Silicone earphone cases are essential accessories that protect your investment from drops, scratches, moisture, and daily wear. While most appear similar at first glance, their long-term performance varies significantly based on material quality and design. Understanding what makes one case more durable than another can save you money and frustration. Not all silicone is created equal—some degrade quickly, crack under pressure, or lose elasticity after just a few months. To make an informed decision, it’s critical to evaluate specific physical and chemical properties that directly impact resilience.
Material Composition: Not All Silicone Is the Same
Silicone may seem like a generic term, but in reality, it encompasses a range of formulations with different additives and polymer structures. High-quality cases use platinum-cured silicone, which undergoes a cleaner, more stable curing process than cheaper tin-cured alternatives. Platinum-cured silicone resists yellowing, maintains flexibility over time, and is less likely to develop surface stickiness—a common sign of degradation.
Low-grade silicone often contains fillers such as calcium carbonate or other non-silicone materials to reduce production costs. These fillers compromise structural integrity, making the case brittle or prone to cracking. A simple test: stretch a small portion gently. If it turns white (a phenomenon called “stress whitening”), it likely contains excessive fillers. Durable silicone should return to its original shape without discoloration.
“Silicone purity directly correlates with longevity. Cases made with medical-grade or food-safe silicone typically outperform off-brand options by years.” — Dr. Lena Torres, Materials Scientist at PolyShield Labs
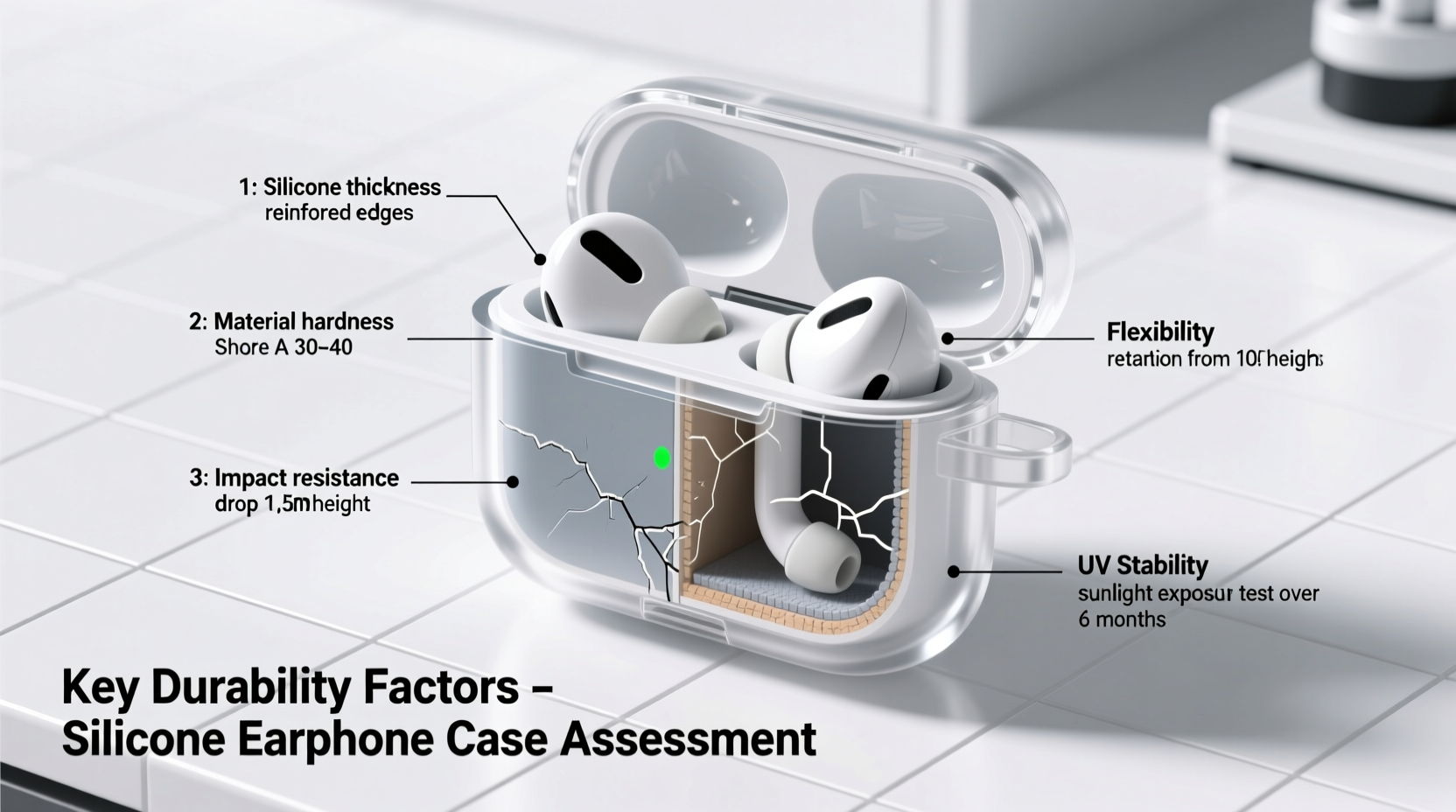
Shore Hardness: Balancing Flexibility and Protection
Durability isn’t just about toughness—it’s also about how well the material absorbs impact. Shore hardness measures the firmness of rubber and plastic materials on a scale from 0 (softest) to 100 (hardest). For earphone cases, the ideal range is between 40 and 60 on the Shore A scale.
A case below 40 Shore A may be too soft, offering poor structural support and allowing sharp objects to puncture through easily. One above 60 may be too rigid, reducing shock absorption and increasing the risk of internal damage during drops. The sweet spot provides enough give to cushion impacts while maintaining shape retention.
Wall Thickness and Structural Design
The physical build of the case plays a crucial role in its ability to withstand stress. Thicker walls generally offer better protection, but only up to a point. Excessive thickness can make the case bulky and difficult to close, while insufficient thickness leaves components vulnerable.
An optimal wall thickness ranges from 1.5 mm to 2.5 mm. This provides adequate cushioning without compromising portability. Additionally, look for reinforced corners and raised edges around contact points—these design features prevent direct impact on latches or hinges when dropped.
Some manufacturers incorporate ribbing or internal air channels into the mold. These structural enhancements distribute force across a wider area, reducing localized stress and preventing cracks from propagating.
Resistance to Environmental Stressors
Durability extends beyond physical strength—it includes resistance to environmental factors like UV exposure, temperature fluctuations, and chemicals.
- UV Resistance: Prolonged sun exposure breaks down polymer chains in low-quality silicone, leading to fading, brittleness, and cracking. Look for cases labeled “UV-stable” or those using pigments that block ultraviolet light.
- Temperature Tolerance: Standard silicone performs well between -40°C and 200°C (-40°F to 392°F), but cheaper blends may stiffen in cold weather or soften in heat. If you live in extreme climates, verify thermal stability before purchase.
- Chemical Exposure: Everyday items like hand sanitizer, sunscreen, and cleaning wipes contain alcohol or solvents that degrade silicone. High-purity silicone resists these agents far better than filled or poorly cured versions.
| Factor | Ideal Range/Feature | Risk of Poor Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Shore Hardness | 40–60 Shore A | Too soft = punctures; too hard = poor shock absorption |
| Wall Thickness | 1.5–2.5 mm | Thin = fragile; overly thick = bulky and inflexible |
| Curing Process | Platinum-cured | Tin-cured yellows and degrades faster |
| Filler Content | Minimal to none | Fillers cause cracking and loss of elasticity |
| UV & Heat Resistance | Stable under sunlight and temp swings | Fading, warping, or embrittlement over time |
Real-World Performance: A Mini Case Study
Consider two users purchasing seemingly identical silicone earphone cases online—one for $4.99, the other for $14.99. After six months, both report frequent pocket and bag use, occasional drops, and regular handling with hands exposed to lotion and sanitizer.
The budget case begins showing signs of deterioration within three months: micro-cracks near the hinge, visible stress whitening, and a sticky film developing on the surface. By month five, the lid no longer seals tightly, leaving the earbuds exposed.
In contrast, the premium case retains its smooth texture, shows no discoloration, and continues to snap shut securely. Despite similar usage patterns, the difference lies in material formulation—laboratory analysis later reveals the cheaper model contained over 30% filler material and used outdated tin-cure technology.
This example underscores that initial cost savings often lead to higher long-term expenses due to replacement frequency and reduced device protection.
Step-by-Step Guide to Testing Durability Before Purchase
- Check Product Specifications: Look for mentions of “platinum-cured,” “medical-grade,” or “high-purity” silicone. Avoid vague terms like “soft rubber” or “flexible TPU blend” unless clearly defined.
- Examine Weight and Density: A heavier case of similar size may indicate denser, higher-quality material.
- Perform a Stretch Test: Gently pull a corner. It should elongate smoothly and return without permanent deformation or whitening.
- Smell the Material: High-grade silicone is odorless. A strong chemical or plastic smell suggests impurities or volatile compounds.
- Review Warranty or Return Policy: Brands confident in durability often offer extended warranties or satisfaction guarantees.
Common Misconceptions About Silicone Durability
Many consumers assume that “silicone” automatically means durable and long-lasting. However, this is misleading. Just as not all plastics are equally tough, silicone quality varies dramatically based on manufacturing standards.
Another myth is that color affects durability. In truth, dark colors don’t inherently degrade faster—but they may show fading more visibly. What matters more is whether UV inhibitors were added during production.
Lastly, some believe softer cases offer better protection. While softness aids grip and comfort, excessive softness reduces structural rigidity, making the case more susceptible to tearing or misshaping under load.
FAQ
Can I clean my silicone earphone case with alcohol wipes?
Limited use is acceptable, but repeated exposure to isopropyl alcohol accelerates degradation. Instead, clean with mild soap and water, then dry thoroughly. For disinfection, dilute alcohol (below 70%) and rinse afterward.
How long should a good silicone earphone case last?
With proper care, a high-quality case should last 2–3 years under normal conditions. Signs it’s time to replace include persistent stickiness, visible cracks, loss of seal, or deformation that prevents closure.
Is thicker always better for protection?
No. Beyond 2.5 mm, additional thickness adds bulk without proportional protection gains. Well-designed cases use geometry—like curved walls and internal ribs—to enhance strength efficiently.
Final Checklist Before Buying
- ✅ Confirmed platinum-cured silicone
- ✅ Shore hardness between 40–60 A
- ✅ Wall thickness between 1.5–2.5 mm
- ✅ Reinforced corners or impact zones
- ✅ No strong chemical odor
- ✅ Positive long-term user reviews
- ✅ Resistant to UV and temperature changes
Conclusion
Assessing the durability of a silicone earphone case goes far beyond aesthetics or price. It requires attention to material science fundamentals—hardness, composition, design, and environmental resistance. By focusing on measurable qualities rather than marketing claims, you ensure lasting protection for your devices. Don’t settle for short-lived accessories that fail when you need them most. Invest in proven durability today and enjoy reliable performance tomorrow.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?