MathWorks' MATLAB is a powerful platform for numerical computing, data analysis, algorithm development, and visualization. While the base installation offers robust tools, its true potential unfolds when extended with specialized toolboxes. These add-ons provide domain-specific functions—ranging from signal processing and image analysis to machine learning and control systems. Installing them correctly ensures seamless integration and optimal performance. This guide walks through the entire process of installing MATLAB toolboxes, covering both built-in and third-party options, common pitfalls, and best practices.
Understanding MATLAB Toolboxes
A MATLAB toolbox is a collection of functions, apps, and documentation that extend the software’s core capabilities. Toolboxes are developed either by MathWorks (official) or by external contributors (community or third-party). They are organized as packages with a specific folder structure and can be added to your MATLAB path to make their functions available.
Official toolboxes—such as Signal Processing Toolbox, Image Processing Toolbox, and Optimization Toolbox—are rigorously tested and fully supported. Third-party toolboxes, often shared via GitHub or File Exchange, offer niche solutions but require careful vetting before use.
“Toolboxes transform MATLAB from a general-purpose environment into a specialized lab for engineers, scientists, and researchers.” — Dr. Lena Patel, Computational Systems Engineer
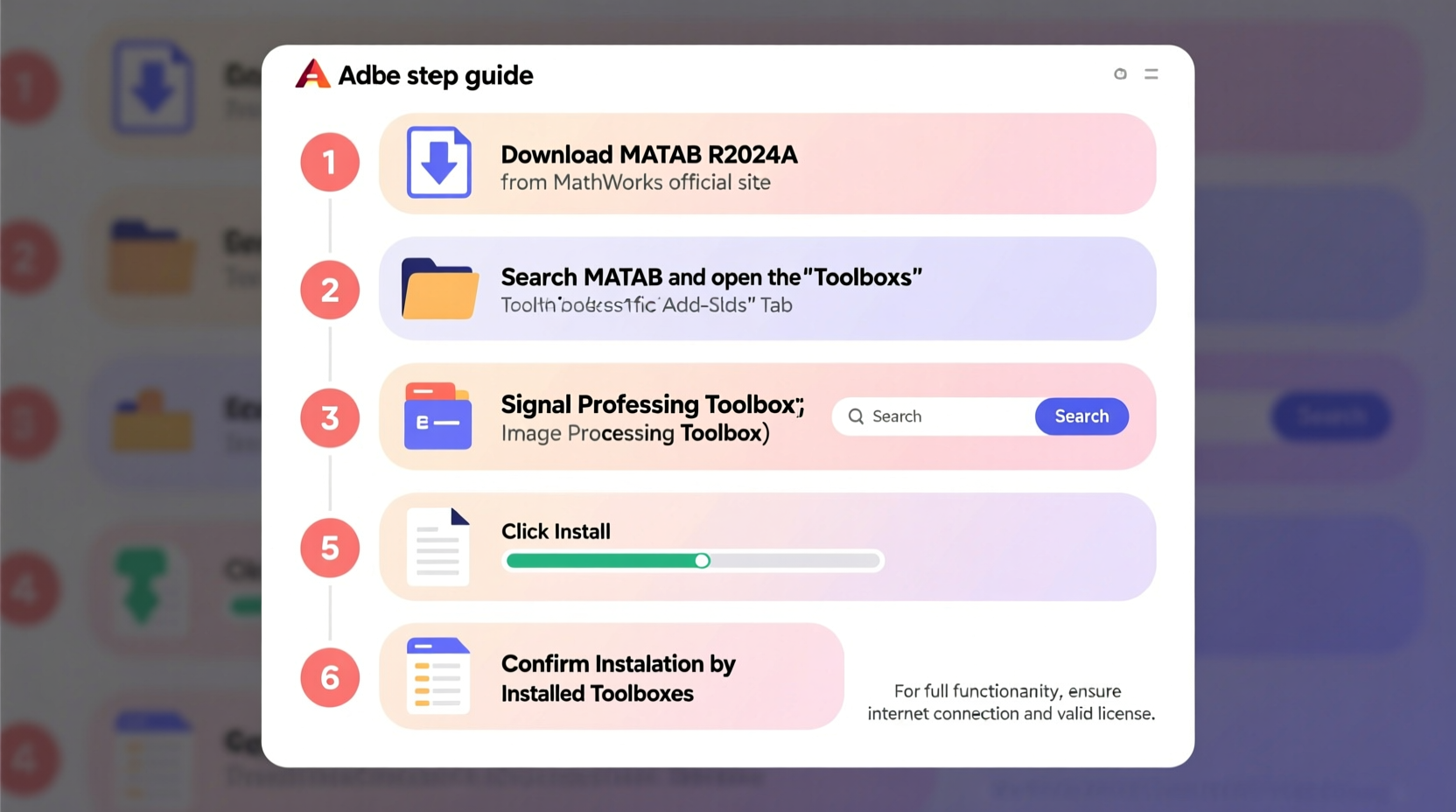
Installing Official Toolboxes via Add-On Explorer
The easiest and most reliable method to install official MATLAB toolboxes is through the integrated Add-On Explorer. This graphical interface allows users to browse, install, update, and manage toolboxes without leaving the MATLAB environment.
Step-by-Step Installation Process
- Launch MATLAB and ensure you are logged into your MathWorks account.
- Navigate to the Home tab on the top ribbon.
- Click on Add-Ons > Get Add-Ons. This opens the Add-On Explorer window.
- Browse categories or use the search bar to find a specific toolbox (e.g., “Curve Fitting Toolbox”).
- Select the desired toolbox and click Install.
- If prompted, accept the license agreement.
- Wait for the download and installation to complete. MATLAB will automatically configure paths and dependencies.
- Verify installation by typing the toolbox name in the Command Window (e.g.,
ver curvefit).
Installing Third-Party Toolboxes from File Exchange or GitHub
Many advanced or research-oriented toolboxes are shared through MATLAB File Exchange or GitHub. These require manual installation but follow standardized procedures.
From MATLAB File Exchange
- Visit MATLAB Central File Exchange.
- Search for the desired toolbox (e.g., “EEGLAB” for EEG data analysis).
- Click Download and save the file (usually a .mltbx file).
- In MATLAB, double-click the downloaded .mltbx file, or go to Home > Add-Ons > Manage Add-Ons and select Install from File.
- Follow the prompts to complete installation.
From GitHub or Source Code
- Download the toolbox folder from the repository (ZIP or via Git clone).
- Extract the contents to a permanent location (e.g.,
C:\\MATLAB\\Toolboxes\\CustomToolbox). - In MATLAB, go to Home > Set Path > Add with Subfolders.
- Select the main toolbox directory and confirm.
- Save the path using Save so it persists across sessions.
- Test by calling a function from the toolbox in the Command Window.
Best Practices and Common Pitfalls
Even with correct installation steps, issues can arise due to configuration errors, version mismatches, or conflicting functions. Adhering to best practices minimizes such risks.
| Action | Do | Avoid |
|---|---|---|
| Toolbox Location | Store in user-defined folders outside MATLAB root | Placing in toolbox/ subdirectories of MATLAB install |
| Path Management | Use “Set Path” and save changes | Manually editing path via script every session |
| Version Compatibility | Check toolbox requirements before installation | Using toolboxes built for older MATLAB versions without testing |
| Updates | Regularly check for updates via Add-On Explorer | Ignoring update notifications for critical toolboxes |
Mini Case Study: Installing the Wavelet Toolbox for Research
Dr. Alan Zhou, a researcher in biomedical signal processing, needed to analyze ECG signals using wavelet transforms. His institution had a campus-wide MATLAB license but did not include the Wavelet Toolbox by default. He followed these steps:
- Opened MATLAB and accessed Add-On Explorer.
- Searched for “Wavelet Toolbox” and found it under Signal Processing & Communications.
- Clicked Install and authenticated with his institutional MathWorks account.
- After installation, he ran
waveletAnalyzerto launch the GUI and verified functionality. - Integrated
cwt(continuous wavelet transform) into his existing scripts successfully.
The entire process took under 10 minutes, and his analysis pipeline was operational the same day.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Despite careful setup, users may encounter problems. Below are frequent issues and their solutions.
- Toolbox functions not recognized: Ensure the toolbox is in the MATLAB path. Run
pathtooland verify the folder is listed. - Licensing errors: Confirm your license includes the toolbox. Use
license('inuse')to see active licenses. - Conflicting functions: If two toolboxes define the same function, MATLAB uses the one highest in the path. Reorder paths or rename local copies.
- Installation fails silently: Check firewall settings or proxy configurations that might block downloads.
Checklist: Preparing for Toolbox Installation
- ✅ Verify MATLAB version compatibility with the toolbox.
- ✅ Log in to your MathWorks account within MATLAB.
- ✅ Ensure sufficient disk space (toolboxes range from 50 MB to over 1 GB).
- ✅ Back up your current path settings using
savepathbefore major changes. - ✅ Review toolbox documentation for special installation instructions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I install toolboxes without an internet connection?
Yes. Download the toolbox installer or files on a connected machine, transfer them via USB, and install offline using “Install from File” in the Add-On Manager. For large suites, MathWorks provides offline installers upon request.
How do I uninstall a toolbox?
Go to Home > Add-Ons > Manage Add-Ons. Select the installed toolbox and click Uninstall. For manually added toolboxes, remove the folder from the path via pathtool and delete the files.
Are third-party toolboxes safe to use?
Most are safe, especially those from reputable sources like university labs or well-rated File Exchange entries. However, always scan downloaded files, review code for suspicious commands (e.g., !system calls), and test in a sandboxed environment first.
Conclusion: Unlock MATLAB’s Full Potential
Installing MATLAB toolboxes is a straightforward yet crucial step in tailoring the software to your technical needs. Whether leveraging official add-ons for industrial applications or integrating open-source tools for academic research, proper installation ensures reliability and efficiency. By following structured methods, maintaining clean path configurations, and staying updated, users can continuously expand MATLAB’s functionality. The ability to integrate new capabilities on demand makes MATLAB not just a program, but a scalable computational ecosystem.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?