When the power goes out, a portable generator can keep essential appliances running and maintain comfort in your home. However, connecting a generator directly to your home’s electrical system is not as simple as plugging it into an outlet. Improper connections—such as using a \"suicide cord\"—can lead to backfeeding, electrocution risks, fire hazards, and even legal consequences. To ensure safety, compliance with local codes, and reliable operation, homeowners must use approved, professional-grade methods to integrate a generator with their home power system.
Understanding the Risks of Improper Generator Connections
Many people attempt to power their homes during outages by plugging a generator into a wall outlet using a homemade extension cord. This practice, known as \"backfeeding,\" bypasses circuit breakers and safety mechanisms designed to protect both utility workers and household members. When backfeeding occurs, electricity flows backward through the service panel and into the utility lines—even if the main breaker is off. This poses a lethal risk to line workers repairing downed lines and can damage your generator or home wiring.
The National Electrical Code (NEC) strictly prohibits backfeeding and requires transfer equipment for any permanent or semi-permanent connection between a generator and a home’s electrical system. Understanding these dangers is the first step toward making informed, responsible decisions about backup power.
“Improper generator connections are among the most preventable causes of electrical fatalities during storms.” — National Fire Protection Association (NFPA)
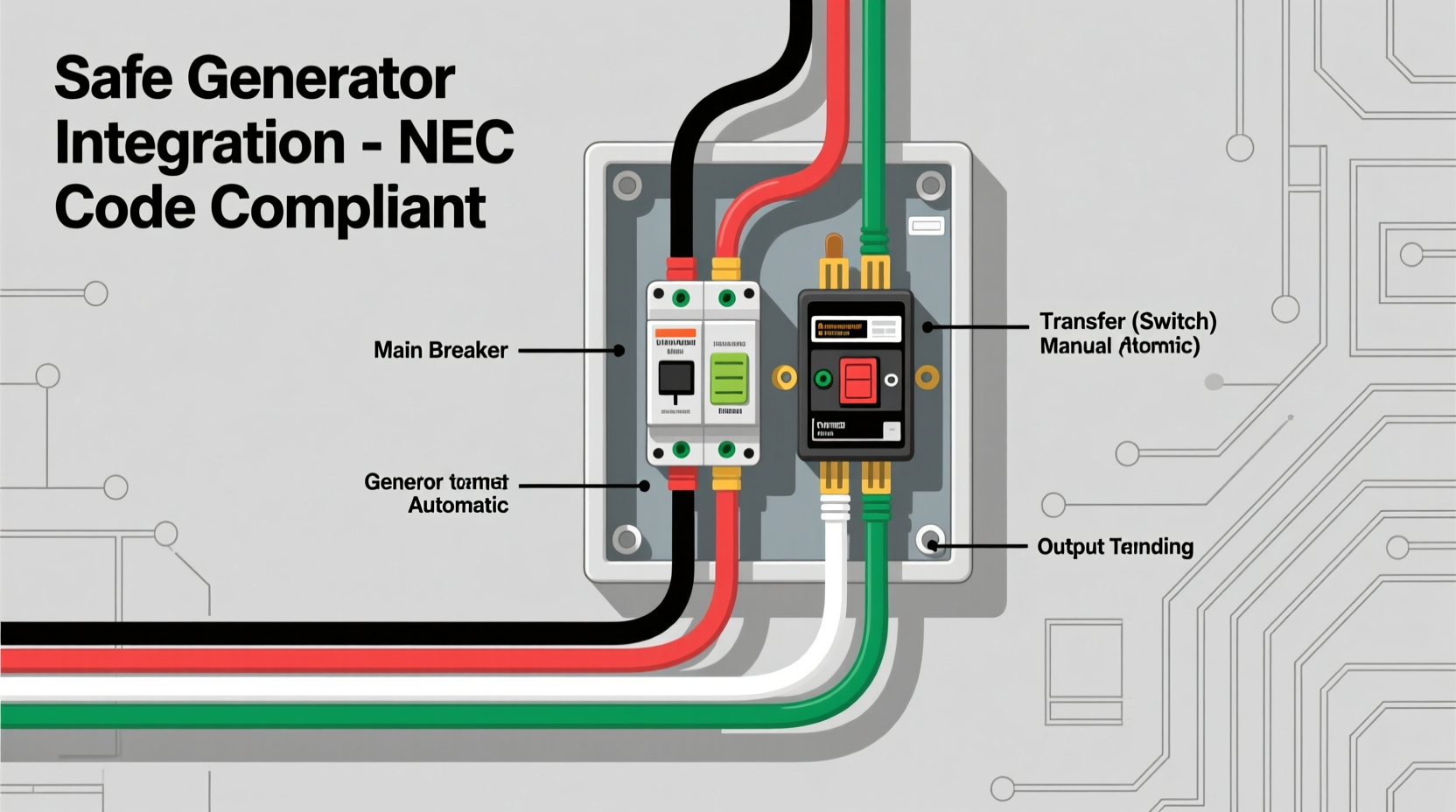
Approved Methods for Connecting a Generator Safely
There are three primary, code-compliant ways to connect a generator to your home: manual transfer switches, automatic transfer switches, and interlock kits. Each has its advantages depending on your budget, technical skill, and power needs.
1. Manual Transfer Switch
A manual transfer switch (MTS) is one of the safest and most widely used solutions. Installed next to your main electrical panel, it allows you to disconnect from the utility grid and switch to generator power using a physical lever. Only designated circuits—such as refrigerators, lights, sump pumps, or well pumps—are powered, preventing overload.
2. Automatic Transfer Switch
An automatic transfer switch (ATS) offers hands-free operation. It monitors utility power continuously and automatically starts your generator and transfers the load when an outage is detected. Ideal for whole-house coverage, ATS systems require a permanently installed standby generator but eliminate the need for manual intervention.
3. Interlock Kit
An interlock kit is a cost-effective alternative that physically prevents the main breaker and generator inlet breaker from being on simultaneously. It uses a metal or plastic slider installed inside the panel to block access to the main breaker when the generator breaker is engaged. While less expensive than a full transfer switch, it still requires precise installation by a licensed electrician and compatibility with your specific panel model.
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing a Manual Transfer Switch
Installing a transfer switch is not a DIY project for beginners. However, understanding the process helps you communicate effectively with your electrician and verify proper execution.
- Assess Power Needs: List essential circuits and calculate total wattage required.
- Select Switch Size: Choose a transfer switch rated for your generator output (e.g., 30A or 50A).
- Install Inlet Box: Mount a weatherproof inlet on the exterior wall near the electrical panel.
- Mount Transfer Switch: Secure the switch adjacent to the main panel.
- Run Conduit: Connect inlet box to transfer switch with rigid metal conduit.
- Wire Circuits: Re-route selected branch circuits through the transfer switch. <7> Connect Neutral & Ground: Bond neutrals correctly; follow manufacturer instructions. <8> Test System: With utility power off, start generator and verify voltage and circuit operation.
This process typically takes 4–8 hours and should only be performed by a licensed electrician familiar with local permitting requirements.
Do’s and Don’ts of Generator Integration
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Use a transfer switch or interlock kit certified to UL 1008 standards | Never plug a generator into a wall outlet (\"suicide cord\") |
| Size your generator appropriately for your load | Don’t overload the generator or run too many high-wattage devices at once |
| Ground the generator properly according to manufacturer specs | Don’t operate a generator indoors or in enclosed spaces |
| Have a licensed electrician perform all permanent installations | Don’t modify your electrical panel without permits or inspections |
| Label circuits clearly on your transfer switch | Don’t assume all outlets will work during generator mode |
Real-World Example: A Homeowner’s Storm Preparedness Upgrade
After enduring multiple winter storms that knocked out power for over 48 hours, Sarah Thompson, a homeowner in upstate New York, decided to upgrade her backup plan. She owned a 7,500-watt portable generator but had been relying on extension cords to power individual appliances—a tedious and inefficient method.
Sarah consulted a local electrician who recommended a 30-amp manual transfer switch with a NEMA L14-30 inlet. The electrician identified six critical circuits: kitchen receptacles, furnace blower, refrigerator, master bedroom, bathroom, and sump pump. After installation and inspection, Sarah could now power her essentials safely within minutes of an outage.
During the next storm, she connected the generator in under ten minutes, isolated the utility feed, and maintained heat and refrigeration without risk. “Knowing my family is safe—and that I’m not endangering anyone outside—is worth every penny,” she said.
Essential Checklist Before Connecting Your Generator
- Confirm your generator's output matches your home’s voltage (120/240V)
- Purchase a transfer solution compliant with NEC Article 702 and local codes
- Hire a licensed electrician for installation and permitting
- Obtain necessary inspections from your municipality
- Label all circuits on the transfer switch or interlock panel
- Test the system monthly under no-load conditions
- Keep generator manuals, transfer switch diagrams, and contact info for your electrician accessible
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I install a transfer switch myself?
While technically possible for experienced individuals with electrical knowledge, most jurisdictions require permits and inspections. Unless you are a licensed electrician, hiring a professional ensures safety, code compliance, and insurance validity.
What size generator do I need for whole-house power?
A true whole-house setup typically requires a standby generator of 10,000 watts or more. Most portable generators (3,000–8,500W) are better suited for powering select circuits via a transfer switch. Calculate your peak wattage by adding startup surges of motors (fridge, AC, well pump).
Is an interlock kit as safe as a transfer switch?
Yes, when installed correctly on a compatible panel. Interlock kits are approved by the NEC and UL-listed for certain brands (like Square D, Siemens). However, they offer less circuit flexibility and rely on user discipline to operate safely.
Final Recommendations for Safe, Efficient Operation
Connecting a generator to your home is not just about convenience—it’s about responsibility. Every year, preventable accidents occur due to improper generator use. By investing in a proper transfer mechanism, working with qualified professionals, and following best practices, you protect your family, your property, and your community.
Whether you choose a manual transfer switch, automatic system, or interlock kit, prioritize safety over speed and always adhere to local regulations. Regular testing, clear labeling, and proper maintenance ensure your backup power system functions when you need it most.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?