In today’s connected homes, seamless Wi-Fi isn’t a luxury—it’s a necessity. Whether you’re streaming 4K video in the bedroom, working remotely from the basement, or gaming in the backyard, dead zones and buffering can disrupt your daily life. Two popular solutions for expanding Wi-Fi coverage are mesh networks and range extenders. But when it comes to delivering smooth, reliable whole-home connectivity, which one truly wins?
The answer depends on your home layout, internet usage, and expectations for performance. While both technologies aim to eliminate weak signals, they operate very differently under the hood. Understanding these differences is key to choosing the right solution for uninterrupted browsing, streaming, and smart device operation across every room.
How Wi-Fi Range Extenders Work
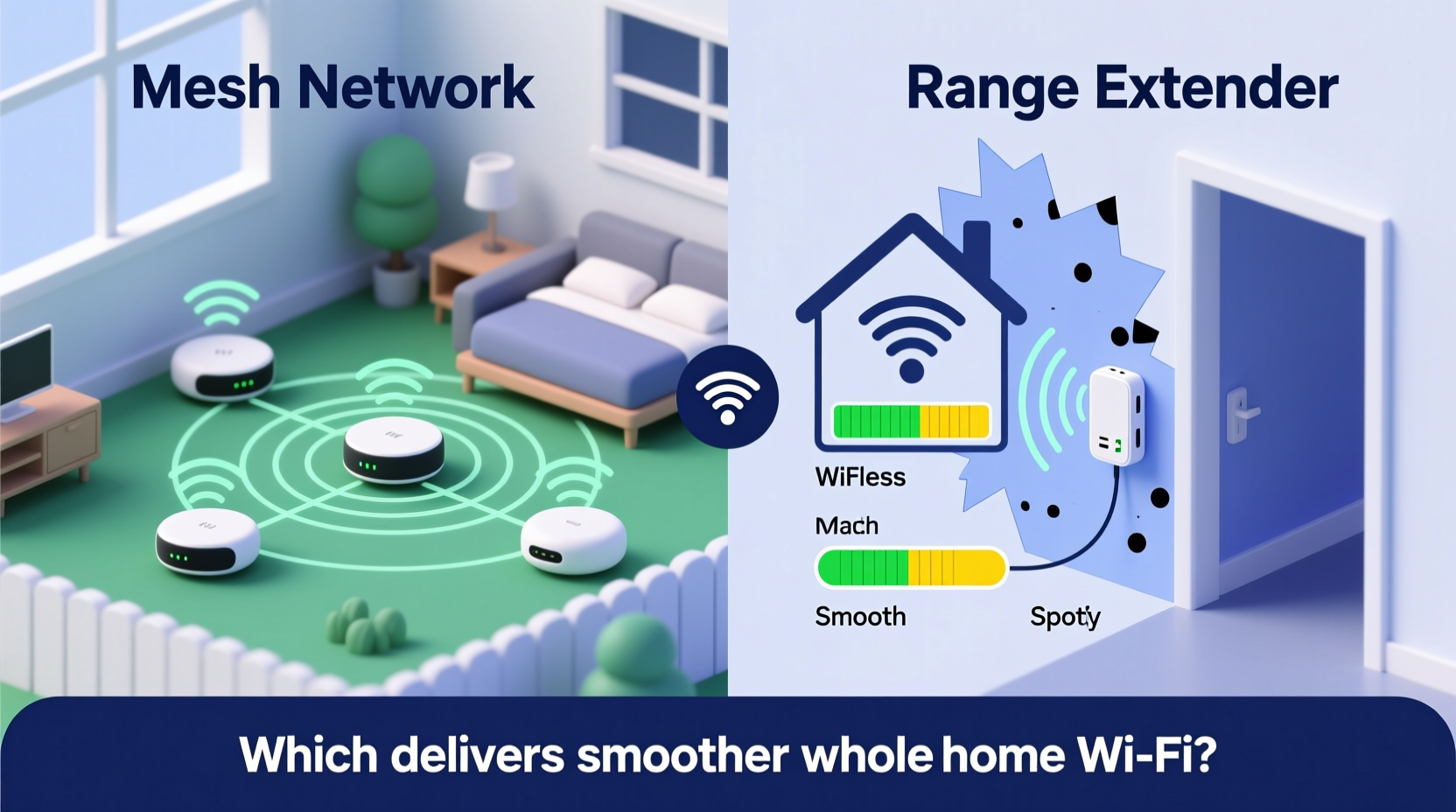
A Wi-Fi range extender, sometimes called a repeater, is a simple device that captures your existing router’s signal and rebroadcasts it further into areas where the original signal is weak. It essentially acts as a middleman between your main router and devices located at the edge of your network.
Extenders are typically plug-and-play. You place them halfway between your router and the dead zone, pair them with your network, and they begin repeating the signal. Most modern extenders support dual-band frequencies (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz), allowing some flexibility in bandwidth distribution.
However, because they rely on repeating the same signal, extenders inherently cut available bandwidth in half. Every time data passes through the extender, it must first receive the signal from the router and then transmit it again—this “hop” introduces latency and reduces throughput. The farther the extender is from the router, the weaker the backhaul connection becomes, further degrading performance.
The Evolution of Whole-Home Wi-Fi: Mesh Networks Explained
Mesh Wi-Fi systems represent a significant leap forward in home networking technology. Instead of relying on a single router and repeated signals, mesh networks use multiple interconnected nodes—typically one primary unit connected to your modem and two or more satellite units placed strategically around your home.
These nodes communicate with each other over dedicated wireless or Ethernet backhaul channels, forming a unified network with a single SSID (network name). Devices automatically connect to the strongest node without requiring manual switching—a process known as seamless roaming.
Unlike traditional extenders, mesh systems intelligently route data through the most efficient path. High-end models use tri-band radios: one band for communication with client devices and two dedicated bands for node-to-node communication. This separation ensures that backhaul traffic doesn’t compete with user data, preserving speed and reducing lag.
“Modern mesh networks are designed for dynamic environments. They adapt to interference, manage traffic loads, and provide consistent performance even in large, multi-story homes.” — David Lin, Senior Network Engineer at NetSignal Labs
Key Differences: Performance, Coverage, and User Experience
To understand which system provides smoother whole-home Wi-Fi, let’s compare mesh networks and range extenders across several critical factors.
| Feature | Range Extender | Mesh Network |
|---|---|---|
| Setup Complexity | Simple, often app-free setup | Requires mobile app; slightly more involved |
| Network Name (SSID) | Often creates a second network (e.g., \"Home_Ext\") | Single SSID across all nodes |
| Seamless Roaming | No—devices may stick to weak signals | Yes—automatic handoff between nodes |
| Backhaul Efficiency | Shares bandwidth with client devices | Dedicated radio or Ethernet backhaul |
| Latency & Speed Loss | High—especially over distance | Low to moderate, optimized routing |
| Coverage Flexibility | Limited by single-hop design | Scalable—add nodes as needed |
| Price (Entry-Level) | $30–$70 | $150–$300 for 2–3 pack |
| Smart Features | Minimal (basic firmware updates) | App control, parental controls, guest networks, QoS |
The data shows a clear trade-off: extenders offer affordability and simplicity but fall short in performance and intelligence. Mesh systems cost more upfront but deliver a superior experience, especially in larger or structurally complex homes.
Real-World Example: A 2,200-Square-Foot Home with Dead Zones
Consider Sarah, who lives in a two-story suburban home with thick interior walls and a finished basement. Her ISP-provided router sits in the living room on the first floor. Upstairs bedrooms get spotty service, and the basement media room frequently drops video calls.
She first tried a $50 dual-band range extender in the hallway upstairs. Initially, signal bars improved on her phone, but streaming still buffered, and her laptop often stayed connected to the distant main router instead of switching to the extender. When she moved downstairs, she had to manually reconnect to a different network named “Basement_Ext,” which only worked intermittently.
Frustrated, Sarah invested in a three-node mesh system. She placed the main unit near the modem and added satellites at opposite ends of the second floor and one in the basement. Within minutes of setup using the companion app, all devices began connecting seamlessly. Video calls stabilized, 4K streaming resumed without interruption, and smart lights responded instantly from any room.
The difference wasn’t just about coverage—it was consistency. With mesh, there were no manual switches, no sudden drops, and no confusion about which network to join. The system self-optimized based on device location and traffic demand.
When a Range Extender Might Be Enough
Despite their limitations, range extenders still have a place in certain scenarios:
- Small apartments or condos: If your dead zone is just one room away from the router, an extender can bridge the gap affordably.
- Budget constraints: For users who can’t justify spending $200+ on networking gear, an extender offers a quick fix.
- Temporary setups: Renters or those hosting short-term guests may prefer non-permanent solutions.
Even in these cases, success depends heavily on placement and environment. Avoid placing extenders behind metal furniture, microwaves, or thick masonry walls, all of which degrade signal quality.
Why Mesh Delivers Smoother Whole-Home Wi-Fi
Smoother Wi-Fi means more than just strong signal bars—it means low latency, consistent speeds, fast roaming, and reliability under load. Here’s how mesh networks achieve this:
- Intelligent Band Steering: Mesh systems direct devices to the best available frequency band (2.4 GHz for range, 5 GHz for speed) without user input.
- Seamless Roaming (802.11k/v/r): Supported by high-end mesh systems, these protocols allow devices to switch nodes quickly during movement, crucial for video calls or gaming.
- Self-Healing Networks: If one node fails or experiences interference, traffic reroutes automatically through others.
- Ethernet Backhaul Support: Many mesh systems allow wired connections between nodes, eliminating wireless backhaul bottlenecks entirely.
- Regular Firmware Updates: Vendors push security patches and performance improvements over time, extending the system’s lifespan.
For households with multiple users, numerous smart devices, or high-bandwidth needs, these features translate directly into fewer interruptions and better responsiveness.
Step-by-Step Guide to Choosing and Installing the Right System
Follow this sequence to ensure optimal results regardless of your choice:
- Map Your Home’s Layout: Sketch out room dimensions, note wall materials (drywall vs. concrete), and identify current router placement.
- Identify Dead Zones: Use your phone’s Wi-Fi analyzer app or walk around testing video playback to locate weak spots.
- Assess Internet Usage: Count how many devices stream, game, or work remotely simultaneously. Heavy usage favors mesh.
- Select Based on Size:
- Under 1,500 sq ft: A single extender might suffice.
- 1,500–3,000 sq ft: Start with a 2–3 node mesh system.
- Over 3,000 sq ft: Consider a mesh system with expandability or professional installation.
- Install and Test: Place equipment according to guidelines, then test speed and ping in previously problematic areas.
- Optimize Placement: Adjust node positions iteratively. Avoid corners, closets, and appliances that emit interference.
Checklist: Mesh vs Extender Decision Tool
Answer the following to determine the best fit:
- ✅ Do you have more than 1,800 square feet to cover? → Choose mesh
- ✅ Are there multiple floors or thick walls? → Choose mesh
- ✅ Do you stream 4K, game online, or host video calls regularly? → Choose mesh
- ✅ Is your budget under $80? → Extender may be acceptable
- ✅ Do you want one network name throughout the house? → Choose mesh
- ✅ Can you run Ethernet cables between potential node locations? → Makes mesh even more effective
FAQ: Common Questions About Mesh and Extenders
Can I use a mesh node and a range extender together?
Technically yes, but it’s not recommended. Mixing systems can create conflicting SSIDs, inefficient routing, and increased interference. Stick with one ecosystem for best results.
Do mesh networks replace my ISP router?
Most do. You connect the primary mesh node to your modem and disable the ISP router’s Wi-Fi to avoid double-NAT issues. Some users keep the ISP router in bridge mode for modem functionality only.
Will a range extender slow down my internet for everyone?
It won’t slow down your overall internet plan speed, but devices connected to the extender will experience reduced bandwidth due to signal repetition. Other devices on the main network remain unaffected unless the extender causes congestion.
Final Recommendation: Invest in Smoothness
While range extenders offer a quick, inexpensive patch for minor coverage gaps, they lack the sophistication needed for truly smooth, whole-home Wi-Fi. Mesh networks, though pricier, deliver a cohesive, adaptive, and future-proof solution that aligns with modern household demands.
If your home has more than one floor, spans over 1,500 square feet, or hosts multiple connected devices, a mesh system is the smarter long-term investment. The seamless roaming, consistent speeds, and intelligent management make everyday digital life noticeably smoother—from morning smart speaker alarms to late-night movie binges.
Technology should serve you quietly and reliably. When your Wi-Fi works so well you forget it’s there, you know you’ve chosen the right solution.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?