In an age where mobile data is often limited or expensive, transferring and viewing videos between phones without consuming bandwidth is a valuable skill. Whether you're traveling with friends, sharing memories at a family gathering, or simply conserving your monthly data allowance, knowing how to move video files seamlessly between devices can save time, money, and hassle. The good news? You don’t need an internet connection to do it. Using built-in tools and simple third-party solutions, you can share and stream videos directly from one phone to another—wirelessly and without touching your data plan.
Why Avoid Data When Sharing Videos?
Mobile data isn't always reliable or unlimited. Streaming or sending large video files over the internet consumes significant bandwidth and can quickly eat into your data cap. In remote areas or countries with expensive roaming charges, relying on data becomes impractical. Additionally, uploading videos to cloud services like Google Drive or WhatsApp may compromise privacy or require waiting for uploads and downloads.
Transferring videos locally—directly from one device to another—bypasses these issues entirely. It's faster, more secure, and completely free. Most modern smartphones come equipped with multiple offline-sharing capabilities that make this process straightforward.
Common Methods for Offline Video Sharing
There are several proven ways to transfer and view videos between mobile devices without using mobile data. These rely on short-range wireless technologies or direct file access. Below are the most effective methods available today.
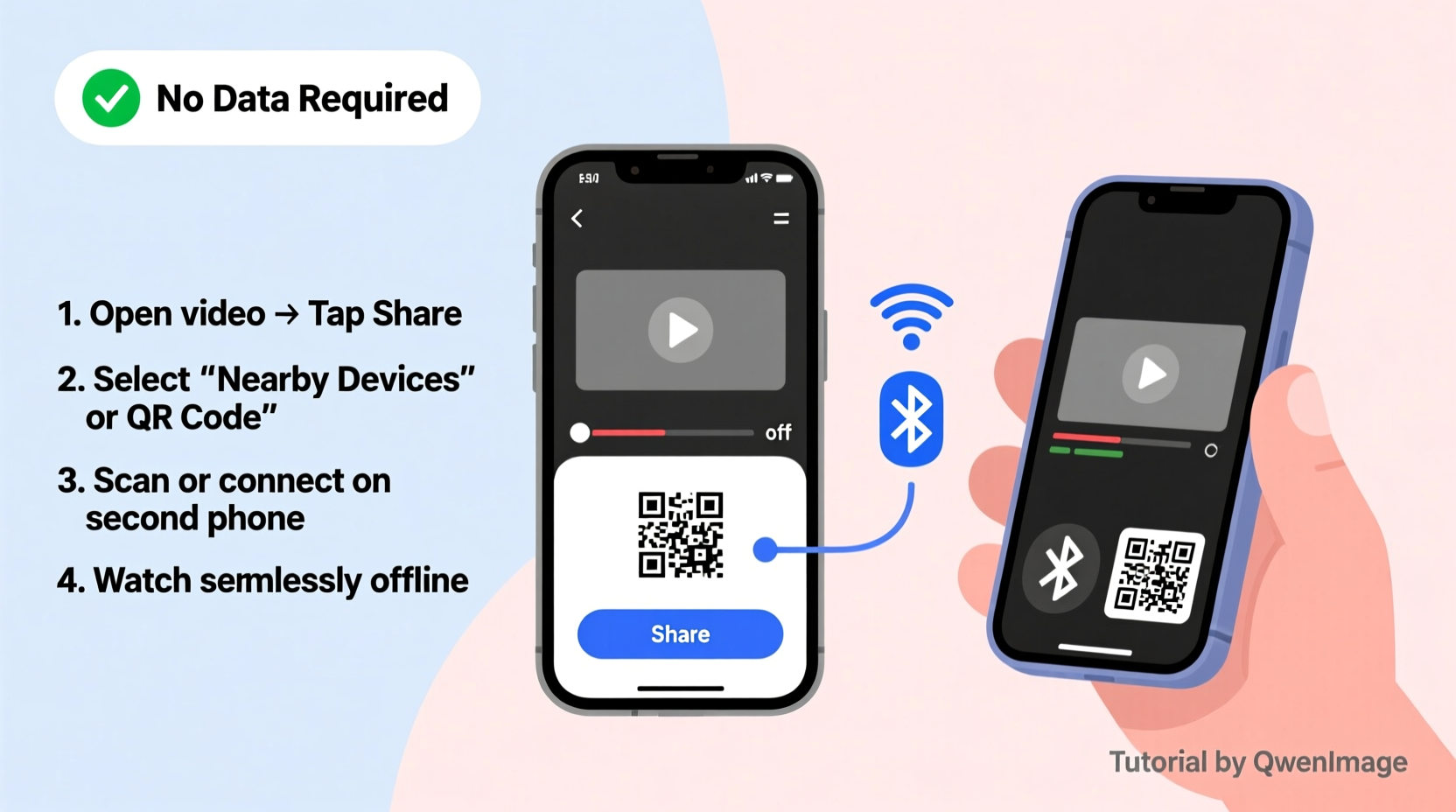
1. Bluetooth File Transfer
Bluetooth has been a staple of mobile connectivity for decades. While slower than newer options, it remains universally supported across Android and iOS devices (with some limitations on iPhone).
- Enable Bluetooth on both devices.
- Pair the two phones by selecting each other in the Bluetooth menu.
- On the sending phone, open your file manager or gallery, select the video, and tap “Share.”
- Choose Bluetooth as the sharing method and select the paired device.
- Accept the incoming file on the receiving phone.
Note: Large videos may take several minutes to send via Bluetooth due to its lower transfer speed (typically under 3 Mbps).
2. Wi-Fi Direct & Local Hotspot Streaming
A faster alternative is using Wi-Fi Direct or creating a local hotspot to enable direct communication between devices. This doesn’t use mobile data—it creates a private network between the two phones.
To use a local hotspot:
- On the sending phone, go to Settings > Network & Internet > Hotspot & Tethering and turn on Wi-Fi hotspot.
- Set a password and note the network name.
- On the receiving phone, connect to this hotspot just like any Wi-Fi network.
- Use a file-sharing app such as Xender, SHAREit, or Send Anywhere on both devices.
- Select the video on the sender’s phone and send it over the local network.
These apps create a peer-to-peer connection over the hotspot, enabling high-speed transfers—often up to 50 Mbps depending on signal strength.
“Wi-Fi Direct eliminates the need for routers or internet while allowing near-LAN speeds for media sharing.” — Dr. Rajiv Mehta, Wireless Communications Researcher
3. Near Field Communication (NFC)
NFC allows two phones to exchange data by simply tapping them together. While primarily used for payments, it can initiate file transfers when paired with Android Beam (on older Androids) or Samsung’s S Beam.
Steps:
- Ensure both devices have NFC enabled.
- Place the backs of the phones together.
- Tap to confirm transfer when prompted.
- The video will begin transferring wirelessly.
Limitation: NFC itself doesn’t transfer large files; it initiates a Wi-Fi Direct or Bluetooth connection to complete the transfer. Available only on select Android models.
4. USB OTG + Physical Transfer
If wireless isn’t an option, use a USB On-The-Go (OTG) cable. This method involves physically connecting the two phones or using a flash drive as an intermediary.
- Connect one end of the OTG cable to the sending phone and the other to the receiving phone (if supported).
- Alternatively, copy the video to a USB drive, then plug it into the second phone.
- Use the file manager to locate and move the video.
This is ideal for very large files or when battery life is a concern with wireless transmission.
Watch Videos in Real-Time Without Full Transfer
Sometimes, you don’t need to copy the entire video—just watch it together. Several apps allow real-time streaming over a local network.
Using Local DLNA Servers:
- Install a media server app like MxPlayer or VideoStream on the sending phone.
- Start the local server and play the video.
- On the receiving phone, connect to the same hotspot and open a compatible player.
- Browse local network devices and stream the video directly.
No copying required. The second phone streams the video over the local Wi-Fi network, reducing wait time and storage usage.
Comparison of Offline Sharing Methods
| Method | Speed | Compatibility | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bluetooth | Slow (1–3 Mbps) | Universal (Android), Limited (iOS) | Small clips, quick shares |
| Wi-Fi Hotspot + App | Fast (10–50 Mbps) | Android & iOS (via apps) | High-quality videos, group sharing |
| NFC + Wi-Fi Direct | Moderate to Fast | Android Only | Tap-and-send convenience |
| USB OTG | Very Fast (up to 60 Mbps) | Most Android phones | Large files, no battery drain |
| Local DLNA Streaming | Fast (streaming optimized) | Android, some iOS apps | Watching together instantly |
Mini Case Study: Sharing Vacation Videos at a Family Dinner
Rahul returned from a trip to the Himalayas with over 30 minutes of 4K footage. At a family dinner, his cousins wanted to see the trek highlights. Instead of uploading to YouTube or draining his data, Rahul turned on his phone’s Wi-Fi hotspot and launched Xender. His cousins connected to the hotspot and opened the app on their phones. Within seconds, he sent three key clips totaling 1.2 GB. One cousin even mirrored her phone to a TV using Chromecast over the same hotspot, allowing everyone to enjoy the videos on a big screen—all without a single byte of mobile data used.
Checklist: How to Share Videos Offline – Step-by-Step
- ✅ Decide on transfer method (Bluetooth, hotspot, USB, etc.)
- ✅ Enable necessary features (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, NFC)
- ✅ Pair or connect devices securely
- ✅ Use a compatible file-sharing or streaming app if needed
- ✅ Select video and initiate transfer or stream
- ✅ Verify receipt and playback on the second device
- ✅ Turn off hotspot or Bluetooth when done to save battery
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I share videos between Android and iPhone without data?
Yes. Use cross-platform apps like Send Anywhere or AirDroid that work over a local Wi-Fi hotspot. While direct Bluetooth sharing from Android to iPhone is limited (iOS restricts file reception via Bluetooth), hotspot-based methods are fully compatible.
Do these methods work when airplane mode is on?
Yes—with exceptions. If you enable Wi-Fi or Bluetooth manually while in airplane mode, you can still use hotspot, Bluetooth, or NFC transfers. Just remember to turn on Wi-Fi or Bluetooth after activating airplane mode.
Is it safe to use third-party file-sharing apps?
Most reputable apps like Xender, Send Anywhere, and Portal by Pushbullet use encrypted local connections and do not upload your files to the cloud. Always download apps from official stores and check permissions before installing.
Final Tips for Seamless Offline Sharing
Keep file-sharing apps updated for better performance and security. Also, ensure both devices have sufficient storage and battery before starting large transfers.
Conclusion
Sharing and watching videos between mobile phones without using data is not only possible—it’s efficient and often faster than cloud-based alternatives. By leveraging Bluetooth, Wi-Fi hotspots, NFC, USB OTG, or local streaming protocols, you maintain control over your content, privacy, and data usage. These methods are practical for everyday situations, from showing photos to friends to collaborating on video projects remotely.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?