Becoming a certified ethical hacker is one of the most sought-after goals in the cybersecurity field. As cyber threats grow in complexity, organizations rely on skilled professionals who can think like attackers to protect digital assets. Ethical hackers use their knowledge of vulnerabilities and penetration techniques to identify weaknesses before malicious actors exploit them. This guide walks you through the essential skills, required certifications, exam preparation strategies, and realistic career progression paths to help you build a successful future in ethical hacking.
Understanding the Role of an Ethical Hacker
An ethical hacker, also known as a penetration tester or white-hat hacker, is authorized to simulate cyberattacks on systems, networks, and applications to uncover security flaws. Unlike malicious hackers, ethical hackers operate within legal boundaries and with explicit permission from the organization they are testing.
Their work includes scanning for open ports, identifying misconfigurations, exploiting software vulnerabilities, and reporting findings with actionable remediation steps. These professionals play a critical role in risk assessment, compliance audits, and strengthening organizational defenses.
“Ethical hacking isn’t about breaking into systems—it’s about making them unbreakable.” — Kevin Mitnick, former hacker and global cybersecurity advocate
Core Skills Required for Ethical Hacking
Success in ethical hacking depends on a combination of technical expertise, analytical thinking, and continuous learning. The following skills form the foundation of a competent ethical hacker:
- Networking Fundamentals: Deep understanding of TCP/IP, DNS, firewalls, routing, and network protocols.
- Operating Systems: Proficiency in Linux (especially Kali Linux) and Windows environments, including command-line tools.
- Programming & Scripting: Knowledge of Python, Bash, PowerShell, and JavaScript for automation and exploit development.
- Cybersecurity Concepts: Familiarity with encryption, authentication, access control, and common attack vectors (e.g., SQL injection, XSS).
- Vulnerability Assessment Tools: Experience with Nmap, Wireshark, Metasploit, Burp Suite, and Nessus.
- Problem-Solving & Curiosity: A mindset geared toward exploring how systems work and where they might fail.
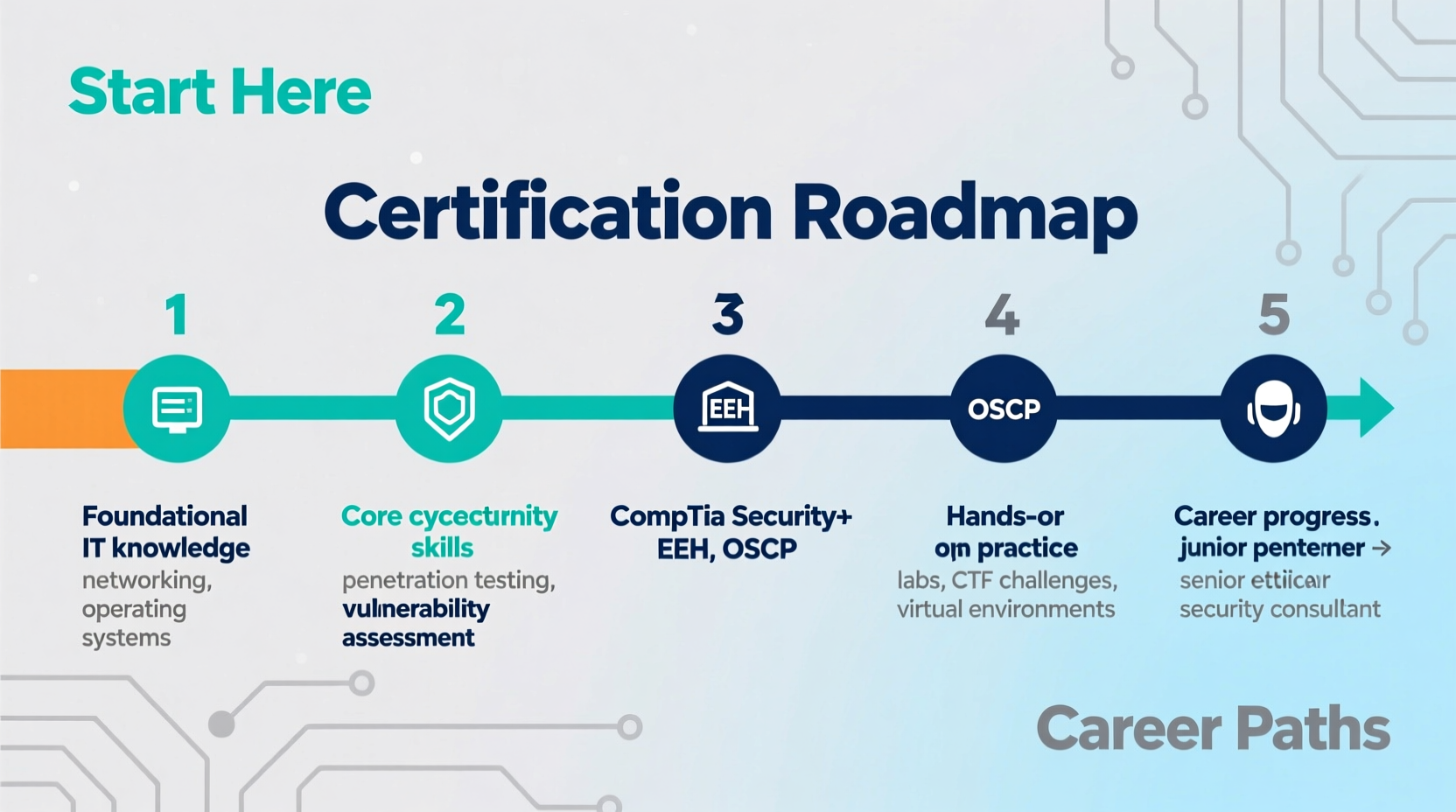
Step-by-Step Path to Certification
Earning recognized credentials validates your expertise and opens doors to job opportunities. Follow this structured timeline to become a certified ethical hacker:
- Learn the Basics (1–3 months): Study networking, operating systems, and foundational security concepts. Use free resources like Cybrary, Coursera, or Professor Messer’s YouTube channel.
- Gain Hands-On Practice (Ongoing): Set up a virtual lab with tools like VirtualBox and install Kali Linux. Practice tasks such as port scanning, packet analysis, and password cracking in controlled environments.
- Earn the CEH Certification (Months 4–6): Prepare for the EC-Council’s Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) exam (312-50). Enroll in official training or self-study using CEH v12 materials. Schedule and pass the exam.
- Advance with OSCP (6–12 months after CEH): Pursue Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP), widely regarded as one of the most hands-on and respected penetration testing certifications.
- Specialize and Expand (Year 2+): Choose advanced paths such as web application security (e.g., OSWA), cloud security (CCSP), or red team operations (CRTO).
Key Certifications at a Glance
| Certification | Provider | Focus Area | Exam Format | Average Salary Range (US) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker) | EC-Council | Broad ethical hacking principles | Multiple choice + performance-based | $70,000 – $110,000 |
| OSCP (Offensive Security Certified Professional) | Offensive Security | Hands-on penetration testing | 24-hour practical exam | $90,000 – $140,000 |
| CompTIA PenTest+ | CompTIA | Vulnerability identification and reporting | Performance-based + multiple choice | $80,000 – $120,000 |
| CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) | (ISC)² | Security management and architecture | Adaptive MCQ exam | $100,000 – $160,000 |
Real-World Example: From IT Support to Ethical Hacker
Jamal worked as a desktop support technician for three years, troubleshooting hardware and software issues. Interested in security, he began studying at night, completed the CEH certification, and volunteered to assist his company’s internal audit team with vulnerability scans. After six months of additional training and earning his OSCP, Jamal transitioned into a junior penetration tester role at a cybersecurity consultancy. Within two years, he was leading client assessments and advising financial institutions on threat mitigation strategies.
His journey highlights that while formal education helps, dedication, hands-on experience, and certification are what truly propel careers forward.
Career Paths After Certification
Earning your CEH or OSCP doesn’t lock you into a single role—it opens multiple pathways depending on your interests and growth trajectory:
- Penetration Tester: Conduct authorized attacks on networks, web apps, and mobile platforms to assess security posture.
- Security Analyst: Monitor systems for breaches, analyze logs, and recommend defensive improvements.
- Red Team Member: Simulate real-world attacks as part of an offensive security team.
- Vulnerability Researcher: Discover zero-day exploits and work with vendors to patch them responsibly.
- Security Consultant: Advise businesses on securing infrastructure, achieving compliance (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR), and incident response planning.
With experience, many ethical hackers move into leadership roles such as Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) or start their own cybersecurity firms.
Checklist: Becoming a Certified Ethical Hacker
- ✅ Understand basic networking and system administration
- ✅ Install and explore Kali Linux in a virtual environment
- ✅ Complete self-paced courses on ethical hacking fundamentals
- ✅ Register for and prepare for the CEH exam
- ✅ Pass the CEH certification exam
- ✅ Gain practical experience via labs or internships
- ✅ Consider advancing to OSCP or other specialized certs
- ✅ Apply for entry-level cybersecurity positions
Frequently Asked Questions
Is programming necessary for ethical hacking?
While not all roles require deep coding skills, knowing Python or Bash helps automate tasks, analyze malware, and write custom exploits. It significantly enhances your effectiveness and employability.
Can I become an ethical hacker without a degree?
Yes. Many successful ethical hackers are self-taught or come from non-traditional backgrounds. Demonstrable skills, certifications, and a strong portfolio (e.g., GitHub projects, CTF competition results) often outweigh formal degrees.
How long does it take to become job-ready?
With focused effort, you can earn your first certification and qualify for entry-level roles in 6 to 12 months. Mastery and senior roles typically require 2–5 years of hands-on experience.
Final Thoughts and Next Steps
Becoming a certified ethical hacker is not just about passing an exam—it’s about cultivating a mindset of continuous learning, curiosity, and responsibility. The demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals continues to rise across industries, offering competitive salaries, remote opportunities, and impactful work.
Your journey starts with commitment. Begin building your lab today, enroll in a reputable course, and connect with communities like Hack The Box or TryHackMe to challenge yourself alongside peers. Every exploit mastered and every system secured brings you closer to a rewarding career protecting the digital world.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?