LED headlights have become standard in modern vehicles due to their energy efficiency, longevity, and superior brightness. However, when they begin to flicker, it can be more than just an annoyance—it can compromise visibility and safety during night driving or adverse weather. Unlike traditional halogen bulbs, LED systems operate differently, making flickering symptoms harder to diagnose without understanding the underlying electronics. This guide breaks down the root causes of LED headlight flickering and provides actionable, tested solutions.
Why LED Headlights Flicker: The Core Causes
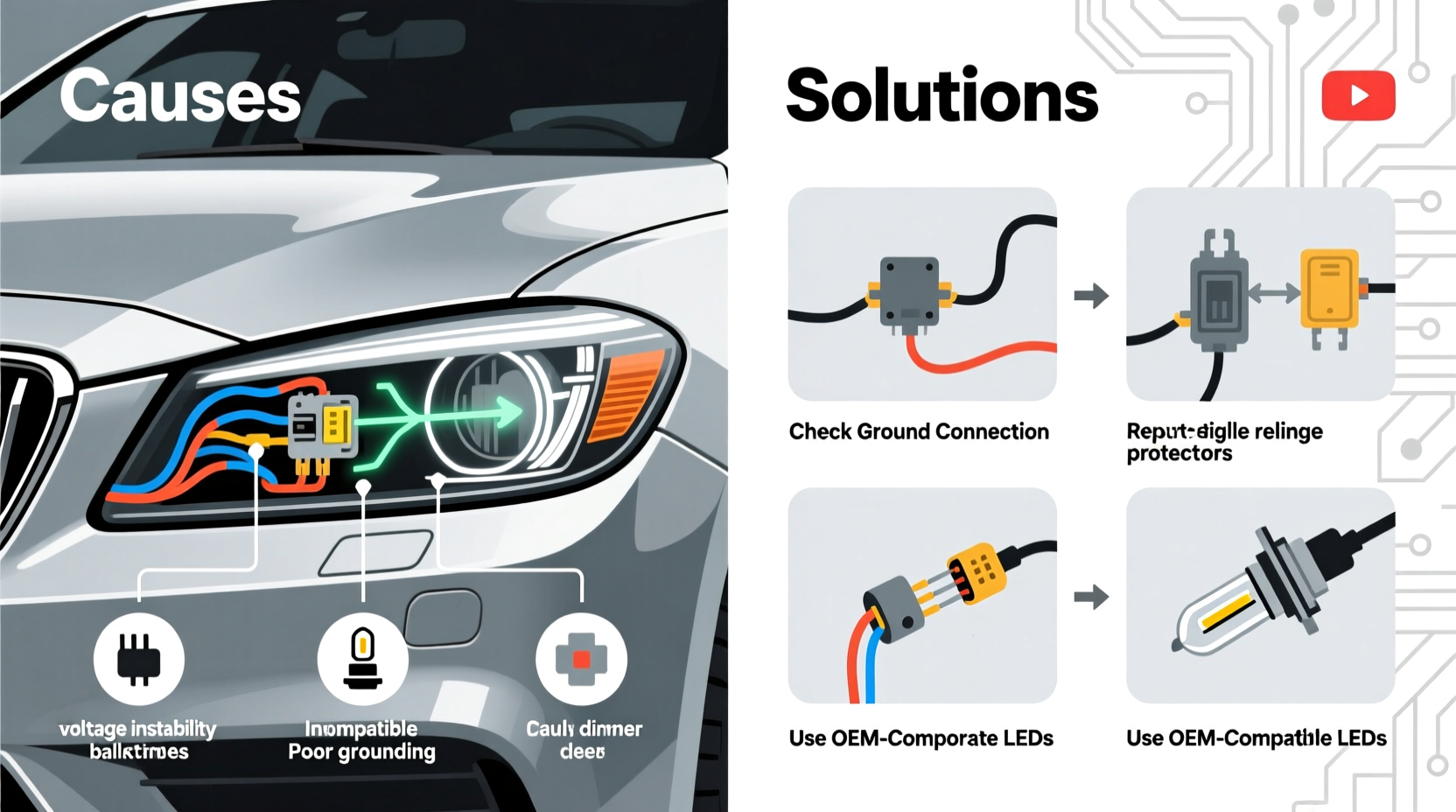
Flickering in LED headlights is rarely random. It usually stems from one or more specific issues related to power delivery, compatibility, or system design. Understanding these causes is the first step toward a reliable fix.
- Voltage fluctuations: LEDs require stable voltage. If your vehicle’s alternator or battery delivers inconsistent power, flickering may occur.
- Incompatible CANBUS system: Many modern cars use a Controller Area Network (CANBUS) to monitor bulb status. Aftermarket LEDs may not draw enough current to satisfy the system, triggering false \"bulb out\" warnings and flickering.
- Poor grounding: A weak or corroded ground connection disrupts current flow, causing intermittent light behavior.
- Low-quality LED bulbs: Cheap LEDs often lack proper drivers or heat dissipation, leading to unstable performance.
- Heat buildup: Excessive heat inside the headlight housing can cause thermal throttling, where the LED dims or flickers to protect itself.
Step-by-Step Diagnosis and Fixes
Resolving flickering requires a methodical approach. Follow this timeline to isolate and correct the problem efficiently.
- Inspect the bulbs: Remove each LED bulb and examine for visible damage, loose connections, or discoloration. Reinstall firmly, ensuring no gaps in contact.
- Test with known-good bulbs: Swap in halogen bulbs temporarily. If they don’t flicker, the issue is likely LED-specific—either compatibility or driver-related.
- Check ground connections: Locate the headlight ground point (often near the radiator support or fender). Clean any corrosion and tighten the bolt. Use a multimeter to verify continuity between the ground and chassis.
- Measure voltage at the socket: With headlights on, test voltage using a digital multimeter. It should read between 13.5V and 14.5V. Lower or fluctuating readings suggest charging system issues.
- Add CANBUS error cancellers: If your car displays bulb-out warnings or flickers after LED installation, install load resistors or CANBUS decoders to simulate halogen-level power draw.
- Upgrade to high-quality LED kits: Replace budget bulbs with reputable brands featuring built-in drivers, aluminum heat sinks, and waterproof ratings.
Common Mistakes That Worsen the Problem
Well-intentioned fixes can sometimes make flickering worse. Avoid these pitfalls:
| Mistake | Why It’s Harmful | Better Alternative |
|---|---|---|
| Using non-CANBUS-compatible LEDs in modern cars | Triggers error messages and unstable power cycling | Choose CANBUS-ready LED kits or add decoders |
| Ignoring ground wire condition | Even minor corrosion increases resistance and causes flicker | Clean and secure all ground points |
| Installing LEDs without checking housing ventilation | Trapped heat reduces LED lifespan and triggers thermal protection | Ensure airflow or use fans-equipped LED models |
| Assuming the alternator is fine because the battery charges | Alternators can overvolt or undervolt without obvious symptoms | Test voltage under load (e.g., lights, AC on) |
Real-World Example: Solving Persistent Flicker in a 2020 Toyota Camry
A technician received a 2020 Toyota Camry with complaints of both headlights flickering intermittently. Initial inspection showed OEM-style LED bulbs recently installed. The owner had already replaced the bulbs once, suspecting failure.
The technician began by testing voltage at the headlight socket. Readings fluctuated between 12.1V and 14.8V—unstable for LED operation. Further testing revealed a failing voltage regulator within the alternator, causing surges. After replacing the alternator and installing CANBUS-compatible LED units with integrated capacitors, the flickering ceased entirely.
This case highlights how flickering isn't always about the bulb. System-wide electrical health must be evaluated.
“Many customers assume LED flicker means a bad bulb, but more often it's a symptom of deeper electrical issues. Always test the entire circuit before replacing parts.” — Marcus Lin, ASE-Certified Automotive Electrician
Preventive Checklist for Stable LED Performance
To keep your LED headlights running smoothly, follow this maintenance checklist every six months or after major electrical work:
- ✅ Inspect bulb seating and connections for tightness
- ✅ Clean ground terminals and ensure metal-to-metal contact
- ✅ Verify alternator output under load (headlights, heater, radio on)
- ✅ Confirm CANBUS compatibility if using aftermarket LEDs
- ✅ Check for firmware updates (some luxury vehicles control lights via software)
- ✅ Monitor for signs of overheating: dimming after prolonged use, plastic warping near housing
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a weak battery cause LED headlights to flicker?
Yes. A weak or aging battery cannot stabilize voltage effectively, especially at idle. When the engine is off or running at low RPM, insufficient voltage can cause LEDs to flicker or pulse. Test your battery’s health with a load tester and replace if capacity falls below 75%.
Do I need resistors for my LED headlights?
You may need them if your vehicle has a CANBUS monitoring system. These systems expect higher wattage from halogen bulbs. LEDs draw less power, so the car thinks the bulb is out. Adding load resistors or CANBUS decoders tricks the system into recognizing the LED as functional, preventing flicker and error codes.
Why do my LED headlights flicker only when I turn on the AC or radio?
This typically indicates voltage sag under load. When additional accessories activate, demand increases. If your alternator or wiring can’t keep up, voltage drops momentarily, causing LEDs to flicker. Upgrade your alternator or add a supplemental capacitor to buffer power delivery.
Final Thoughts: Safety Starts with Reliable Lighting
Flickering LED headlights aren’t just inconvenient—they’re a safety risk. Dim or erratic lighting reduces reaction time and makes your vehicle harder to see. While some fixes are simple, like cleaning a ground wire, others require deeper electrical diagnostics. Never ignore persistent flickering, even if it seems minor.
Investing in quality components, understanding your vehicle’s electrical architecture, and performing regular checks can prevent most issues before they start. Whether you're upgrading to LEDs or troubleshooting existing ones, precision and patience pay off in reliability and peace of mind.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?