Luteinizing hormone (LH) plays a pivotal role in regulating the menstrual cycle and triggering ovulation. When LH levels are too low, the entire reproductive system can be thrown off balance, leading to irregular cycles, anovulation, and difficulty conceiving. Understanding why LH drops, how it affects fertility, and what actionable steps you can take is essential for anyone trying to optimize their reproductive health.
What Is Luteinizing Hormone and Why It Matters
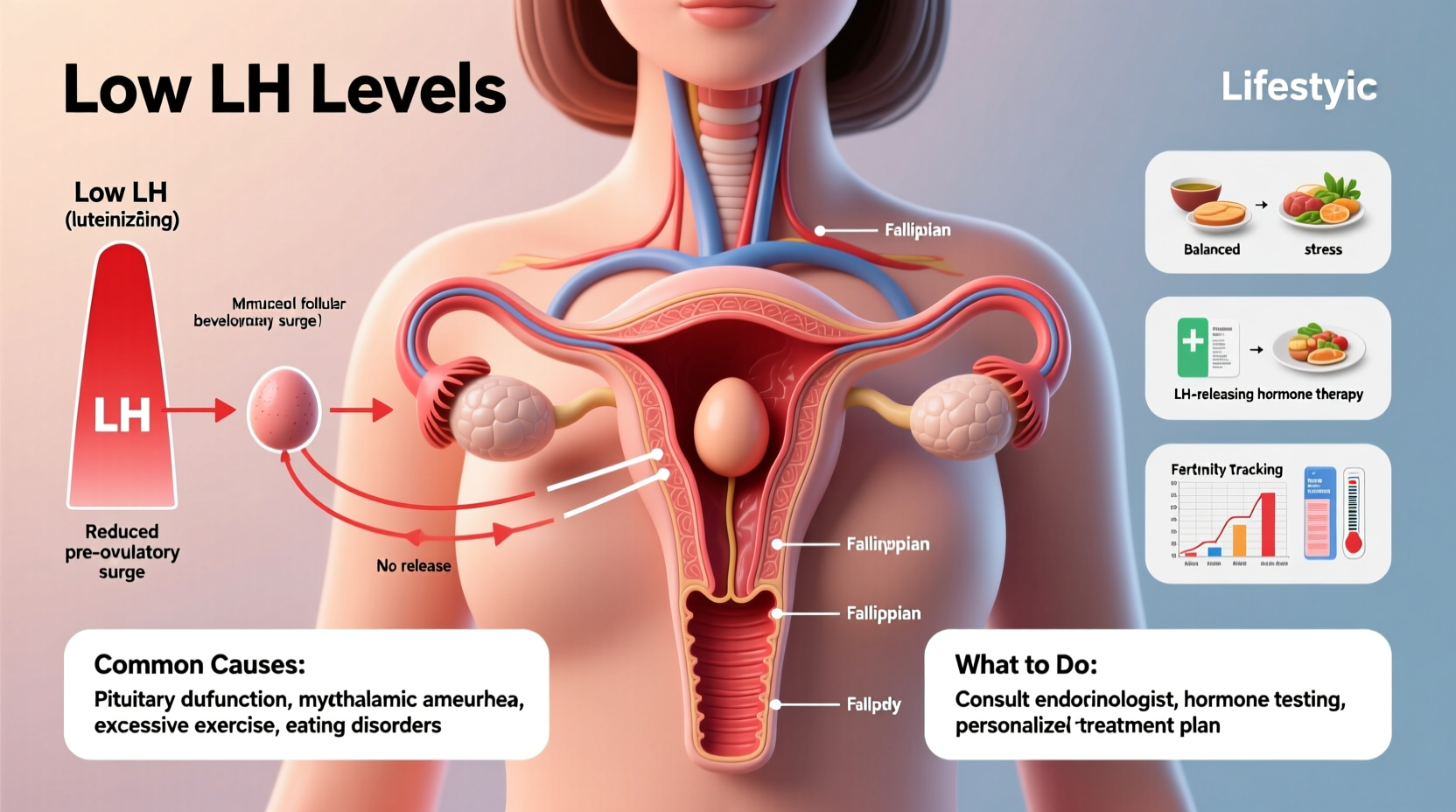
LH is produced by the pituitary gland and released into the bloodstream in pulses throughout the menstrual cycle. Its primary function is to signal the ovaries to release a mature egg during ovulation. A sharp rise in LH—known as the LH surge—typically occurs 24 to 36 hours before ovulation and is the key trigger for follicular rupture.
Beyond ovulation, LH also stimulates the corpus luteum to produce progesterone after ovulation, which prepares the uterine lining for potential implantation. Without adequate LH, this cascade fails to initiate properly, resulting in disrupted cycles or absent ovulation.
“LH is the hormonal ‘spark’ that ignites ovulation. If that spark is weak or missing, conception becomes significantly more difficult.” — Dr. Rebecca Tran, Reproductive Endocrinologist
Common Causes of Low LH Levels
Low LH doesn’t occur in isolation—it’s often a symptom of broader hormonal or physiological imbalances. The most frequent underlying causes include:
- Hypothalamic dysfunction: Stress, excessive exercise, or low body weight can suppress the hypothalamus, reducing GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone), which in turn lowers LH production.
- Functional hypothalamic amenorrhea (FHA): Common in athletes or individuals with eating disorders, FHA results from energy deficiency disrupting the HPO (hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian) axis.
- Pituitary disorders: Tumors, inflammation, or trauma affecting the pituitary gland can impair LH secretion.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): While PCOS is often associated with high LH, some variants show normal or even low LH, especially in lean or early-stage cases.
- Hyperprolactinemia: Elevated prolactin levels suppress LH and GnRH, interfering with ovulation.
- Thyroid imbalances: Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can disrupt the delicate feedback loop between hormones, indirectly lowering LH.
- Medications: Long-term use of certain drugs like opioids, antipsychotics, or hormonal contraceptives may temporarily suppress LH.
How Low LH Impacts Ovulation and Fertility
Ovulation relies on a precise sequence of hormonal signals. When LH is insufficient, the final maturation and release of the egg fail to occur—an outcome known as anovulation. This directly impacts fertility because no egg means no possibility of fertilization.
Even when ovulation does occur, suboptimal LH levels can result in:
- Incomplete follicular development
- Poor-quality eggs
- Corpus luteum insufficiency, leading to low progesterone
- Shortened luteal phase, making implantation less likely
Women with chronically low LH often experience irregular or absent periods (oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea). Over-the-counter ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) may fail to detect a surge, not because ovulation isn't happening, but because the LH rise is too subtle to register.
Recognizing the Signs of Low LH
Symptoms aren’t always obvious, but common indicators include:
- Absent or infrequent menstrual cycles
- No positive OPK results despite tracking
- Low basal body temperature shifts (indicating lack of progesterone rise)
- Difficulty conceiving despite regular intercourse during fertile window
- Fatigue, low libido, or mood changes linked to hormonal imbalance
Diagnosing Low LH: What Tests You Need
If you suspect low LH, diagnosis should be guided by blood testing timed appropriately in your cycle. Key tests include:
| Hormone | Optimal Timing | Normal Range (IU/L) |
|---|---|---|
| LH | Day 3 of cycle (early follicular) | 3–10 |
| FSH | Day 3 | 3–10 |
| Prolactin | Any time (fasting, morning) | 5–25 |
| TSH | Any time | 0.4–4.0 |
| Progesterone | Mid-luteal phase (~7 days post-ovulation) | ≥10 indicates ovulation |
A single low LH reading isn’t conclusive. Consistently low levels across multiple cycles, especially when paired with low FSH, suggest hypothalamic or pituitary involvement. Your healthcare provider may also order a pelvic ultrasound or MRI if a pituitary tumor is suspected.
What to Do: Natural and Medical Approaches to Raise LH
The right treatment depends on the root cause. Some women respond well to lifestyle adjustments, while others require medical intervention.
Step-by-Step Guide to Addressing Low LH
- Confirm the diagnosis: Get comprehensive hormone testing through a reproductive endocrinologist or functional medicine provider.
- Assess lifestyle factors: Evaluate stress levels, sleep quality, body weight, and exercise intensity.
- Optimize nutrition: Ensure adequate caloric intake, healthy fats, and micronutrients like zinc and vitamin B6, which support pituitary function.
- Reduce physical and emotional stress: Chronic cortisol elevation suppresses GnRH, so prioritize rest, mindfulness, and recovery.
- Consider medical treatments: Depending on the cause, options include pulsatile GnRH therapy, gonadotropin injections, or dopamine agonists (for high prolactin).
Mini Case Study: Recovery from Functional Hypothalamic Amenorrhea
Sarah, a 29-year-old marathon runner, hadn’t had a period in 14 months. She ate 1,400 calories daily, trained six days a week, and was under significant work stress. Bloodwork revealed low LH (1.8 IU/L), low FSH, and low estradiol. Diagnosed with FHA, she worked with a reproductive health dietitian and therapist to increase her calorie intake, reduce training volume, and practice stress reduction techniques. After four months, her LH rose to 5.2 IU/L, and she resumed regular ovulatory cycles without medication.
Checklist: Actions to Support Healthy LH Levels
- ✅ Get hormone bloodwork done on Day 3 of your cycle
- ✅ Track your cycle using BBT, cervical mucus, and OPKs
- ✅ Eat enough calories and include healthy fats (avocado, nuts, olive oil)
- ✅ Limit intense exercise if you have irregular or absent periods
- ✅ Prioritize 7–9 hours of quality sleep per night
- ✅ Manage stress with yoga, meditation, or therapy
- ✅ Consult a specialist if trying to conceive for over 6 months without success
FAQ
Can you ovulate with low LH?
It’s unlikely. Low LH usually prevents the surge needed to trigger ovulation. However, some women may experience “silent ovulation” with minimal hormonal changes that standard tests miss.
Do birth control pills affect LH levels?
Yes. Oral contraceptives suppress natural LH production by providing synthetic hormones, halting ovulation. This suppression is temporary and typically reverses after discontinuation, though recovery can take months.
How long does it take to restore LH levels naturally?
With lifestyle changes, improvements can begin within 2–3 months. Full restoration of regular ovulation may take 3–6 months, depending on severity and adherence to interventions.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Hormonal Health
Low LH levels are a critical but often overlooked factor in unexplained infertility and irregular cycles. Whether the cause is stress, under-eating, or an underlying medical condition, identifying and addressing it early can make a profound difference. You don’t have to accept irregular periods or failed conception attempts as inevitable. With the right testing, targeted lifestyle changes, and professional guidance, many women successfully restore healthy LH levels and achieve ovulation.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?