Automatic app updates are designed to keep your Android device secure and running smoothly by delivering the latest features and bug fixes. But they can also be disruptive—consuming data at inopportune times, interrupting workflows, or introducing unwanted changes to apps you rely on daily. The good news is that you don’t have to sacrifice internet connectivity to gain control over when and how your apps update. With a few targeted adjustments in your device settings, you can disable automatic updates while still staying connected and browsing freely.
This guide walks through the exact steps to manage automatic app updates across different Android versions and Google Play Store configurations. Whether you're trying to preserve limited data plans, avoid forced UI changes, or simply maintain consistency in your workflow, these methods will give you full autonomy—without disconnecting from the web.
Understanding Automatic App Updates on Android
By default, the Google Play Store is configured to automatically update installed apps over Wi-Fi. This behavior ensures that security patches and performance improvements are applied promptly. However, it doesn't account for user preferences such as timing, bandwidth constraints, or stability concerns with new app versions.
The key distinction here is between connectivity and update behavior. Disabling Wi-Fi or mobile data stops all network activity, which isn’t necessary—or practical—if you only want to halt automatic downloads. Android provides granular controls within the Play Store app that allow selective management of updates while preserving full internet access.
Before making changes, it's important to understand the trade-offs:
- Security: Delaying updates may leave known vulnerabilities unpatched for longer.
- Performance: Some updates include critical bug fixes that improve app stability.
- User Experience: New features might enhance functionality, but others could alter interfaces in ways users dislike.
The goal is not to abandon updates altogether, but to shift from passive acceptance to active management—choosing when and how updates occur based on your schedule and priorities.
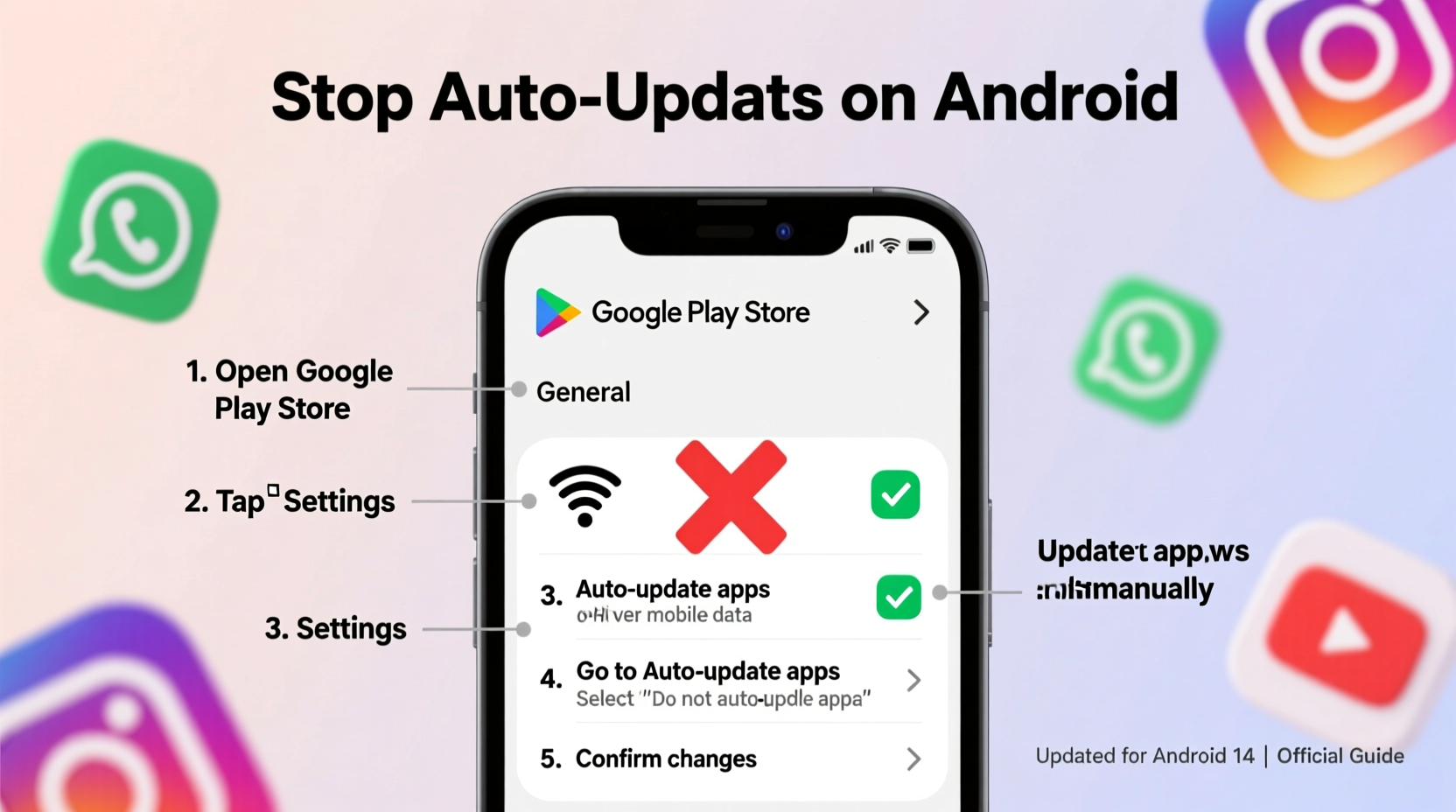
Step-by-Step Guide to Disable Automatic App Updates
Follow this sequence to disable auto-updates while keeping your device online:
- Open the Google Play Store app. Tap the menu icon (three horizontal lines) in the top-left corner.
- Select “Settings” from the side menu.
- Tap “Network preferences” or “Auto-update apps,” depending on your device layout.
- Choose “Do not auto-update apps.” This setting prevents any background downloads.
Once selected, apps will no longer install updates unless you initiate them manually. You’ll still receive notifications about available updates, allowing you to review changelogs and decide whether to proceed.
If you'd like more flexibility, consider using the alternative option: “Auto-update over Wi-Fi only.” While this doesn’t fully stop updates, it limits them to trusted networks and avoids unexpected data usage. For complete control, however, the “Do not auto-update” selection remains the most effective.
Managing Individual App Update Settings
Sometimes, you may want certain essential apps (like banking or messaging tools) to stay current while freezing updates for less critical ones (such as games or social media). Android allows per-app control via the Play Store’s individual listing pages.
To customize an app’s update behavior:
- Open the Play Store and search for the specific app.
- Navigate to its product page.
- Tap the three-dot menu (⋮) in the top-right corner.
- Select “Turn off auto-update” if it’s currently enabled.
This method is especially useful for apps that frequently roll out intrusive changes—like TikTok altering its algorithm or Instagram testing new navigation layouts. By opting out individually, you maintain control without affecting system-wide settings.
Alternative Methods Across Devices and Launchers
While the standard Play Store settings work on most Android devices, some manufacturers and custom ROMs offer additional layers of control. Samsung, OnePlus, Xiaomi, and others often include built-in software managers that can override or supplement Google’s default behaviors.
For example:
- Samsung Galaxy devices: Use “Galaxy Store” and “App Management” settings to restrict background installations.
- Xiaomi MIUI: Go to Settings > Apps > Permissions > Auto-start management to block silent launches and updates.
- OnePlus/OxygenOS: Navigate to Settings > Apps & notifications > Special app access > Install unknown apps, and limit permissions for third-party updaters.
These manufacturer-specific options don’t replace Play Store settings but add another layer of protection against unwanted background activity. They’re particularly helpful if you suspect non-Google apps are triggering updates independently.
Using Data Saver Mode Strategically
Android’s built-in Data Saver mode indirectly affects app updates by restricting background data usage. When activated, it prevents apps from downloading content—including updates—unless you're on Wi-Fi or explicitly permit it.
To enable Data Saver:
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Data usage.
- Tap Data Saver.
- Toggle it ON.
Note: This won’t stop updates initiated manually or over Wi-Fi unless combined with Play Store settings. It's best used as a secondary safeguard, especially on metered connections.
“We see increasing demand from professionals who need predictable software environments. Turning off auto-updates gives them stability during high-focus periods.” — Dr. Lena Torres, Mobile Productivity Researcher at TechFlow Labs
Checklist: How to Stop Automatic App Updates Without Losing Connectivity
- ✅ Open the Google Play Store app
- ✅ Access the menu (☰) and go to Settings
- ✅ Select “Network preferences” or “Auto-update apps”
- ✅ Choose “Do not auto-update apps”
- ✅ Manually review and update critical apps weekly
- ✅ Use per-app settings to fine-tune exceptions
- ✅ Enable Data Saver for added control on cellular networks
- ✅ Monitor update notifications to stay informed
Real-World Scenario: A Freelancer’s Workflow Protection
Maria, a freelance graphic designer based in Lisbon, relies heavily on Adobe Express and Canva for client projects. She noticed that after a recent automatic update, the layout editor in one app changed dramatically—buttons moved, export options were hidden under new menus, and her usual shortcuts stopped working. What should’ve been a two-hour design task turned into half a day of relearning.
Frustrated, she looked for a way to prevent future disruptions without cutting herself off from email, cloud storage, or communication tools. Using the steps outlined above, Maria disabled auto-updates globally and now reviews each update before installing. She schedules updates on Friday afternoons—after client deadlines—and tests new versions in a sandbox environment first.
“It’s not about resisting change,” she says. “It’s about choosing when to adapt. My productivity has improved because I’m no longer surprised by sudden interface shifts.”
Comparison Table: Update Settings and Their Impact
| Setting | Updates Over Wi-Fi? | Updates Over Cellular? | Connectivity Preserved? | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Do not auto-update apps | No | No | Yes | Full control; minimal disruption |
| Auto-update over Wi-Fi only | Yes | No | Yes | Balanced approach; free Wi-Fi usage |
| Auto-update over any connection | Yes | Yes | Yes | Maximum convenience; high data allowance |
| Data Saver + No Auto-Update | No (unless allowed) | No | Yes | Tight data budgets; sensitive workflows |
This table highlights that disabling auto-updates does not interfere with general connectivity. All settings preserve internet access—the differences lie solely in download behavior.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will stopping automatic updates make my phone less secure?
It can, temporarily. Security patches are often delivered through app updates. However, the risk can be mitigated by performing regular manual checks—ideally once a week—and prioritizing updates for apps handling personal data (e.g., browsers, email clients, financial tools).
Can I still get notified about available updates?
Yes. Even with auto-updates disabled, the Play Store continues to notify you when updates are available. You can view them under “My apps & games” in the Play Store menu, where pending updates are listed with version details and changelogs.
What if an app forces an update to remain functional?
Some services, particularly streaming platforms or banking apps, occasionally require the latest version to function. In such cases, you’ll typically see a prompt blocking access until you update. To avoid last-minute surprises, check for updates before relying on time-sensitive apps.
Conclusion: Regain Control Without Going Offline
Disabling automatic app updates on Android doesn’t mean disconnecting from the world—it means reconnecting with control. You can keep browsing, streaming, and working online while deciding exactly when and how your apps evolve. With just a few taps in the Play Store settings, you shift from reactive to proactive, aligning your device’s behavior with your lifestyle and professional needs.
Technology should serve you, not surprise you. Whether you're protecting creative workflows, conserving mobile data, or simply valuing predictability, taking charge of update settings is a small change with significant impact. Apply these steps today, and experience a smoother, more intentional relationship with your Android device.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?