For decades, sleep researchers and medical professionals have debated the optimal sleep position for overall health. While many people naturally roll onto their right side during the night, questions persist: Is this position harmful? Could it affect digestion, heart function, or circulation? This article dives deep into the physiological effects of right-side sleeping, separating myth from medical evidence and offering practical guidance for improving sleep quality—regardless of your preferred position.
The Physiology of Side Sleeping
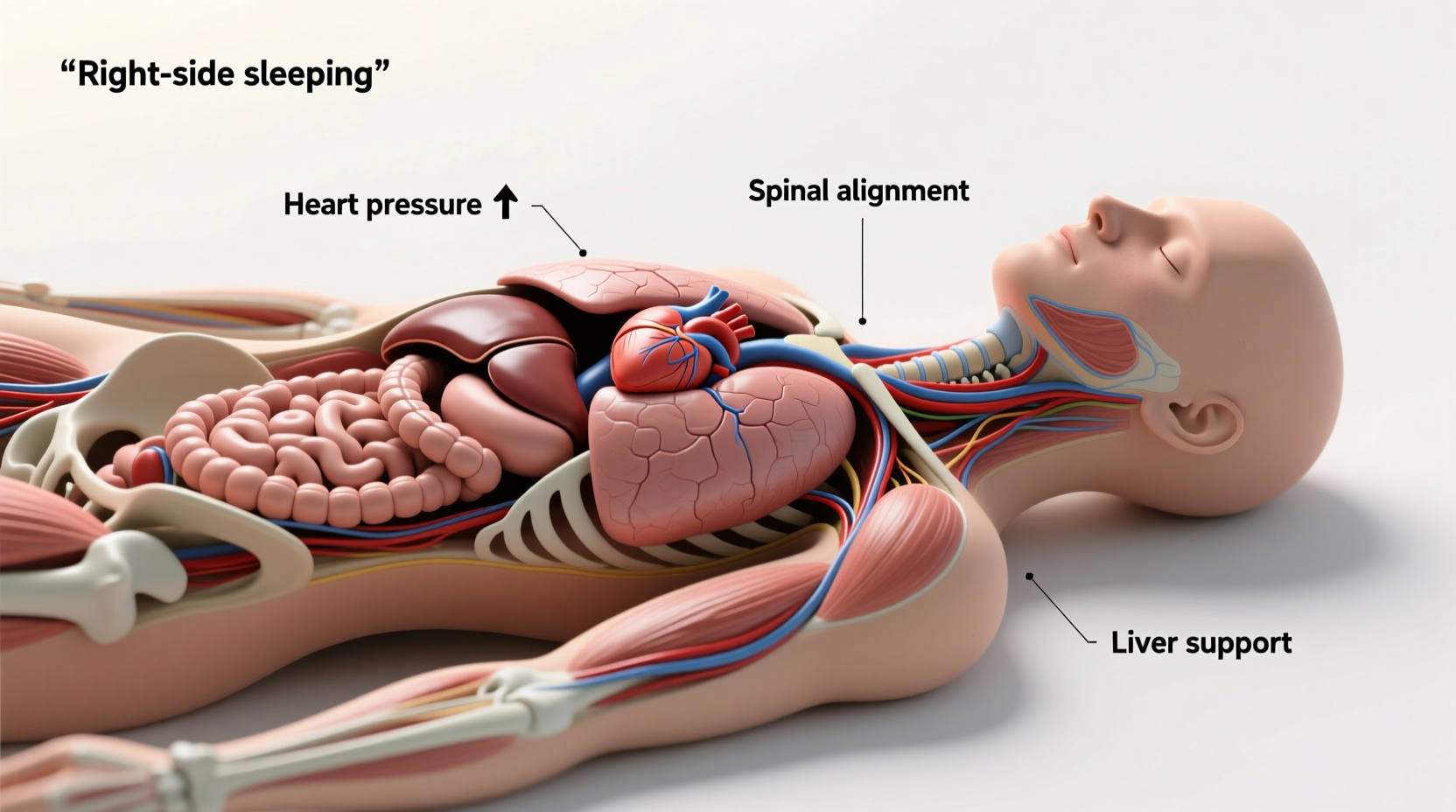
Sleeping on your side—whether left or right—is one of the most common and generally recommended positions. It supports spinal alignment, reduces snoring, and can improve breathing, especially in individuals with obstructive sleep apnea. However, subtle differences exist between left and right side sleeping due to the internal arrangement of organs.
The human heart is located slightly to the left of the chest, and major blood vessels like the aorta arch to the left as well. The stomach, liver, and pancreas are positioned primarily on the right side. These anatomical realities mean that body position can influence organ pressure, blood flow, and digestive processes—even during sleep.
Heart Health and Right-Side Sleeping: What the Research Says
A persistent myth suggests that sleeping on the right side strains the heart because it “rests” on top of the organ. However, modern cardiology dismisses this concern. The pericardium—the sac surrounding the heart—provides protection and allows free movement regardless of body orientation.
According to Dr. Laura Chen, a cardiologist at Boston Medical Center:
“Healthy individuals do not experience adverse cardiac effects from right-side sleeping. The heart is well-supported by connective tissue and functions efficiently in any sleep position.” — Dr. Laura Chen, MD, Cardiologist
That said, certain conditions may warrant caution. Patients with congestive heart failure (CHF) sometimes report increased discomfort when lying on the right, possibly due to changes in venous return and pulmonary congestion. In such cases, doctors often recommend left-side sleeping or elevating the upper body.
Digestive Impact: Liver, Stomach, and Reflux
Your sleep position influences how gravity affects digestion. The stomach’s outlet (pylorus) leads downward toward the small intestine, which lies mostly on the right side of the abdomen. When you lie on your right side, the stomach sits above the duodenum, potentially allowing food and gastric acid to flow more easily into the intestines—but also increasing the risk of acid reflux.
A 2020 study published in *The Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology* found that right-side sleepers experienced significantly more frequent episodes of nighttime acid reflux compared to left-side sleepers. This occurs because the lower esophageal sphincter becomes less effective at preventing backflow when the stomach is higher than the esophagus.
| Sleep Position | Effect on Digestion | Reflux Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Right Side | Faster gastric emptying | Higher |
| Left Side | Slower but safer for esophagus | Lower |
| Back | Neutral digestion | Moderate (if prone to apnea) |
| Stomach | Poor spinal alignment, delayed digestion | High |
On the other hand, right-side sleeping may benefit liver function. The liver, being the largest internal organ, receives about 25% of cardiac output. Some holistic practitioners suggest that right-side sleeping improves hepatic circulation, though clinical evidence remains limited.
Real-Life Example: Managing GERD Through Positional Awareness
James, a 54-year-old teacher from Portland, struggled with chronic nighttime heartburn for years. Despite taking proton pump inhibitors, he woke up with a sour taste in his mouth several times a week. After a sleep study, his gastroenterologist reviewed his positional data and noticed he spent over 70% of the night on his right side.
He was advised to try left-side sleeping using a positional pillow to discourage rolling. Within two weeks, James reported a 60% reduction in reflux episodes. He didn’t eliminate medication entirely, but his sleep quality improved dramatically. This case illustrates how a simple behavioral adjustment—guided by medical insight—can yield meaningful results.
Step-by-Step Guide to Optimizing Your Sleep Position
If you're concerned about the effects of right-side sleeping, follow this actionable plan to assess and adjust your habits:
- Monitor Your Natural Position: For three nights, note which side you fall asleep on and use a sleep-tracking app or partner to observe your typical overnight posture.
- Evaluate Symptoms: Track any heartburn, palpitations, shoulder pain, or numbness upon waking. Keep a brief journal for correlation.
- Try Left-Side Sleeping: Use a body pillow or place a rolled towel behind your back to prevent rolling onto the right side.
- Elevate Your Upper Body: Raise the head of your bed by 6–8 inches using risers to reduce reflux, regardless of side preference.
- Assess After One Week: Re-evaluate symptoms. If improvement occurs, continue the new position. If not, consult a sleep specialist.
When Right-Side Sleeping May Be Beneficial
Despite concerns, right-side sleeping isn’t universally discouraged. In fact, it may offer advantages in specific situations:
- Pregnancy (early stages): Before the third trimester, right-side sleeping is safe and comfortable. Later, left-side sleeping is preferred to optimize blood flow to the placenta.
- Liver drainage support: Some integrative medicine experts suggest right-side lying for 10–15 minutes after meals may assist bile flow, though robust studies are lacking.
- Snoring reduction: For non-reflux sufferers, right-side sleeping can keep airways open better than supine (back) sleeping.
FAQ
Can sleeping on your right side cause heart palpitations?
No direct causal link exists between right-side sleeping and heart palpitations in healthy individuals. However, heightened awareness of heartbeat (due to proximity to the mattress) may create a sensation of palpitations. Those with arrhythmias should consult a cardiologist about optimal sleep positions.
Is it dangerous to sleep on your right side during pregnancy?
In the first and second trimesters, right-side sleeping is generally safe. However, in the third trimester, medical guidelines recommend left-side sleeping to enhance circulation to the fetus. Occasional right-side lying is acceptable, but prolonged positioning should be avoided.
Does right-side sleeping affect blood pressure?
Short-term changes in blood pressure occur with any positional shift, but no evidence shows long-term harm from right-side sleeping. Individuals with orthostatic hypotension or hypertension should focus on gradual movement when waking rather than sleep side alone.
Checklist: Is Your Sleep Position Supporting Your Health?
- ☐ I do not experience frequent nighttime heartburn
- ☐ My spine stays aligned when I sleep (ears, shoulders, hips in line)
- ☐ I use a supportive pillow under my head and between my knees
- ☐ I elevate my upper body if I have reflux or sleep apnea
- ☐ I’ve discussed my sleep position with a doctor if I have heart or digestive conditions
Conclusion
Sleeping on your right side is not inherently bad for you. For most healthy individuals, it poses no significant risks and may even aid digestion in some contexts. However, those with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), late-stage pregnancy, or certain cardiac conditions may benefit from adjusting their position. The key lies in listening to your body, recognizing symptoms, and making informed choices based on both personal comfort and medical advice.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?