Transparent images are essential for graphic designers, web developers, and digital artists who need clean overlays, logos, or composite artwork. Whether you're preparing assets for a website, designing social media graphics, or building layered compositions, mastering transparency in Adobe Photoshop is a foundational skill. This guide walks through proven methods to create perfectly transparent images—without jagged edges, color fringing, or unintended artifacts.
Understanding Transparency in Photoshop
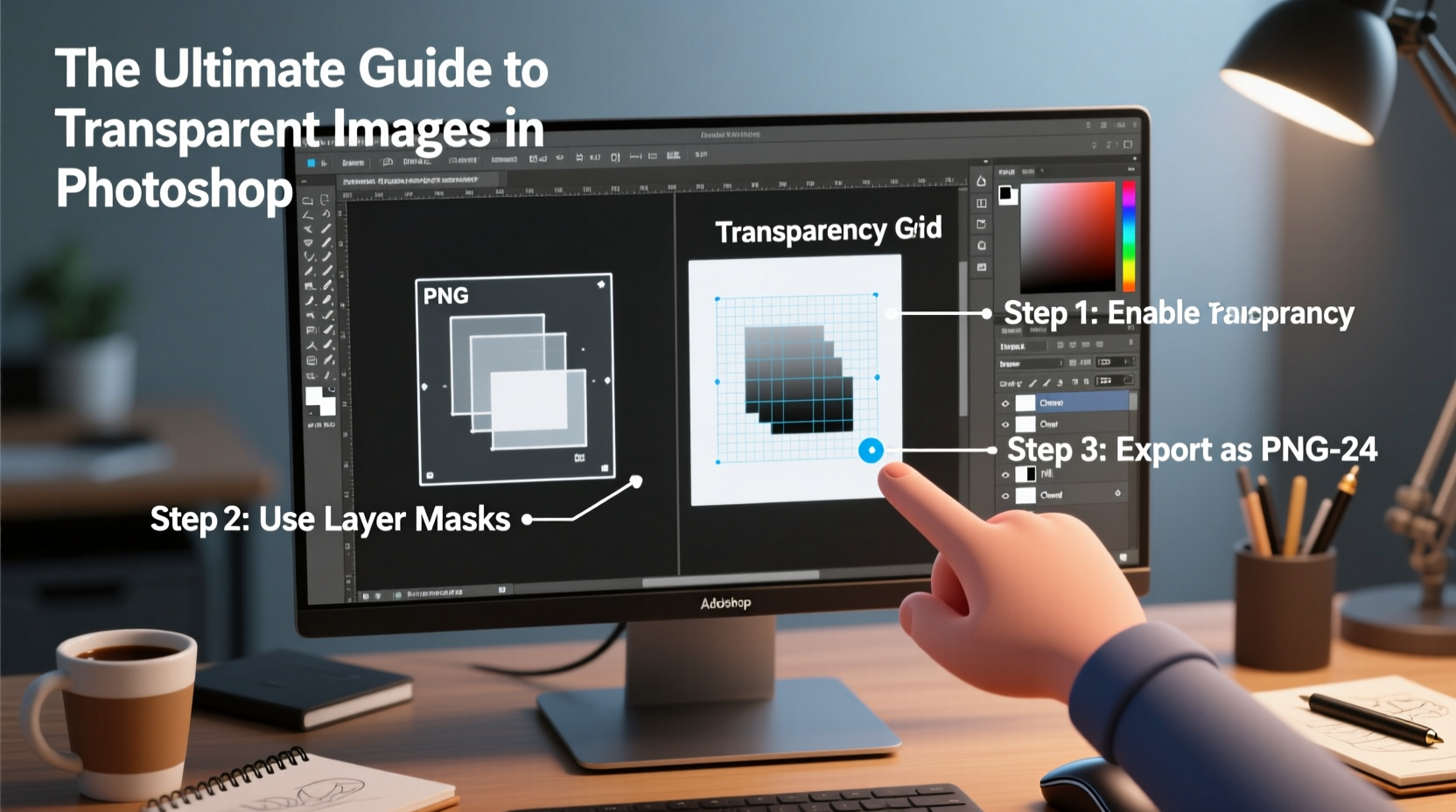
In Photoshop, transparency refers to areas of an image that allow underlying layers or backgrounds to show through. Unlike opaque pixels, which have full color and opacity, transparent areas contain no visible data. The checkerboard pattern in the workspace represents transparency and is not part of the final output.
Transparency is preserved only in certain file formats. JPEG does not support transparency; PNG and GIF do. When saving your work, choosing the correct format is as important as the editing process itself.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Transparent Images
- Open Your Image: Launch Photoshop and open the image you want to edit using File > Open.
- Unlock the Background Layer: If your layer is labeled “Background,” double-click it and click OK to convert it into a regular layer (e.g., “Layer 0”). Only unlocked layers support transparency.
- Select the Subject: Use one of the selection tools:
- Magic Wand Tool – Best for solid, uniform backgrounds.
- Quick Selection Tool – Ideal for objects with defined edges.
- Pen Tool – Most precise for complex shapes like hair or intricate outlines.
- Invert the Selection: Once the background is selected, go to Select > Inverse to switch the focus to your subject.
- Delete the Background: Press the Delete key. The removed area will reveal the checkerboard pattern, indicating transparency.
- Refine Edges: For smoother transitions, especially around hair or soft textures, use Select > Select and Mask. Adjust the radius, smoothness, and contrast sliders to eliminate halos or rough edges.
- Finalize and Save: After refining, click OK. Then choose File > Export > Export As, select PNG format, and ensure \"Transparency\" is checked before saving.
Using Layer Masks for Non-Destructive Transparency
A smarter alternative to permanent deletion is using layer masks. Instead of erasing pixels, you hide them temporarily. To apply a mask:
- Add a layer mask by clicking the Add Layer Mask button at the bottom of the Layers panel.
- With a black brush, paint over areas you want to make transparent.
- Use gray tones for partial transparency (useful for shadows or fading effects).
This method preserves all original pixels, allowing future edits without quality loss.
“Non-destructive editing is the hallmark of professional Photoshop work. Layer masks give you control without sacrificing original data.” — Jordan Lee, Senior Digital Artist at PixelForge Studios
Advanced Techniques for Flawless Transparency
For high-end design work—such as product mockups or logo integration—basic transparency may not suffice. These advanced strategies ensure pixel-perfect results.
Removing Color Fringing
When cutting out subjects from colored backgrounds, residual color edges (fringes) can remain. To fix this:
- Select the layer with transparency issues.
- Go to Layer > Matting > Defringe.
- Enter 1 pixel to remove thin colored outlines.
Alternatively, manually sample nearby colors and use the Clone Stamp Tool gently along the edge.
Dealing with Semi-Transparent Areas
Glass, smoke, or shadow effects often require partial transparency. Use the Channels panel to isolate these elements:
- Navigate to the Channels tab and identify the channel with the highest contrast.
- Duplicate that channel and increase contrast using Levels (Ctrl+L).
- Load the channel as a selection (Ctrl+click on the thumbnail), then return to Layers and apply the selection to your layer mask.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
| Issue | Why It Happens | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| White halo around cut-out object | Color fringe from original background | Use Defringe or reselect with feathering disabled |
| Blurry or jagged edges | Poor selection or low-resolution source | Use Pen Tool or refine edge settings |
| Transparency doesn’t save | Saved as JPEG instead of PNG | Export as PNG or GIF with transparency enabled |
| Gray background appears after export | Checkerboard mistaken for actual background | Test in a dark/light theme or overlay on different colors |
Real-World Example: Preparing a Logo for Web Use
A freelance designer was tasked with placing a client’s logo—a white text with drop shadow—onto various website banners. The original logo had a solid blue background, making it unusable across changing page designs.
The designer followed these steps:
- Opened the logo in Photoshop and unlocked the background.
- Used the Magic Wand to select the blue background.
- Pressed Delete, revealing transparency.
- Applied a layer mask to fine-tune the drop shadow’s fade.
- Exported as PNG-24 with transparency.
The result was a versatile logo asset that seamlessly integrated into multiple layouts, enhancing brand consistency without requiring duplicate versions for different backgrounds.
Checklist: Creating Perfect Transparent Images
Follow this checklist before exporting any transparent image:
- ✅ Convert Background layer to a regular layer
- ✅ Use precise selection tools (Pen Tool for best accuracy)
- ✅ Refine edges using Select and Mask
- ✅ Remove color fringes with Defringe or manual cleanup
- ✅ Verify transparency with zoomed inspection
- ✅ Save in PNG format with transparency enabled
- ✅ Test the image on both light and dark backgrounds
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I make part of an image semi-transparent without deleting pixels?
Yes. Use a layer mask with gray tones. Black hides completely, white reveals fully, and shades of gray create partial transparency. This method is non-destructive and fully editable.
Why does my transparent image look blurry when placed online?
This usually happens due to browser anti-aliasing or improper resizing. Always export at the exact size needed and avoid scaling up small images. Use “Nearest Neighbor” interpolation when reducing size to preserve sharpness.
Is PNG the only format that supports transparency?
No. While PNG is most common for full and partial transparency, GIF supports binary transparency (on/off, no gradients), and TIFF supports transparency but is rarely used for web. SVG is ideal for vector-based transparent graphics.
Conclusion: Elevate Your Design Workflow
Creating transparent images in Photoshop is more than a technical task—it's a gateway to professional-quality design. With the right tools and attention to detail, you can produce clean, reusable assets that adapt seamlessly across platforms and projects. From simple cutouts to complex composites, mastery of transparency empowers creative freedom.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?