Modern smartphones and computers are designed to multitask, allowing multiple applications to run simultaneously. While this enhances user experience, it often comes at a cost: reduced battery life, slower performance, and higher data consumption. Many apps continue running in the background even when you're not actively using them, silently draining resources. The good news is that most devices offer tools and settings to control this behavior. Understanding how to manage background app activity can significantly extend battery life, free up system memory, and reduce unnecessary data use—especially important for users on limited data plans.
Why Background Apps Drain Your Device’s Resources
When an app runs in the background, it may perform tasks like checking for updates, syncing data, sending notifications, or tracking location. These processes consume CPU power, RAM, and network bandwidth. Over time, especially with poorly optimized apps, this constant activity adds up. A 2023 study by Battery University found that background processes account for nearly 40% of smartphone battery drain on average. This isn’t just about convenience—it’s about efficiency and longevity.
For example, social media apps like Facebook or Instagram often refresh content in the background to deliver instant updates. Messaging apps such as WhatsApp or Telegram maintain persistent connections to ensure real-time delivery. While useful, these behaviors can be excessive if left unchecked. Similarly, fitness trackers or weather apps might constantly access GPS or internet services, accelerating battery depletion.
“Background app activity is one of the top contributors to poor battery performance. Managing it effectively can extend usable battery life by hours.” — Dr. Lena Patel, Mobile Systems Analyst at TechInsight Labs
Step-by-Step Guide to Restrict Background App Activity
Taking control starts with identifying which apps are consuming the most resources and then applying targeted restrictions. Follow this step-by-step process across major platforms:
1. Identify High-Usage Apps
Begin by reviewing your device’s built-in battery and data usage reports. On Android, go to Settings > Battery > Battery Usage. On iOS, navigate to Settings > Battery. Both systems display a list of apps sorted by energy consumption over the last 24 hours or 7 days. Look for apps that show high background usage despite minimal active engagement.
2. Limit Background Data (Android)
Android gives granular control over background data per app:
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Data Usage.
- Select Mobile data usage.
- Tap on any app from the list.
- Toggle off Background data.
This prevents the app from using mobile data when not in use. Wi-Fi can still be restricted separately under advanced settings.
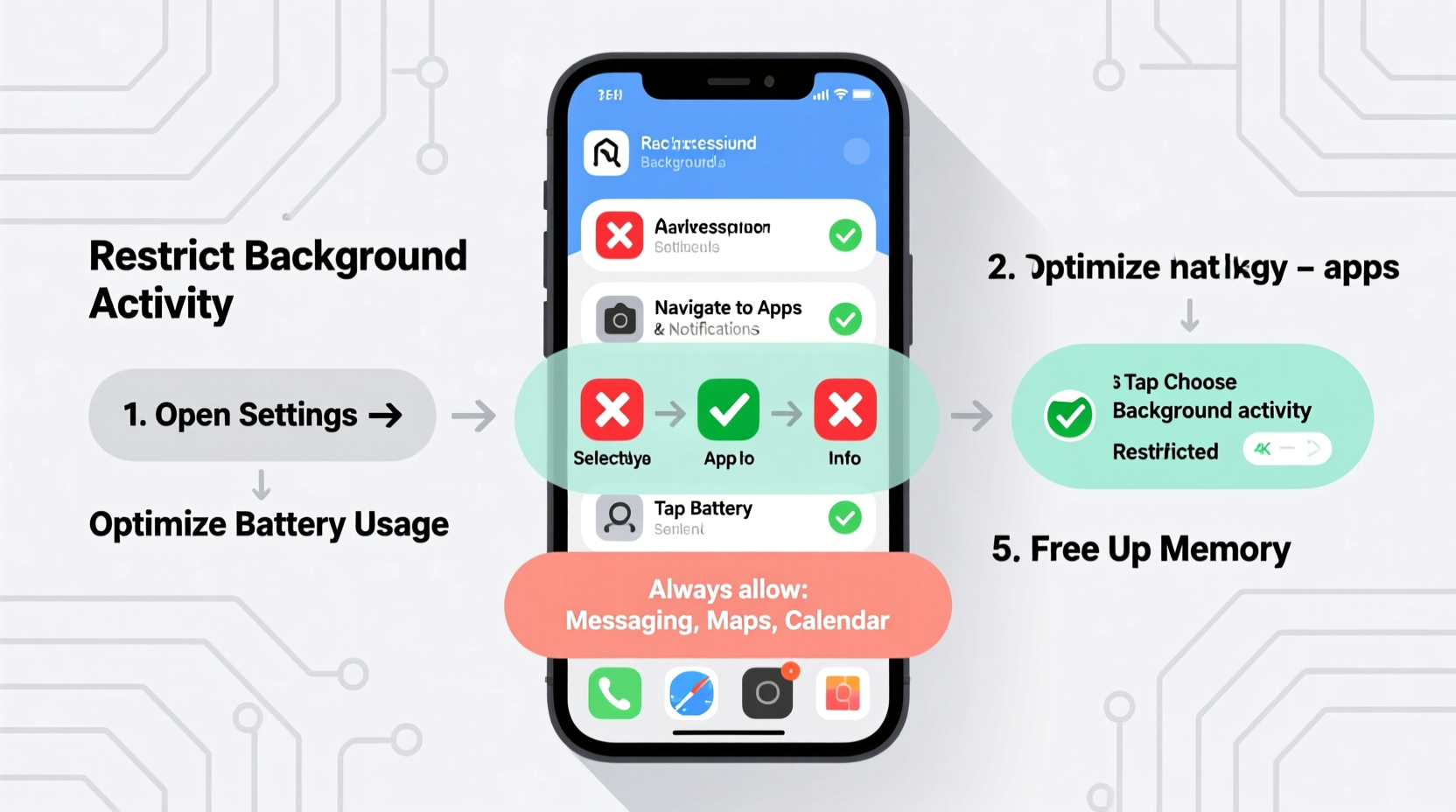
3. Disable Background App Refresh (iOS)
iOS uses “Background App Refresh” to update content in the background:
- Navigate to Settings > General > Background App Refresh.
- You can disable it entirely or select individual apps.
- Choose Wi-Fi Only for apps you want to limit further.
Disabling this feature won’t stop push notifications but will prevent silent content fetching.
4. Use Battery Optimization Settings
On Android, enable adaptive battery features:
- Go to Settings > Battery > Adaptive Battery.
- Allow the system to learn your usage patterns and restrict apps you rarely use.
- Manually add apps to the optimization list via Battery > More battery settings > Optimize battery usage.
On iOS, leverage Low Power Mode (Settings > Battery > Low Power Mode), which automatically suspends background app refresh, mail fetch, and visual effects.
5. Force Stop or Disable Unused Apps
If certain apps are rarely used but still run in the background, consider force stopping or disabling them:
- Android: Settings > Apps > [App Name] > Force Stop or Disable.
- iOS: Offload unused apps via Settings > App Store > Offload Unused Apps.
Offloading removes the app but keeps its documents and data, allowing quick reinstallation later.
Platform-Specific Strategies for Maximum Control
Different operating systems handle background processes differently. Tailoring your approach based on your platform ensures optimal results.
| Platform | Key Feature | How to Access | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android 12+ | Adaptive Battery | Settings > Battery > Adaptive Battery | High – Learns usage patterns |
| iOS 16+ | Background App Refresh | Settings > General > Background App Refresh | High – Granular app control |
| Windows 11 | Background Apps | Settings > Apps > Advanced app settings > Background apps | Moderate – System-wide toggle |
| macOS Ventura | Automatic Termination | System-managed; enabled by default | High – Apps quit when idle |
| Android (Legacy) | Force Stop | Settings > Apps > [App] > Force Stop | Low – Temporary fix |
Note that while desktop operating systems like Windows and macOS also allow background processes, mobile devices are more sensitive due to battery constraints. However, laptops benefit from similar optimizations—especially those running on battery power.
Checklist: How to Minimize Unnecessary Background Activity
Use this checklist monthly to keep your device running efficiently:
- ✅ Review battery usage stats to identify resource-heavy apps.
- ✅ Disable background data for non-essential apps (Android).
- ✅ Turn off Background App Refresh for low-priority apps (iOS).
- ✅ Enable Adaptive Battery or Low Power Mode during heavy usage days.
- ✅ Uninstall or disable apps you no longer use.
- ✅ Update all apps regularly—developers often optimize background behavior in updates.
- ✅ Avoid installing duplicate apps (e.g., multiple weather or flashlight apps).
- ✅ Clear app cache periodically to remove residual background triggers.
Real Example: Sarah’s Smartphone Transformation
Sarah, a freelance graphic designer, noticed her phone was lasting only half a day despite charging it nightly. Her screen-on time was just 3 hours, yet battery usage showed Facebook, TikTok, and a weather app consuming over 60% of her battery combined. After checking her settings, she discovered all three had unrestricted background data and location access.
She took action: disabled background data for TikTok and Facebook, turned off location services for the weather app, and uninstalled a redundant news app that auto-refreshed every 15 minutes. Within two days, her battery lasted nearly 50% longer. She also enabled Adaptive Battery, which further improved performance by limiting background activity for apps she hadn’t opened in over a week.
“I didn’t realize how much invisible activity was happening,” Sarah said. “Now my phone feels faster, and I’m not scrambling for a charger by noon.”
Common Mistakes That Keep Apps Running in the Background
Even tech-savvy users make errors that undermine their efforts to control background processes. Avoid these common pitfalls:
- Swiping away apps instead of adjusting settings: Closing apps from the recent apps menu doesn’t stop background services—they often restart automatically.
- Ignoring location permissions: Apps with continuous location access (like fitness trackers) can wake up frequently, draining battery even when closed.
- Leaving push notifications enabled for every app: Each notification requires network activity. Disable alerts for non-critical apps.
- Not updating apps: Older versions may lack power-saving improvements introduced in newer releases.
- Assuming all background activity is bad: Some apps, like messaging or navigation tools, require background access to function properly. Focus on balance, not elimination.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will stopping background apps affect notifications?
It depends. Disabling background data or refresh may delay notifications until you open the app. However, most major apps (like WhatsApp, Gmail, or Slack) use push services that don’t rely on constant background running. You’ll still receive alerts, though content previews might take slightly longer to load.
Can I completely stop all apps from running in the background?
Technically, yes—but not practically. Core system functions and essential services need background access to operate. Instead of aiming for total shutdown, focus on restricting non-critical third-party apps. Complete lockdown can lead to missed messages, failed syncs, or app crashes.
Do background apps use data even on Wi-Fi?
Yes. Background apps consume data regardless of connection type. While Wi-Fi doesn’t count against your data plan, excessive background traffic can slow down your network, especially on shared connections. It’s wise to manage background usage even when connected to Wi-Fi.
Final Thoughts: Take Control of Your Device’s Performance
Unnecessary background app activity is a silent productivity killer. It slows down your device, shortens battery life, and inflates data usage without delivering tangible benefits. The strategies outlined here—ranging from platform-specific settings to behavioral adjustments—empower you to reclaim control. By conducting regular audits, applying smart restrictions, and uninstalling digital clutter, you create a leaner, more responsive device environment.
Optimization isn’t a one-time task. As new apps are installed and usage habits evolve, periodic review ensures sustained performance. Start today by opening your battery settings and identifying the top three background offenders. Apply the appropriate restrictions, monitor changes over the next few days, and adjust as needed. Small actions compound into significant gains over time.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?