “fix” one app — it breaks functionality system-wide. |
Mini Case Study: Remote Worker in Boulder Facing Location Drift
Sophie, a freelance designer in Boulder, Colorado, relied on Google Maps to schedule client meetups and manage deliveries. One Monday, she noticed Maps placed her in Denver — 30 miles away. Her clients received incorrect availability based on timezone assumptions.
She first checked her Wi-Fi and restarted her router. No change. Then she opened System Settings and found Chrome had been accidentally deselected in Location Services during a recent update. Re-enabling it restored accurate positioning within two minutes.
The root cause? A macOS update reset application-level permissions. Sophie now audits her location settings after every major OS patch — a five-second habit that prevents recurring issues.
“Location accuracy on laptops hinges on consistent permissions and fresh network data. It's not magic — it's maintenance.” — Raj Patel, Senior UX Engineer at a mapping technology firm
Troubleshooting Checklist
Use this checklist whenever Google Maps displays an incorrect location:
- ✅ Restart Wi-Fi and reconnect to your network
- ✅ Confirm Location Services is enabled in System Settings
- ✅ Verify your browser is allowed in Location Services
- ✅ Clear location permissions for maps.google.com in your browser
- ✅ Test Google Maps in an incognito/private window
- ✅ Check your public IP’s geolocation via third-party site
- ✅ Disable any active VPN or proxy software
- ✅ Ensure macOS is up to date (Settings > General > Software Update)
- ✅ Manually search your city on Google Maps as a fallback
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I improve location accuracy without Wi-Fi?
No — MacBooks require Wi-Fi to estimate location. Even with cellular data via hotspot, the MacBook itself uses Wi-Fi signals for positioning. Turning off Wi-Fi disables location services entirely.
Why does Google Maps show a different location on my MacBook vs iPhone?
iPhones have GPS hardware and motion sensors that provide precise real-time location. MacBooks depend on environmental data like nearby networks. While both use similar services, the iPhone’s dedicated hardware gives it superior accuracy.
Does clearing browser cache fix wrong location?
Partially. While general cache clearing helps performance, only resetting location-specific permissions forces Google Maps to request fresh data. Simply clearing history won’t solve persistent inaccuracies.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Digital Location
Google Maps’ location errors on MacBook aren’t inevitable — they’re manageable. With the right combination of system settings, browser hygiene, and network awareness, you can maintain reliable accuracy. The key is understanding that location isn’t a single setting but a chain of permissions, connections, and data sources.
Don’t wait for the next misplaced pin to disrupt your plans. Audit your location settings today. Apply the checklist, verify permissions, and test across browsers. Small habits prevent big frustrations.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?