Understanding how to calculate area is a fundamental skill used in everyday life—from measuring rooms for flooring to planning garden layouts or estimating paint needs. While formulas may seem overwhelming at first, breaking them down into logical steps makes the process accessible to everyone. Whether you're a student, homeowner, or professional, mastering area calculations empowers you to make accurate decisions without relying on guesswork.
Why Area Calculation Matters in Real Life
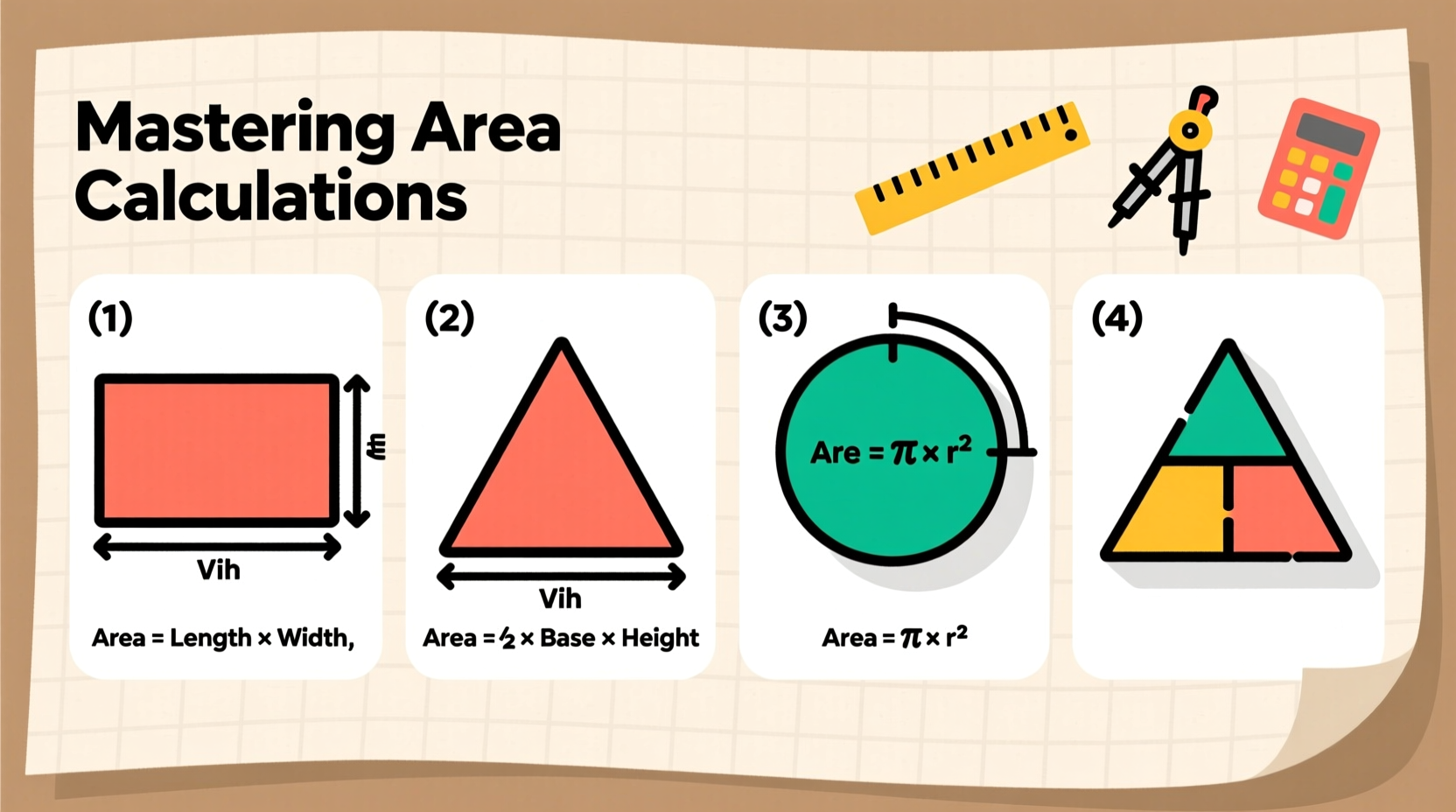
Area isn’t just a math class concept—it has practical applications across many fields. Architects use it to design floor plans, contractors rely on it for material estimates, and even hobbyists use it when crafting or gardening. A precise area measurement ensures efficiency, reduces waste, and saves money.
Mistakes in area calculation can lead to costly errors. Ordering too little tile means a second trip to the store; overestimating fabric leads to unnecessary spending. By learning a few core principles, you can confidently tackle any shape, regular or irregular, with minimal effort.
The Core Principles of Area Measurement
At its heart, area measures the amount of two-dimensional space inside a boundary. It’s expressed in square units—square inches (in²), square meters (m²), etc. The key to mastering area lies in recognizing patterns and applying the right formula based on shape type.
All shapes fall into two broad categories: regular and irregular. Regular shapes have defined formulas. Irregular shapes require decomposition—breaking them into smaller, familiar shapes whose areas can be calculated and summed.
“Accurate area calculation starts with proper identification of shape and consistent unit usage.” — Dr. Alan Reyes, Mathematics Educator and STEM Curriculum Developer
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Area
- Identify the shape: Determine whether it's a rectangle, triangle, circle, trapezoid, or an irregular composite.
- Gather measurements: Use a ruler, tape measure, or digital tool to record necessary dimensions (length, width, base, height, radius).
- Select the correct formula: Match the shape to its standard area equation.
- Convert units if needed: Ensure all measurements are in the same system before calculating.
- Calculate and sum: Apply the formula. For complex shapes, break them down and add individual areas.
- Label your answer: Always include the correct square unit (e.g., cm², ft²).
Common Shapes and Their Formulas
Memorizing a few essential formulas equips you to handle most real-world scenarios. Below is a reference table summarizing the most frequently used equations.
| Shape | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangle | Area = Length × Width | 5 m × 3 m = 15 m² |
| Square | Area = Side² | 4 ft × 4 ft = 16 ft² |
| Triangle | Area = ½ × Base × Height | ½ × 6 in × 4 in = 12 in² |
| Circle | Area = π × Radius² | 3.14 × (3 cm)² ≈ 28.26 cm² |
| Trapezoid | Area = ½ × (Base₁ + Base₂) × Height | ½ × (5 + 7) × 4 = 24 m² |
| Parallelogram | Area = Base × Height | 8 cm × 5 cm = 40 cm² |
When working with circles, remember that π (pi) is approximately 3.1416. For greater precision, use the π button on a scientific calculator. The radius is always half the diameter—never use diameter directly in the formula unless adjusted.
Handling Irregular and Composite Shapes
Not every shape fits neatly into textbook categories. Rooms with alcoves, L-shaped gardens, or oddly designed patios require a different approach. The solution? Break them into standard geometric components.
Imagine a room shaped like an “L.” You can divide it into two rectangles. Measure each separately, compute their areas, then add the results. This method applies universally—whether dealing with floors, walls, or land plots.
Mini Case Study: Renovating a Kitchen Floor
Sarah wanted to install new vinyl tiles in her kitchen. The space included a main rectangular area and a narrow breakfast nook extending off the side. Instead of guessing, she measured both sections:
- Main section: 12 ft × 10 ft = 120 ft²
- Nook: 6 ft × 4 ft = 24 ft²
- Total area: 120 + 24 = 144 ft²
She added 10% extra for cuts and waste (14.4 ft²), rounding up to purchase 159 square feet of material. Her precise calculation prevented shortages and minimized leftover tiles.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
Even experienced individuals make avoidable errors. Awareness is the first step toward prevention. Below is a checklist to ensure accuracy in every calculation.
Area Calculation Checklist
- ✅ Confirm the shape type before choosing a formula
- ✅ Measure all required dimensions accurately
- ✅ Convert all units to the same system (e.g., all in inches or all in meters)
- ✅ Double-check decimal placement, especially with metric units
- ✅ Use parentheses in multi-step formulas to maintain order of operations
- ✅ Add extra material (typically 5–15%) for real-world projects involving cutting or fitting
- ✅ Verify final answer by estimating—does 200 ft² sound reasonable for a small bathroom?
One frequent error involves confusing perimeter with area. Perimeter is the total distance around a shape; area is the space inside. They serve different purposes and use different formulas. Mixing them up leads to incorrect results.
Frequently Asked Questions
What if I don’t know the height of a triangle?
If you have all three side lengths, you can use Heron’s Formula: First calculate the semi-perimeter s = (a+b+c)/2, then Area = √[s(s−a)(s−b)(s−c)]. Alternatively, trigonometry (using angles) can help, but for most practical cases, measuring the height from base to apex is fastest.
How do I calculate the area of a room with curved walls?
Approximate the curve as part of a circle or ellipse. Measure the radius and apply the appropriate circular segment formula. For simplicity, treat the curved section as a rectangle or triangle if high precision isn't critical. Advanced tools like planimeters or CAD software offer greater accuracy for architectural designs.
Can I use online calculators instead?
Yes, many reliable online tools exist. However, understanding the underlying math allows you to verify results, adapt to unique situations, and troubleshoot when digital tools fail. Relying solely on automation limits problem-solving flexibility.
Final Tips for Long-Term Mastery
Becoming proficient in area calculation doesn’t require advanced math skills—just consistency and practice. Start with simple shapes, gradually progressing to compound figures. Keep a reference sheet of formulas handy until they become second nature.
Use real-life opportunities to apply your knowledge: measure your desk, estimate lawn size, or plan a mural. Each application reinforces learning and builds confidence.
“Mathematical fluency begins with practical application. When people see how geometry solves daily problems, it stops being abstract and becomes empowering.” — Dr. Lena Patel, Director of Urban Planning & Education Outreach
Conclusion
Mastering area calculations is within reach for anyone willing to learn a few foundational rules and apply them consistently. From rectangles to irregular layouts, the ability to determine space accurately enhances decision-making in home improvement, design, education, and beyond. With the right approach, what once seemed complex becomes routine.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?