In today’s connected homes, consistent Wi-Fi coverage is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. From streaming 4K video to managing smart home devices, every room should have reliable internet access. Yet, many homeowners still struggle with frustrating dead zones—areas where the signal weakens or disappears entirely. Two popular solutions dominate the market: mesh Wi-Fi systems and traditional range extenders. While both aim to expand coverage, they differ significantly in performance, setup, and long-term reliability. Understanding these differences is key to choosing the right solution for your space.
How Wi-Fi Signals Degrade and Create Dead Zones
Wi-Fi signals travel as radio waves, typically at 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz frequencies. These waves can be absorbed, reflected, or blocked by common household materials. Thick walls, metal framing, mirrors, and even large appliances like refrigerators interfere with signal propagation. Over time, as homes grow larger or adopt open-concept layouts with multiple floors, the router’s ability to maintain strong coverage diminishes.
Dead zones aren’t just inconvenient—they disrupt work-from-home setups, interrupt video calls, and degrade streaming quality. The root cause isn’t always distance alone; interference from neighboring networks, outdated routers, or poor channel selection also plays a role. Before deciding between a mesh system and a range extender, it’s essential to understand how each technology addresses these issues.
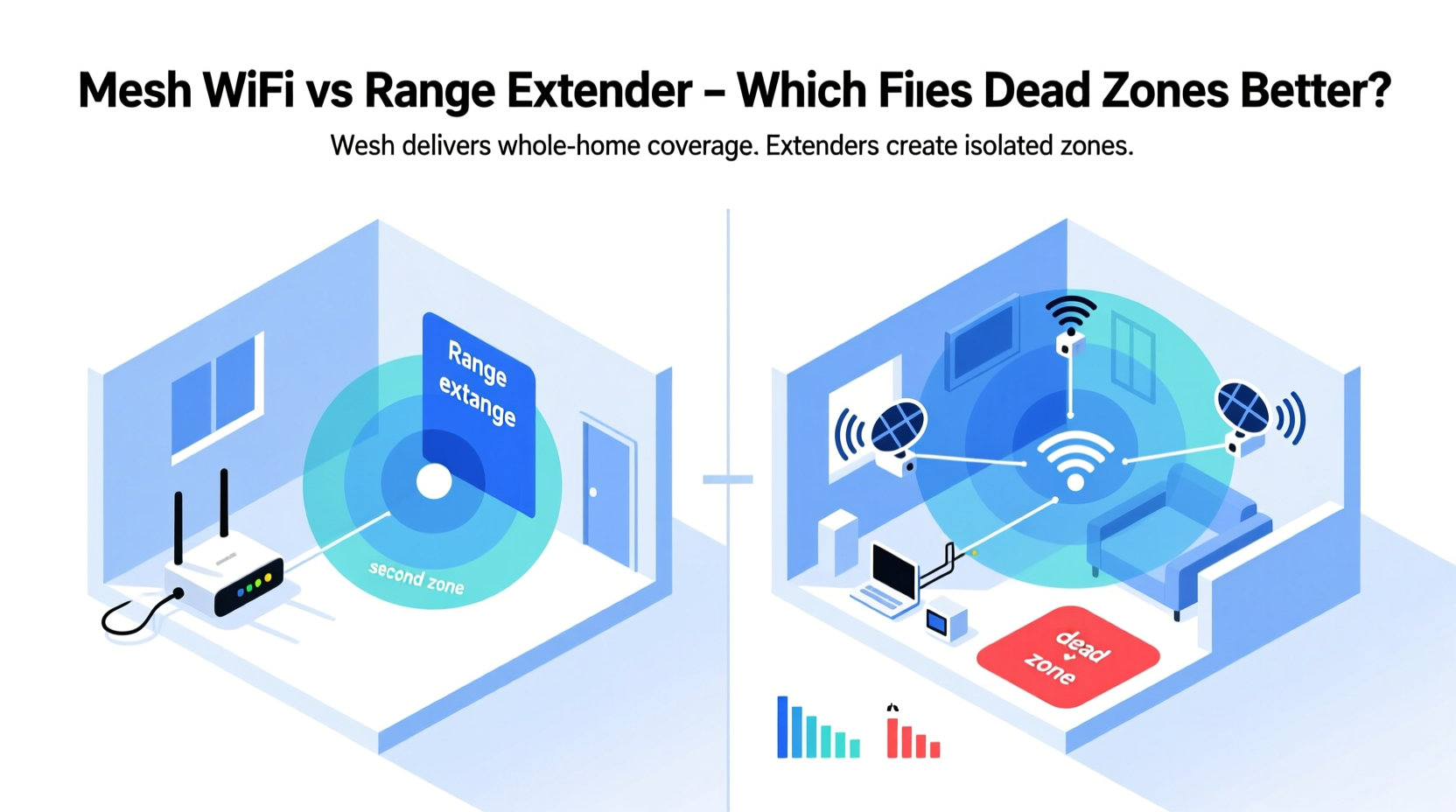
Range Extenders: A Quick Fix with Limitations
A Wi-Fi range extender (also known as a repeater) is a plug-in device that captures your existing router’s signal and rebroadcasts it to areas with poor reception. It's often marketed as an affordable and easy solution to extend coverage without replacing your current equipment.
While extenders can technically reach farther corners of your home, they come with notable drawbacks:
- Signal degradation: Because extenders repeat the signal, they halve the available bandwidth. If your original connection is 100 Mbps, the extended network may deliver only 50 Mbps—or less, depending on distance.
- Separate network names (SSIDs): Many extenders create a second network (e.g., “HomeNetwork_Ext”), forcing users to manually switch between the main router and extender zones.
- Latency spikes: Repeated signals introduce lag, making extenders unsuitable for gaming, video conferencing, or real-time applications.
- Placement sensitivity: To function properly, extenders must be placed within moderate range of the router—not too close, not too far. Poor placement results in minimal improvement.
Despite their low cost, range extenders often fail to deliver a seamless experience. They are best suited for small apartments or temporary use, not comprehensive home coverage.
“Repeaters are like whispering a message across a crowded room—the further it goes, the more distorted it becomes.” — Dr. Alan Reyes, Network Infrastructure Engineer, IEEE Member
Mesh Wi-Fi: Seamless Coverage Through Intelligent Design
Mesh Wi-Fi systems consist of multiple nodes—usually one main unit connected to your modem and satellite units placed throughout your home. Unlike extenders, mesh systems operate as a single, unified network. All nodes share the same SSID and automatically route devices to the strongest available signal.
The technology behind mesh networks enables several advantages:
- Self-healing connections: If one node fails or experiences interference, traffic reroutes through another path without dropping the connection.
- Dedicated backhaul channels: Higher-end mesh systems use tri-band routers, reserving one 5 GHz band exclusively for communication between nodes, preserving bandwidth for end-user devices.
- Smart roaming (802.11k/v/r): Devices seamlessly transition between nodes as you move through the house, similar to cellular handoffs between towers.
- Centralized management: Most mesh systems include mobile apps for monitoring speed, setting parental controls, pausing devices, and updating firmware remotely.
Because mesh nodes communicate intelligently and avoid repeating over public bands, they maintain higher throughput and lower latency than extenders. This makes them ideal for large homes, multi-story buildings, or environments with high device density.
Real-World Example: A Three-Story Townhouse
Consider a townhouse with thick plaster walls and inconsistent coverage. The basement media room and third-floor office frequently lose connectivity. The homeowner first tries a dual-band range extender in the hallway. Initially, signal appears on devices, but streaming buffers constantly, and Zoom calls drop audio. After switching to a tri-band mesh system with three nodes (living room, upstairs hallway, and basement), full-speed gigabit service reaches every floor. Devices automatically connect to the nearest node, and background updates no longer disrupt video playback.
This scenario illustrates why mesh systems outperform extenders in complex environments—they don’t just stretch a signal; they rebuild the network architecture for reliability.
Key Differences: Mesh Wi-Fi vs Range Extender
| Feature | Mesh Wi-Fi System | Range Extender |
|---|---|---|
| Network Name (SSID) | Single, unified network | Often creates a separate network |
| Bandwidth Efficiency | High (especially with tri-band) | Low (halves available bandwidth) |
| Roaming Experience | Seamless, automatic handoff | Manual switching or delayed reconnection |
| Installation Complexity | Simple app-guided setup | Plug-and-play, but finicky placement |
| Cost | Moderate to high ($200–$600) | Low ($30–$100) |
| Ideal For | Homes over 2,000 sq ft, multi-level, dense walls | Small spaces, budget fixes, temporary use |
| Backhaul Connection | Dedicated wireless or Ethernet option | Shared public band |
When to Choose Each Solution
The decision between mesh Wi-Fi and a range extender depends on your specific environment, usage needs, and budget.
Choose a Mesh Wi-Fi System If You:
- Live in a home larger than 2,000 square feet.
- Have multiple floors or thick interior walls.
- Use bandwidth-heavy applications (streaming, gaming, smart home automation).
- Want a single network name and automatic device switching.
- Prefer centralized control via smartphone app.
Consider a Range Extender Only If You:
- Need a quick, low-cost fix for a single dead zone.
- Live in a small apartment or studio under 1,000 sq ft.
- Don’t stream 4K content or play online games regularly.
- Already own a strong AC1900+ router and only need minor reach extension.
Step-by-Step: Upgrading from Extender to Mesh
If you’re currently relying on a range extender and want to upgrade to a more robust solution, follow this sequence:
- Assess your current layout: Walk through your home and note where devices struggle. Use a Wi-Fi analyzer app to measure signal strength in dBm (anything below -70 dBm is weak).
- Determine node count: One mesh node typically covers 1,500–2,000 sq ft. For a 3,000 sq ft home, plan for at least two satellites plus the main unit.
- Choose a system with future-proof specs: Look for Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) support, tri-band radios, MU-MIMO, and OFDMA for handling multiple devices efficiently.
- Install the primary node: Connect it directly to your modem via Ethernet. Follow the app instructions to configure your network name and password.
- Place satellite nodes strategically: Position them halfway between the main router and dead zones, avoiding enclosed cabinets or near microwaves.
- Test performance: Run speed tests in previously weak areas. Compare upload, download, and ping times before and after installation.
- Optimize settings: Enable Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize critical devices, set up guest networks, and schedule device pauses if needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use a mesh system with my existing ISP-provided router?
Yes, but for best results, disable the ISP router’s Wi-Fi and use it as a modem-only device. Then connect your mesh system directly to maintain full control over network settings and performance.
Do mesh systems work with all internet speeds?
Most modern mesh systems support up to 1 Gbps (gigabit) speeds. If you have a faster fiber connection (e.g., 2 Gbps), ensure your mesh hardware has a Gigabit WAN port and supports link aggregation or multi-gig ports for optimal throughput.
Is Wi-Fi 6 necessary for eliminating dead zones?
Wi-Fi 6 improves efficiency and device handling but doesn’t inherently increase range. However, its advanced features (like beamforming and OFDMA) help maintain stable connections in congested environments, making it a worthwhile upgrade when paired with mesh topology.
Conclusion: Building a Smarter, Stronger Home Network
When it comes to fixing dead zones, mesh Wi-Fi systems offer a superior, long-term solution compared to range extenders. They eliminate the trade-offs of reduced speed, fragmented networks, and unreliable roaming. While the upfront cost is higher, the return on investment lies in uninterrupted productivity, smoother entertainment, and smarter home integration.
Range extenders may seem appealing due to their low price, but they often fall short in real-world performance. For anyone serious about whole-home coverage, a mesh system isn’t just an upgrade—it’s a fundamental shift toward a more intelligent network.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?