QR codes are everywhere—on restaurant menus, product packaging, event tickets, and digital ads. These square barcodes store information that can be instantly accessed with a camera or scanner. Despite their growing popularity, many users still hesitate to interact with them, assuming they require special apps or technical know-how. The truth is, accessing QR codes has never been easier, especially with modern smartphones and built-in tools. This guide walks you through everything you need to know to scan, interpret, and act on QR codes—regardless of your device.
Understanding What QR Codes Do
Quick Response (QR) codes are two-dimensional barcodes capable of storing various types of data: URLs, text, contact information, Wi-Fi credentials, payment details, and even calendar events. Unlike traditional barcodes, which only encode data horizontally, QR codes use both horizontal and vertical patterns, allowing them to hold significantly more information in a compact space.
When scanned, a QR code typically triggers an action such as opening a website, displaying a message, connecting to a network, or initiating a payment. The key to using them lies in understanding how your device interprets the data once it’s read.
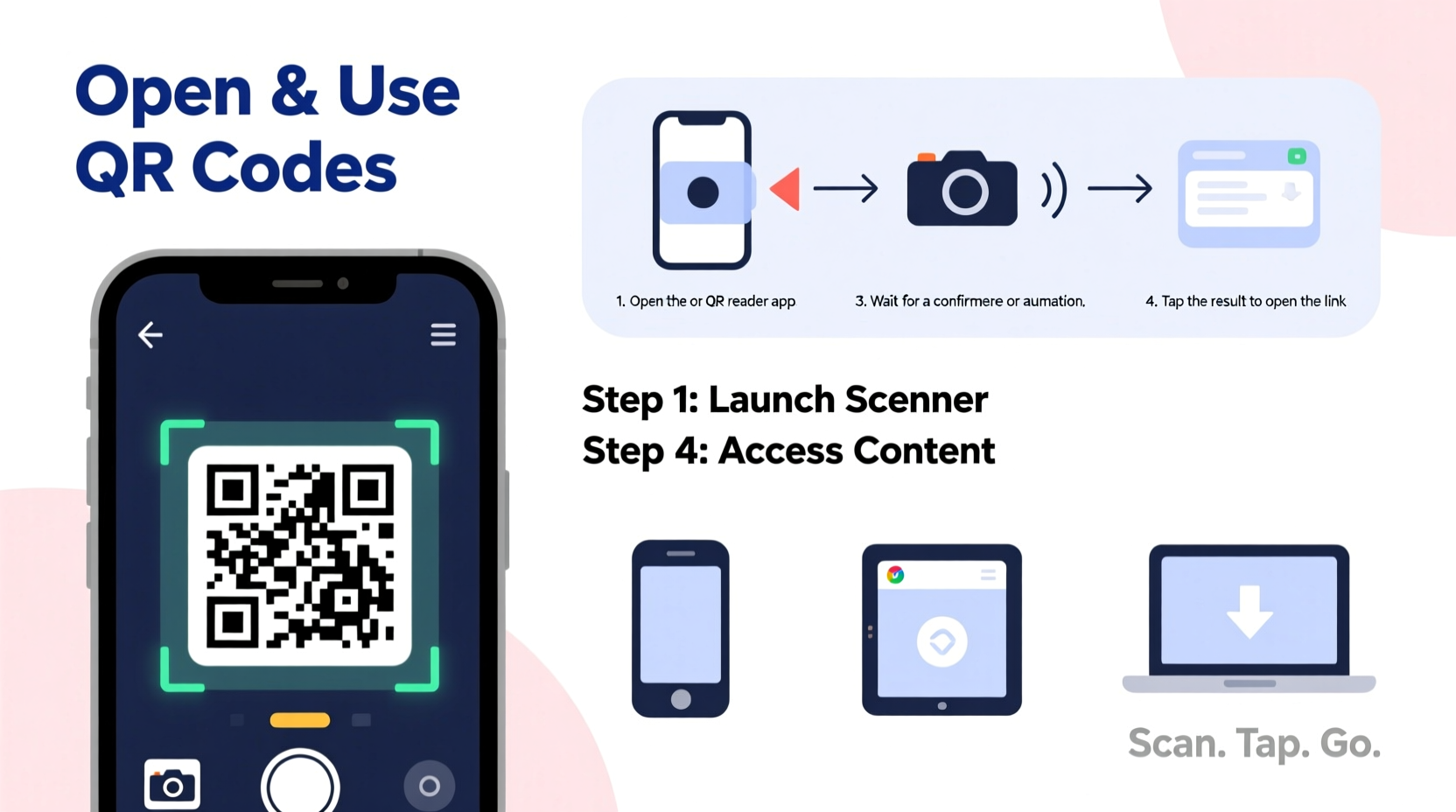
Step-by-Step Guide to Scanning QR Codes
Scanning a QR code takes seconds and requires minimal effort. Follow these steps based on your device type:
- Unlock your device and ensure the camera is functional.
- Open the camera app — no additional downloads needed on most modern phones.
- Aim the camera at the QR code, keeping it centered and within frame.
- Wait for recognition. A notification or banner will appear at the top or bottom of the screen.
- Tap the notification to open the linked content.
This process works seamlessly on iPhones running iOS 11 or later and Android devices with Android 9 (Pie) or newer. Both operating systems have native QR code readers built into their default camera applications.
What If Your Device Doesn’t Recognize the Code?
If nothing happens after pointing your camera at a QR code, consider the following:
- The lighting may be too dim; try scanning in a well-lit area.
- The code might be damaged, smudged, or poorly printed.
- Your camera app may not support QR scanning natively.
In such cases, installing a dedicated QR scanner app from your app store can resolve the issue.
Using QR Codes on Different Devices
Not all devices access QR codes the same way. Here's how to handle them across platforms:
Smartphones (iPhone and Android)
iPhones automatically detect QR codes through the Camera app. Simply point, wait for the alert, and tap. No settings need to be enabled under normal conditions.
On Android, Google Lens integration allows instant QR detection. Some manufacturers (like Samsung) also include scanner features in their camera apps. If scanning doesn’t work, go to your camera settings and ensure “Scan QR codes” is turned on.
Tablets
iPads and Android tablets function similarly to smartphones. iPads with iOS 11+ support QR scanning via the Camera app. For Android tablets without native support, downloading a free QR reader like “QR & Barcode Scanner” by Scan or “Kaspersky QR Scanner” ensures compatibility.
Computers (Windows and Mac)
Desktops and laptops don’t have cameras positioned for easy scanning, but there are workarounds:
- Use your phone to scan the code and send the link to your computer via messaging or email.
- Install browser extensions like “QR Code Reader for Chrome” that allow you to upload screenshots of QR codes.
- Use web-based tools such as webqr.com to decode images of QR codes uploaded from your device.
“Over 85% of smartphone users now regularly scan QR codes for convenience, security, and speed.” — TechInsight Report, 2023
Common Uses and How to Act on Them
QR codes serve practical purposes across industries. Knowing what to expect helps avoid confusion or hesitation when scanning.
| Type of QR Code | Action Triggered | User Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Website URL | Opens a webpage | Review site legitimacy before entering data |
| Wi-Fi Network | Prompts connection request | Confirm network name and password accuracy |
| Contact Info (vCard) | Downloads contact | Save to address book if desired |
| Payment Link | Opens payment app | Verify recipient and amount before sending |
| Event Invite | Displays calendar event | Add to calendar manually or accept invite |
Mini Case Study: Contactless Menus During Travel
Sophia, a frequent traveler, visited a café in Tokyo during her layover. The menu was available only via QR code posted on each table. Using her iPhone, she opened the Camera app, pointed it at the code, and within seconds, a Safari window launched with the full digital menu in English. She browsed selections, placed an order through the embedded form, and paid contactlessly—all without touching shared surfaces or waiting for staff assistance.
This real-world example highlights how QR codes streamline experiences while reducing physical contact—a benefit that gained global traction post-pandemic.
Security Best Practices When Scanning
While convenient, QR codes aren't immune to misuse. Cybercriminals can embed malicious links into seemingly harmless codes. Protect yourself with these practices:
- Never scan codes from untrusted sources like flyers on streets or unsolicited emails.
- Check where the link leads before proceeding. On some Android devices, you can preview the destination URL before opening.
- Avoid granting unnecessary permissions when prompted after scanning.
- Use antivirus apps with QR scanning protection, such as Norton or Kaspersky.
Checklist: Safe QR Code Scanning Habits
- ✅ Confirm the code is from a legitimate, visible location (e.g., official signage).
- ✅ Ensure your device’s operating system and security apps are up to date.
- ✅ Preview the URL if your scanner supports it.
- ✅ Avoid public Wi-Fi when acting on sensitive QR-triggered actions (like logging in).
- ✅ Delete temporary tabs or apps opened via QR codes after use.
FAQ
Can I generate my own QR code?
Yes. Free online tools like QRCode Monkey, GoQR, or Bitly let you create custom QR codes for URLs, text, or contact info. Most are free for basic use and allow customization with colors and logos.
Do I need internet to scan a QR code?
You don’t need internet to read the code itself, but you’ll need connectivity to access most linked content—especially websites or online forms. Offline codes (like vCards) may work without a connection.
Why does my phone not scan QR codes anymore?
This could be due to a disabled camera setting, outdated OS, or third-party app interference. Restart your phone, update your system, or test with a different QR code. If issues persist, reinstall the camera app or reset settings.
Conclusion
QR codes bridge the physical and digital worlds with remarkable efficiency. Whether you're connecting to Wi-Fi, making a payment, or accessing a document, the ability to quickly and securely scan these codes enhances daily productivity and safety. With native support on nearly every smartphone today, there’s no excuse to overlook this simple yet powerful tool.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?