Installing a fresh version of Android on your mobile phone can breathe new life into aging hardware, unlock advanced features, or simply give you more control over your device. Whether you're upgrading to a newer Android version not officially supported by your manufacturer or switching to a custom ROM like LineageOS for better performance, the process requires precision and caution. Done incorrectly, it can result in a bricked phone—one that won’t power on or function at all.
This comprehensive guide walks you through each phase of installing Android safely, from verifying compatibility to flashing the firmware and restoring your data. By following these steps carefully, you can modernize your device without risking permanent damage.
Understanding the Basics: What Does Installing Android Mean?
When we talk about \"installing Android,\" we typically refer to flashing a new system image onto your phone’s internal storage. This could be an official Over-The-Air (OTA) update, a factory image from Google, or a community-developed custom ROM. The installation replaces the existing operating system with a new one, which may offer improved speed, updated security patches, or additional customization options.
Unlike updating apps or resetting settings, this process modifies core system partitions such as boot, system, and recovery. As such, it requires unlocking the bootloader and using specialized tools like Fastboot and ADB (Android Debug Bridge).
“Flashing a new ROM isn't just about getting the latest features—it's about reclaiming ownership of your device.” — Rafael Torres, Mobile Firmware Engineer at /e/ Foundation
Pre-Installation Checklist: Prepare Your Device and Environment
Before touching any code or downloading files, ensure your setup meets essential requirements. Skipping preparation is the most common cause of failed installations.
Essential Tools You’ll Need
- A compatible computer (Windows, macOS, or Linux)
- A USB cable certified for data transfer
- USB debugging enabled on your phone
- ADB and Fastboot tools installed on your computer
- The correct firmware or ROM file for your exact device model
- Backup of all personal data
Key Compatibility Notes
Using the wrong ROM—even for a similar model—can corrupt your system. For example, installing a Galaxy S21 Ultra ROM on a Galaxy S21 will fail because they have different hardware configurations. Always verify your device’s codename (e.g., “polaris” for OnePlus 5T) before downloading.
| Device Brand | Common Codenames | Where to Find Official Images |
|---|---|---|
| Google Pixel | redfin, raven, bluejay | developers.google.com/android/images |
| OnePlus | fajita, enchilada, kebab | OnePlus Community Forums |
| Xiaomi | laurus, vayu, sweet | XDA Developers or MIUI forums |
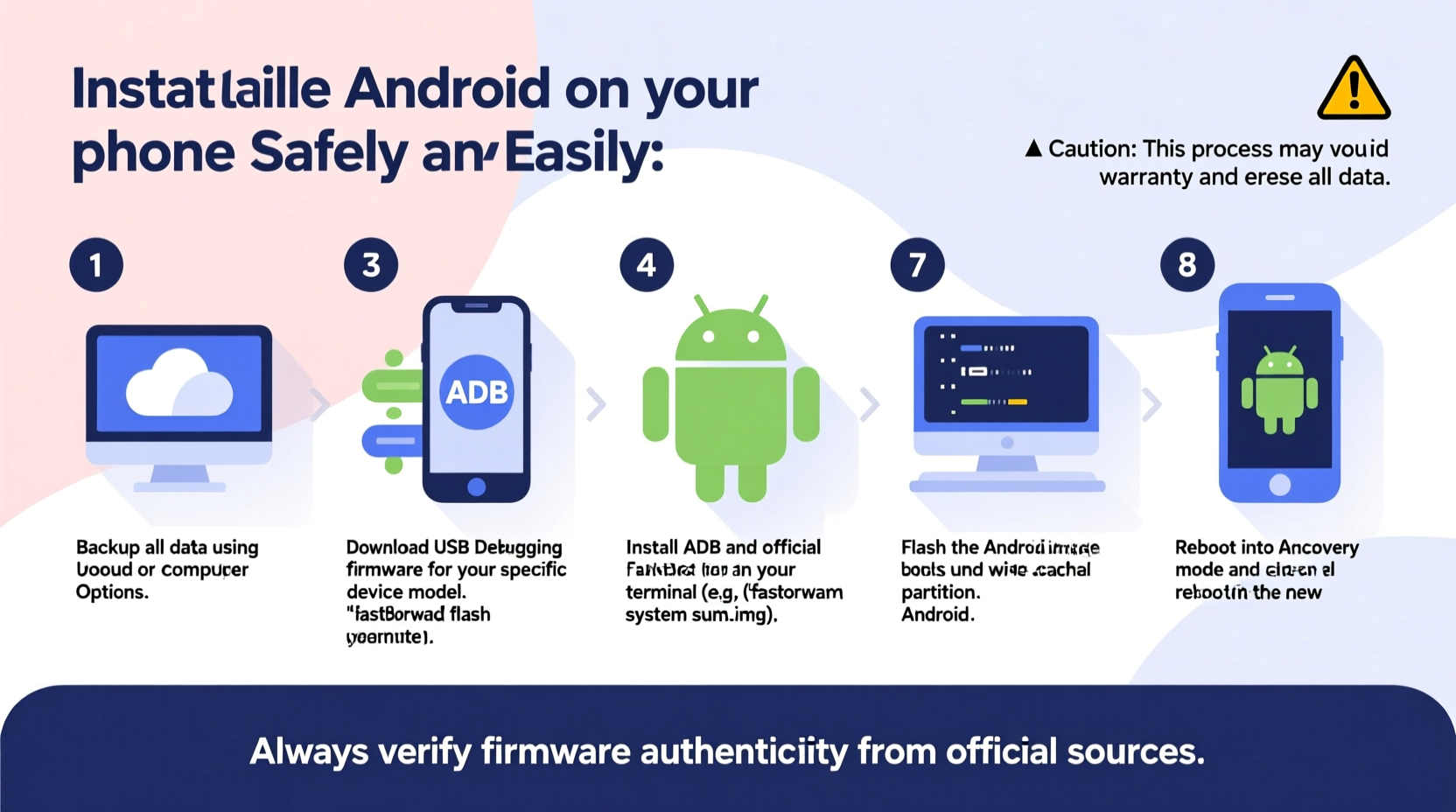
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing Android
Follow this sequence precisely. Each step builds on the previous one, and deviating can lead to irreversible issues.
- Back up all data: Use Google Drive, Samsung Cloud, or local backup tools to save contacts, messages, photos, and app data.
- Enable Developer Options: Go to Settings > About Phone and tap “Build Number” seven times.
- Turn on USB Debugging and OEM Unlocking: Found under Developer Options. OEM Unlocking allows bootloader modification.
- Download ADB and Fastboot: Get the minimal platform tools from the Android Developer site.
- Unlock the Bootloader:
- Power off the phone.
- Hold Volume Down + Power to enter Fastboot mode.
- Connect to PC and run:
fastboot oem unlockorfastboot flashing unlockdepending on device. - Confirm unlock on-screen. This wipes all data.
- Download the Correct ROM: Choose between official factory images (for stock Android) or trusted custom ROMs like LineageOS, crDroid, or Pixel Experience. Verify checksums (SHA-256) to ensure file integrity.
- Flash Recovery (if needed): Some ROMs require TWRP (Team Win Recovery Project). Flash it via:
fastboot flash recovery twrp.img - Boot into Custom Recovery: From Fastboot, use:
fastboot reboot recovery - Wipe Data/Factory Reset: In TWRP, go to Wipe > Format Data, then confirm with “I accept.”
- Install the ROM ZIP File: Transfer the downloaded ROM .zip to your phone via MTP. In TWRP, select Install > choose ZIP > navigate to file > swipe to flash.
- Reboot System: After completion, select “Reboot System Now.” First boot may take 10–15 minutes.
Real Example: Reviving a Dying OnePlus 6
Jamal had a OnePlus 6 that stopped receiving updates after Android 10. The phone felt sluggish, and several newer apps refused to install due to API level restrictions. Instead of buying a new device, he researched how to install LineageOS 18.1 (based on Android 11).
He followed the XDA Developers guide specific to the “fajita” model, unlocked the bootloader, flashed TWRP, and installed the ROM along with an accompanying GApps package. After initial hiccups with fingerprint sensor functionality (resolved by flashing a newer kernel), his phone ran faster than it had in years—with full security updates and gesture navigation support.
This case illustrates how a well-documented process, combined with community resources, can extend a phone’s useful life by three or more years.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will installing a new Android version void my warranty?
Yes, unlocking the bootloader typically voids the manufacturer warranty. However, some brands like Google allow relocking the bootloader to restore warranty status. Check your device policy before proceeding.
Can I go back to the original Android version if something goes wrong?
Yes, as long as you have access to the official factory image for your model. Re-flash the stock ROM using Fastboot commands or a tool like Xiaomi’s Mi Flash Tool or Samsung’s Odin.
Is rooting necessary when installing a custom ROM?
Not always. Many custom ROMs come with root access built-in (e.g., LineageOS with AddonSU), while others are designed to remain unrooted for safety and OTA update compatibility. Rooting adds privileges but also potential security risks.
Final Tips for Long-Term Success
After successfully installing Android, maintain stability by only installing trusted mods and keeping regular backups of your ROM configuration using TWRP. Avoid random ZIP files from unknown sources—even if they promise performance boosts.
Stay engaged with developer communities. Platforms like XDA Developers, Reddit’s r/LineageOS, and Telegram groups provide timely updates, bug fixes, and troubleshooting help.
“Your phone should age gracefully, not abruptly stop working because a company ended support.” — Priya Mehta, Open Source Mobile Advocate
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Device’s Future
Installing Android on your mobile phone isn’t just a technical exercise—it’s an act of digital self-reliance. With the right knowledge and careful execution, you can bypass planned obsolescence, enhance privacy, and tailor your smartphone experience exactly to your needs.
No longer must you wait for manufacturers to deliver updates—or replace a perfectly functional device just to get newer software. Armed with this guide, you now have the power to upgrade, customize, and preserve your mobile investment.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?