In today’s connected world, access to the internet isn’t just convenient—it’s essential. Whether you’re working remotely, traveling, or facing an unexpected home network outage, your smartphone can serve as a powerful Wi-Fi hub. Most modern phones come equipped with built-in hotspot functionality, allowing you to share your cellular data with laptops, tablets, smart TVs, and more. Yet many users underutilize this feature or struggle with setup, security, and performance issues. This guide walks you through everything you need to know to turn your phone into a reliable, secure, and efficient Wi-Fi source—anytime, anywhere.
How Mobile Hotspots Work
A mobile hotspot converts your phone’s cellular data connection into a wireless signal that other devices can use to access the internet. It functions like a portable router, broadcasting a Wi-Fi network powered by your SIM card’s data plan. The technology behind it is called tethering, and it comes in three forms: Wi-Fi hotspot (most common), Bluetooth tethering, and USB tethering. While all three methods work, Wi-Fi hotspot mode is the most versatile because it supports multiple devices simultaneously and doesn’t require physical connections.
Your phone acts as both a modem and a router. When enabled, it creates a local network with its own SSID (network name) and password. Devices within range can connect just as they would to a home router. However, unlike a fixed broadband connection, a mobile hotspot depends on your cellular signal strength and data allowance. Performance varies based on network congestion, distance from cell towers, and your carrier’s throttling policies.
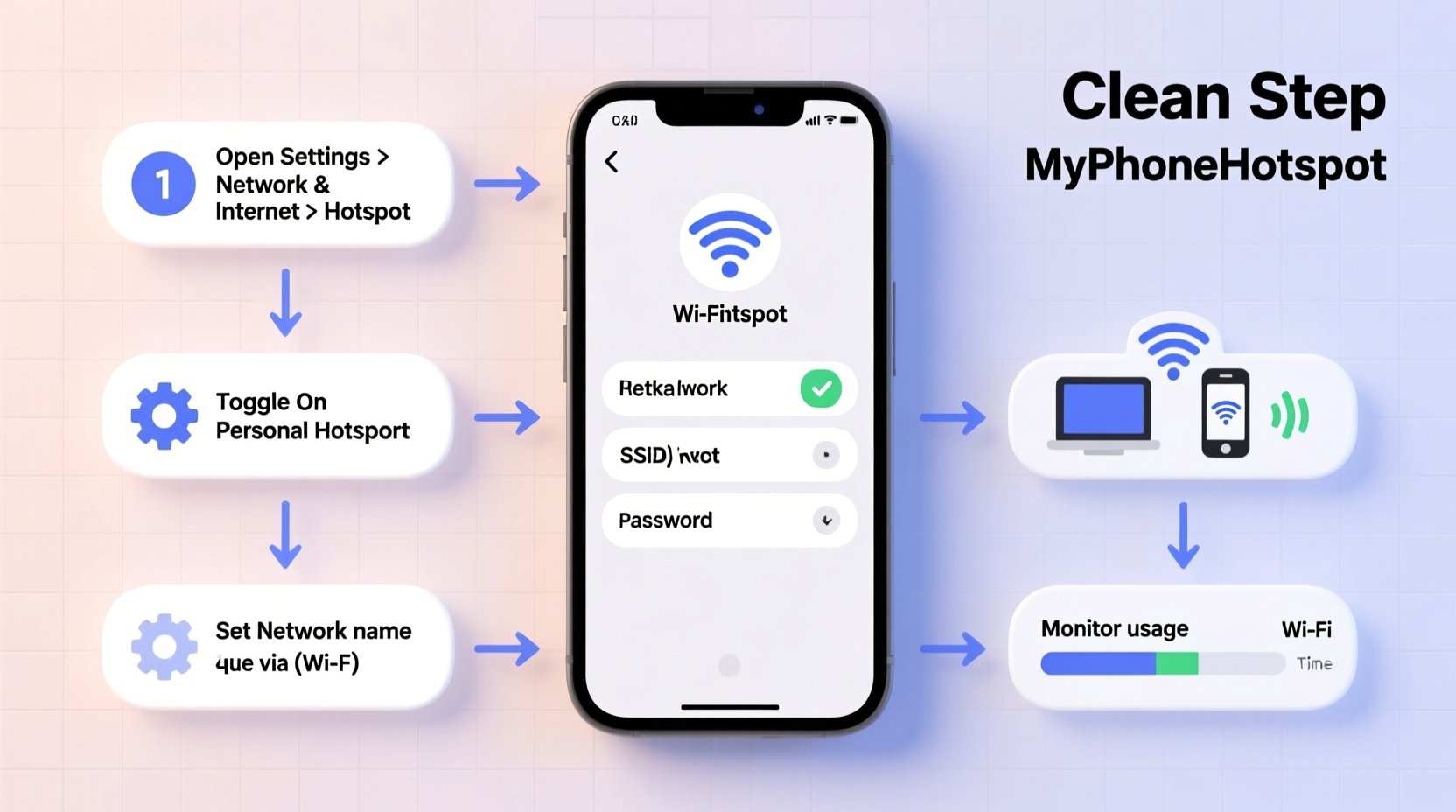
Step-by-Step: Setting Up Your Mobile Hotspot
Setting up a hotspot is straightforward, but exact steps vary slightly between Android and iOS devices. Below is a universal process broken down into clear stages.
- Check Your Data Plan – Before enabling the hotspot, confirm how much high-speed data you have left. Streaming video or downloading large files over a hotspot consumes data quickly. Exceeding your limit may result in throttled speeds or extra charges.
- Ensure Strong Cellular Signal – A weak signal leads to slow or unstable connections. Look for at least two bars of LTE or 5G service before proceeding.
- Enable Hotspot Functionality
- Android: Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Hotspot & Tethering > Wi-Fi Hotspot. Tap “Set up Wi-Fi hotspot” to configure the network name and password.
- iOS: Navigate to Settings > Personal Hotspot. Toggle it on and set a secure password under “Wi-Fi Password.”
- Connect Your Devices – On your laptop or tablet, open Wi-Fi settings and look for the network name (SSID) you just created. Enter the password and connect.
- Monitor Connection Status – Once active, your phone will display a hotspot icon in the status bar. You can view connected devices and manage usage in the hotspot settings menu.
After setup, test the connection by loading a webpage or running a speed test. If speeds are slower than expected, check your signal strength and consider restarting the hotspot or switching to airplane mode briefly before re-enabling it.
Optimizing Performance and Battery Life
Using your phone as a hotspot places significant demands on both battery and processor. Continuous data transmission generates heat and drains power rapidly—sometimes depleting a full charge in under two hours during heavy use.
| Factor | Impact on Hotspot Use | Best Practice |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Rapid drain during prolonged use | Use while charging; carry a power bank |
| Signal Strength | Poor signal increases power consumption | Stay near windows or higher ground |
| Number of Connected Devices | More devices = slower speeds and higher load | Limited to 3–5 devices max for stability |
| Data Usage Type | Streaming uses far more data than browsing | Download content in advance when possible |
“Hotspot efficiency hinges on balancing connectivity, power management, and data conservation. Users who monitor these factors see significantly better long-term reliability.” — David Lin, Wireless Network Engineer at NetSecure Labs
Security Best Practices for Public Use
While convenient, public hotspot use introduces risks. An improperly secured hotspot can be accessed by nearby individuals, potentially exposing your data or enabling unauthorized bandwidth usage.
- Always set a strong Wi-Fi password using a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Avoid using default network names like “AndroidAP” or “iPhone 14,” which make targeting easier for attackers.
- Disable WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup), which has known vulnerabilities.
- Limit visibility by turning off hotspot broadcast when not actively pairing new devices.
- Never conduct sensitive transactions (e.g., online banking) over a hotspot unless connected through a trusted device and secured with a VPN.
Some Android models allow you to restrict connections to specific MAC addresses—a method known as device filtering. While more complex to configure, it adds an extra layer of control.
Real-World Example: Remote Work During Travel
Sophia, a freelance graphic designer, frequently travels for client meetings. During a recent trip to a rural area with no hotel Wi-Fi, she relied on her phone’s hotspot to deliver time-sensitive design revisions. She began by conserving data—downloading cloud files early in the morning when signal was strongest. She connected her laptop via Wi-Fi and used a wall charger to keep her phone powered. To avoid slowdowns, she paused automatic updates and limited background apps. By scheduling large uploads during off-peak hours, she maintained stable upload speeds. Her proactive approach ensured she met her deadline without interruption.
This scenario highlights how strategic planning transforms a basic feature into a professional-grade tool.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Even experienced users encounter issues. Here are frequent problems and their solutions:
- Devices won’t connect: Restart the hotspot, ensure Wi-Fi is enabled on the connecting device, and double-check the password.
- Slow speeds: Check signal bars, move closer to a window, or switch carriers if consistently poor.
- Overheating phone: Reduce the number of connected devices and avoid direct sunlight.
- Unexpected data overages: Set a monthly data warning in your phone settings and track usage weekly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use my hotspot abroad?
Yes, but international roaming charges can be extremely high. Purchase a local SIM card or an international data package before traveling to avoid bill shocks.
Does using a hotspot affect call quality?
On older 3G networks, voice and data couldn’t operate simultaneously. Modern 4G LTE and 5G networks support VoLTE (Voice over LTE), allowing calls and hotspot use at the same time without degradation.
Is USB tethering better than Wi-Fi hotspot?
USB tethering often provides faster, more stable connections with lower latency and reduced battery drain. It’s ideal for single-device use, especially for tasks requiring consistent throughput like video conferencing.
Final Checklist Before Going Live
- ✅ Verify available data balance
- Prevent overages by checking your carrier’s app or dialing your provider’s code (e.g., *#DATA#).
- ✅ Name your network uniquely
- Avoid generic names; choose something identifiable but not personally revealing.
- ✅ Set a strong password
- Use at least 12 characters with uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols.
- ✅ Connect one device first
- Test stability before adding additional users.
- ✅ Keep your phone cool and charged
- Use a cooling pad or remove the case if overheating occurs.
Conclusion
Your smartphone is more than a communication device—it’s a portable internet hub capable of keeping you productive wherever you go. Mastering your mobile hotspot means understanding not only how to turn it on, but how to use it wisely, securely, and efficiently. From adjusting settings for optimal performance to avoiding hidden pitfalls like data caps and battery drain, informed usage makes all the difference. With the right habits, your phone becomes a dependable lifeline in emergencies, a productivity booster on the road, and a flexible alternative to traditional broadband.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?