Percentages are everywhere—on price tags, financial reports, nutrition labels, and test scores. Despite their ubiquity, many people hesitate when asked to calculate percentages without a reference or formula sheet. The good news is that with a basic understanding of the concept and access to any standard calculator, you can perform these calculations quickly and accurately. Whether you're calculating a tip, analyzing a discount, or interpreting data, this guide breaks down percentage math into manageable, repeatable steps.
Understanding the Basics: What Is a Percentage?
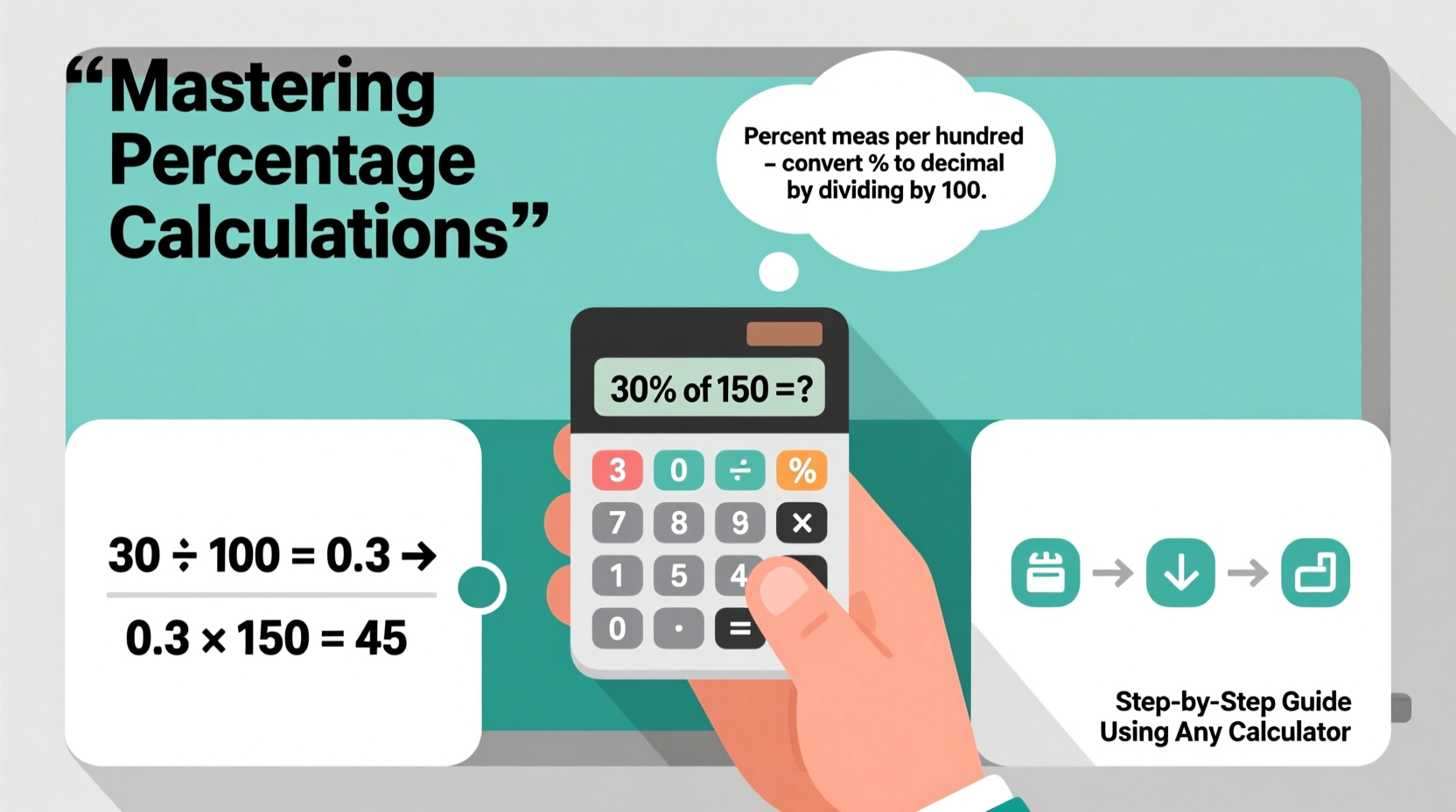
A percentage is a way of expressing a number as a fraction of 100. The word “percent” literally means “per hundred.” For example, 25% equals 25 per 100, or 0.25 in decimal form. This conversion between percentages, decimals, and fractions is the foundation of all percentage calculations.
To convert a percentage to a decimal, divide by 100. So:
- 50% = 50 ÷ 100 = 0.50
- 7% = 7 ÷ 100 = 0.07
- 125% = 125 ÷ 100 = 1.25
To reverse the process—convert a decimal to a percentage—multiply by 100. For instance, 0.33 becomes 33%, and 2.0 becomes 200%.
The Core Percentage Formula and Variations
Every percentage problem revolves around one fundamental formula:
Part = Whole × (Percentage ÷ 100)
This formula allows you to find the part when you know the whole and the percentage. But real-world problems often ask for different components—sometimes you need to find the percentage itself, or the whole amount. Let’s explore the three primary variations:
- Finding the Part: What is 20% of 150? → 150 × (20 ÷ 100) = 30
- Finding the Percentage: 30 is what percent of 150? → (30 ÷ 150) × 100 = 20%
- Finding the Whole: 30 is 20% of what number? → 30 ÷ (20 ÷ 100) = 150
These three forms cover nearly every percentage scenario you’ll encounter, from budgeting to grading.
Step-by-Step Guide: Solving Common Percentage Problems
Follow this structured approach to solve any percentage calculation using a basic calculator:
Step 1: Identify what you’re solving for
Determine whether you need the part, the percentage, or the whole. Read the question carefully. Words like “of” usually indicate multiplication, while “is” often means “equals.”
Step 2: Convert percentage to decimal (if needed)
If the percentage isn’t already in decimal form, divide it by 100. For example, 15% becomes 0.15.
Step 3: Apply the appropriate formula
Use the core equation or its rearrangement based on your unknown.
Step 4: Enter values into your calculator
Type the numbers and operations in order. Be mindful of parentheses if dividing or multiplying multiple terms.
Step 5: Verify reasonableness
Ask yourself: Does the answer make sense? If 10% of 200 is 20, then 20% should be 40—not 4 or 400.
Real-Life Example: Shopping with Discounts
Sarah sees a jacket originally priced at $80 marked “30% off.” She wants to know the sale price and how much she’ll save.
Step 1: Find the amount saved (the part). 30% of $80 = 80 × (30 ÷ 100) = 80 × 0.30 = $24 saved.
Step 2: Subtract from original price. $80 – $24 = $56 final price.
Alternatively, she could calculate what percentage she’s actually paying: 100% – 30% = 70%. Then, 70% of $80 = 0.70 × 80 = $56. Same result, fewer steps.
“Efficiency in percentage calculations saves time and reduces errors, especially in fast-paced environments like retail or finance.” — Dr. Alan Reeves, Mathematics Educator
Common Scenarios and How to Handle Them
Here’s a breakdown of frequent use cases and how to tackle them:
| Scenario | What to Calculate | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tipping at a restaurant | Part (tip amount) | Bill × (Tip % ÷ 100) | $75 bill, 18% tip → 75 × 0.18 = $13.50 |
| Sales tax addition | Total cost | Price × (1 + Tax Rate) | $50 item, 8% tax → 50 × 1.08 = $54 |
| Grade improvement | Percentage increase | ((New – Old) ÷ Old) × 100 | From 70 to 84 → (14 ÷ 70) × 100 = 20% increase |
| Budget allocation | Part of income | Total Income × % Allocation | $3,000 income, 25% for rent → 3000 × 0.25 = $750 |
Checklist: Mastering Percentages with Any Calculator
Use this checklist to ensure accuracy and build confidence:
- ☑ Identify whether you're finding the part, whole, or percentage
- ☑ Convert percentages to decimals before multiplying
- ☑ Use parentheses on your calculator when dividing or combining operations
- ☑ Estimate the answer first to catch major errors
- ☑ Recheck inputs—especially decimal points and zeros
- ☑ Practice with real-life examples like receipts or bills
- ☑ Memorize common conversions (e.g., 50% = 0.5, 25% = 0.25)
Avoiding Common Mistakes
Even simple percentage problems can go wrong due to mental shortcuts or calculator misuse. Here are key pitfalls to avoid:
- Mixing up “of” and “off”: “30% of $80” is a portion; “30% off $80” means subtraction after calculation.
- Forgetting to convert % to decimal: Entering 80 × 30 instead of 80 × 0.30 leads to a tenfold error.
- Misusing the % button: Not all calculators handle % the same way. Test yours: enter 100 + 10 % — does it give 110? If so, it's reliable for quick adds.
- Confusing percentage points with percent change: Growing from 10% to 15% is a 5-percentage-point increase, but a 50% relative increase.
FAQ
Can I use the % button on my calculator for all problems?
Yes, but cautiously. On many calculators, pressing 200 × 15 % returns 30 (15% of 200), which is helpful. However, complex expressions may not interpret % correctly. When in doubt, convert manually to decimals.
How do I calculate percentage increase or decrease?
Subtract the old value from the new one, divide by the old value, then multiply by 100. For example: (90 – 75) / 75 × 100 = 20% increase.
What if the percentage is over 100%?
No issue. 150% of 60 is simply 60 × 1.50 = 90. Percentages over 100 indicate values greater than the original whole.
Conclusion
Mastering percentage calculations isn’t about memorizing formulas—it’s about understanding relationships between numbers and applying consistent logic. With any calculator, even a basic one, you can confidently compute tips, discounts, increases, and proportions. The key is practice, precision, and a clear method. Start with small, everyday applications and gradually take on more complex scenarios. Before long, percentage math will feel intuitive, saving you time and boosting your numeracy in both personal and professional settings.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?