Calculating the height of a pyramid might seem like a challenge reserved for archaeologists or mathematicians, but it’s a practical skill applicable in architecture, engineering, education, and even DIY projects. Whether you're analyzing the Great Pyramid of Giza or designing a model for a school project, understanding how to determine a pyramid's height with precision is essential. This guide walks through multiple methods—using geometry, trigonometry, and field measurements—to help you compute the vertical height of any pyramid, regardless of size or complexity.
Understanding Pyramid Geometry
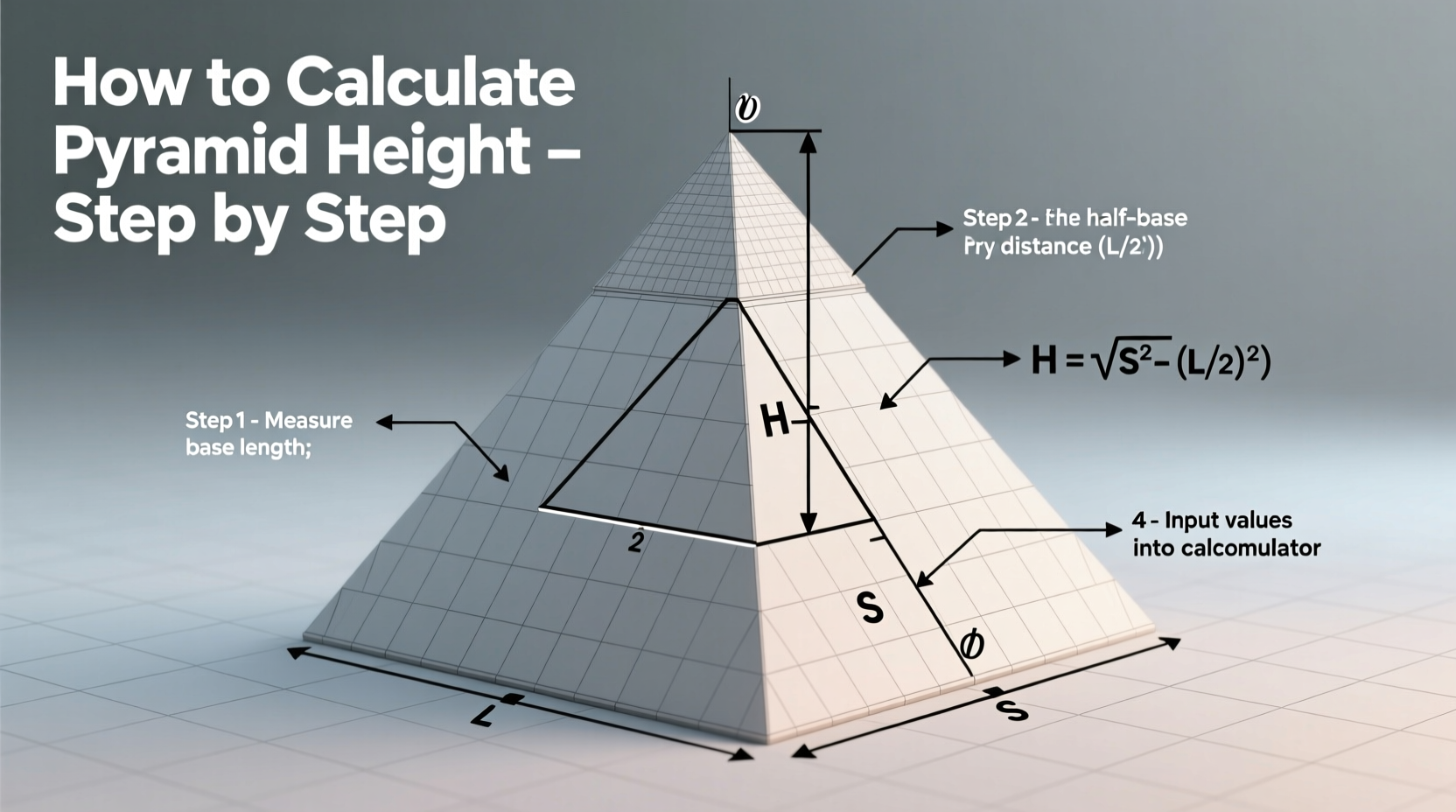
A pyramid is a polyhedron with a polygonal base and triangular faces that converge at a single point called the apex. The height of a pyramid is defined as the perpendicular distance from the apex to the plane of the base. This is not the same as the slant height (the length along a triangular face), which is often confused with true vertical height.
The shape of the base can vary—square, rectangular, triangular, or even pentagonal—but the method for calculating height depends on knowing either:
- The volume and base area
- The slant height and base dimensions
- Angular measurements from a distance (for real-world structures)
For regular pyramids (where the apex is directly above the center of the base), calculations are more straightforward. Irregular pyramids require additional measurements to locate the projection of the apex onto the base.
Step-by-Step Method 1: Using Volume and Base Area
If you know the volume of the pyramid and the area of its base, you can derive the height algebraically using the standard volume formula:
Volume (V) = (1/3) × Base Area (B) × Height (h)
Rearranging for height:
h = (3V) / B
- Determine the total volume of the pyramid (in cubic units).
- Calculate the area of the base (e.g., for a square base: side²; for rectangle: length × width).
- Multiply the volume by 3.
- Divide the result by the base area.
Example: A pyramid has a volume of 150 m³ and a square base measuring 6 meters per side. The base area is 6 × 6 = 36 m². Then:
h = (3 × 150) / 36 = 450 / 37.5 = 12.5 meters.
The height is 12.5 meters.
Step-by-Step Method 2: Using Slant Height and Base Dimensions
This method applies when you can measure the slant height—the distance from the apex down the center of a triangular face to the midpoint of a base edge.
For a regular square pyramid:
- Measure the slant height (l).
- Measure the length of one side of the base (s).
- Find half the base length: s/2.
You now have a right triangle formed by:
- The height (h) — unknown, vertical leg
- Half the base (s/2) — horizontal leg
- The slant height (l) — hypotenuse
h² + (s/2)² = l²
Therefore: h = √(l² – (s/2)²)
Example: A pyramid has a base side of 10 m and a slant height of 13 m.
h = √(13² – (10/2)²) = √(169 – 25) = √144 = 12 m.
The height is 12 meters.
Method 3: Measuring Height in the Field Using Trigonometry
When dealing with large, inaccessible pyramids—like ancient monuments—you can’t physically measure slant height or volume. Instead, use angular measurement and distance.
Stand at a known horizontal distance (d) from the base of the pyramid. Use a clinometer or smartphone app to measure the angle of elevation (θ) from your eye level to the apex.
The vertical height from your eye level to the apex is: d × tan(θ). Add your eye height above ground to get total height.
Total height = d × tan(θ) + eye_height
“Trigonometric surveying has been used since the 19th century to estimate the heights of ancient structures without invasive tools.” — Dr. Alan Reyes, Archaeological Surveyor
Example: You stand 50 meters from a pyramid. Your eye level is 1.6 m. The angle to the apex is 35°.
Height above eye level = 50 × tan(35°) ≈ 50 × 0.7002 = 35.01 m
Total height = 35.01 + 1.6 = 36.61 meters.
Checklist: How to Accurately Calculate Pyramid Height
- ✅ Identify the type of pyramid and confirm if it’s regular or irregular
- ✅ Measure or obtain the base dimensions accurately
- ✅ Determine available data: volume, slant height, or angular measurements
- ✅ Use consistent units across all measurements
- ✅ Apply the correct formula based on available inputs
- ✅ Double-check calculations using an alternate method if possible
- ✅ Account for observer height when measuring in the field
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Use precise measuring tools (laser rangefinders, digital protractors) | Assume the pyramid is perfectly symmetrical without verification |
| Convert all measurements to the same unit system before calculating | Mix metric and imperial units without conversion |
| Take multiple angle readings for field measurements to average out error | Rely on a single unverified measurement |
| Verify results using two different methods when possible | Ignore the difference between slant height and vertical height |
Mini Case Study: Estimating the Height of a School Project Pyramid
Jessica, a high school student, built a scale model of the Pyramid of Khafre for a history project. She knew the base was 30 cm square and the slant height measured 25 cm along the center of a face. To find the vertical height, she applied the Pythagorean method:
Half the base = 15 cm
h = √(25² – 15²) = √(625 – 225) = √400 = 20 cm.
She then verified her result by suspending a weighted string from the apex to the base center, measuring exactly 20 cm. Her accurate calculation helped her present a mathematically sound model and earned top marks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I calculate the height of a pyramid without knowing the volume?
Yes. If you have the slant height and base dimensions, or can take angular measurements from a distance, you can determine the height using geometry or trigonometry.
What if the pyramid is not regular?
For irregular pyramids, the apex is not centered over the base. In such cases, you must locate the orthogonal projection of the apex onto the base plane, then measure the perpendicular distance. This may require 3D coordinate mapping or advanced surveying tools.
Is there a difference between height and altitude in pyramids?
No. In geometric terms, the height and altitude of a pyramid refer to the same thing: the shortest (perpendicular) distance from the apex to the base plane.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Accurately calculating the height of a pyramid combines timeless geometric principles with modern measurement techniques. Whether you’re solving a textbook problem or estimating the stature of an ancient wonder, the methods outlined here provide reliable, step-by-step pathways to precision. Mastery of these skills enhances understanding in mathematics, architecture, and historical analysis.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?