Water management for trees—especially in arid climates, urban landscapes, or agricultural orchards—is no longer just about regular watering. It's about precision. With climate volatility increasing, evaporation rates can spike unexpectedly due to heatwaves, wind, or low humidity, rapidly depleting soil moisture even after recent irrigation. This creates a hidden risk: trees may appear healthy one day and show stress symptoms the next. The solution lies in early detection systems. Two primary tools dominate this space: digital water level sensor apps and traditional physical float indicators. But which one offers better protection when it matters most—before evaporation spikes cause irreversible damage?
Digital Water Level Sensor Apps: Real-Time Intelligence
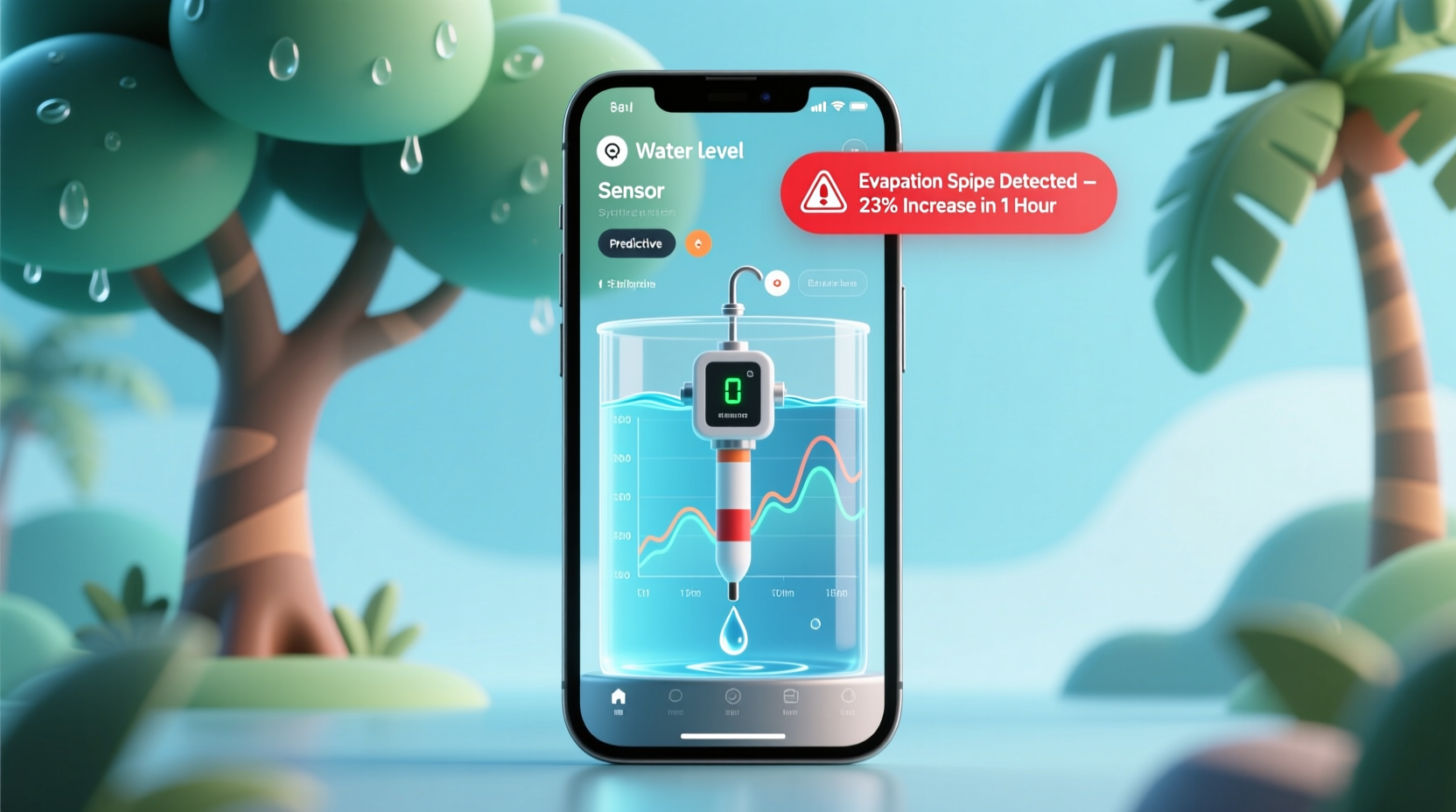
A tree water level sensor app integrates with wireless soil moisture probes buried near a tree’s root zone. These sensors measure volumetric water content (VWC) in real time and transmit data via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi to a smartphone or cloud dashboard. The app analyzes trends, sets customizable thresholds, and sends push notifications when moisture drops below optimal levels—often hours before visible signs of stress appear.
Advanced models use predictive analytics powered by local weather forecasts. For example, if the app detects rising temperatures and low humidity—conditions that signal an impending evaporation spike—it can send a preemptive alert even if current moisture levels are still adequate. This proactive capability is a game-changer for orchard managers, landscapers, and homeowners with high-value trees.
Some apps also offer historical data logging, allowing users to identify seasonal patterns, optimize watering schedules, and reduce overuse. Integration with platforms like Apple HomeKit, Google Assistant, or IFTTT enables voice alerts and home automation triggers.
Physical Float Indicators: Simplicity with Limitations
Physical float indicators, often used in conjunction with reservoir tanks or drip irrigation systems, operate on a mechanical principle. A buoyant float rises and falls with the water level in a chamber connected to the supply line. When the water drops below a certain point, the float triggers a visual flag or audible alarm.
These devices are valued for their reliability in off-grid settings, lack of dependency on power or internet, and minimal maintenance. However, they monitor only the source tank—not the actual soil moisture around the tree. This creates a critical blind spot: a full reservoir does not guarantee adequate root zone hydration, especially during rapid evaporation periods.
For instance, during a sudden 15°F temperature rise, transpiration increases dramatically. Roots draw water faster, but the float won’t react until the tank itself runs low—potentially days after the tree has begun to suffer. By then, leaf scorch, reduced fruit yield, or long-term decline may already be underway.
“Monitoring the tank level is like checking the fuel gauge without knowing how fast the engine is burning gas.” — Dr. Lena Torres, Agricultural Hydrologist, University of Arizona
Comparative Analysis: Key Decision Factors
| Feature | Sensor App | Float Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Measures Actual Soil Moisture | Yes | No |
| Early Evaporation Spike Alerts | Yes (predictive) | No |
| Power Dependency | Battery/solar-powered | None |
| Connectivity Required | Yes (Wi-Fi/Bluetooth) | No |
| Maintenance Frequency | Low (clean sensor annually) | Medium (check for clogs, debris) |
| Cost (Initial) | $80–$200 | $20–$60 |
| Scalability | High (multiple trees, zones) | Low (per-tank basis) |
The table reveals a clear divergence in functionality. While float indicators are cost-effective and robust, they lack the contextual awareness needed to anticipate environmental shifts. Sensor apps, though more expensive upfront, deliver actionable intelligence tailored to each tree’s micro-environment.
Real-World Example: Avocado Orchard in Southern California
In spring 2023, two adjacent avocado groves in Temecula faced identical weather conditions: a forecasted heatwave with temperatures jumping from 78°F to 98°F over 36 hours. Grove A relied on float-based reservoir monitoring. Grove B used a network of soil moisture sensors linked to a mobile app with weather integration.
On Day 1, both reservoirs were full. No alarms triggered in Grove A. Grove B’s app, however, detected rising vapor pressure deficit (VPD) and issued a “High Evaporation Risk” alert at noon, prompting immediate irrigation adjustment. By Day 2, Grove A’s trees showed early wilting; soil tests confirmed moisture depletion despite full tanks. Grove B maintained optimal hydration, with no stress symptoms observed.
Post-event analysis showed Grove B used 18% less water overall due to precise timing, while Grove A overcompensated later, leading to runoff and wasted resources. The sensor system paid for itself within one growing season through improved yield and reduced water costs.
Step-by-Step: Choosing and Implementing the Right System
- Assess Your Environment: Determine whether you’re managing a single ornamental tree or multiple plants across a large area. High-value or drought-sensitive species benefit more from sensor apps.
- Evaluate Connectivity: Ensure reliable Wi-Fi or cellular signal at the installation site. If none exists, consider solar-powered LoRaWAN sensors that transmit over long distances with low bandwidth.
- Install Sensors Correctly: Place probes at 6–12 inches deep near the dripline—the area beneath the outermost branches where roots absorb most water. Avoid proximity to trunks or direct sunlight.
- Set Thresholds: Configure alerts based on species-specific needs. For example, citrus trees prefer 20–30% VWC, while oaks thrive at 15–25%. Use manufacturer guidelines or consult local extension services.
- Integrate Weather Data: Enable forecast syncing so the app can warn of evaporation surges before soil moisture drops.
- Monitor and Adjust: Review weekly reports. If alerts trigger too frequently, fine-tune sensitivity. Seasonal adjustments may be needed as root depth and canopy size change.
When a Float Indicator Still Makes Sense
Despite technological advances, physical float indicators retain value in specific scenarios:
- Backup Monitoring: Use alongside sensor apps as a failsafe during power outages or network disruptions.
- Simple Drip Systems: Ideal for small gardens where water source visibility is limited, such as buried reservoir bottles.
- Budget Constraints: For users who prioritize basic leak detection or refill reminders without needing soil-level insights.
However, relying solely on floats for evaporation-prone environments is risky. They answer “Is the tank full?” but not “Is the tree hydrated?” That distinction is crucial when prevention beats recovery.
Expert Insight: The Future of Tree Hydration Monitoring
“The next frontier isn’t just sensing moisture—it’s understanding plant demand. We’re moving toward systems that combine soil data, leaf temperature, and sap flow to predict stress before it happens.” — Dr. Rajiv Mehta, Plant Biophysicist, UC Davis
This vision is already emerging. Some advanced sensor apps now integrate with infrared thermometers to detect subtle increases in leaf temperature—a physiological precursor to drought stress. Such multimodal systems represent the gold standard for proactive tree care.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can sensor apps work in rainy climates?
Yes. In fact, they’re equally valuable in wet regions by preventing overwatering and root rot. Many apps include drainage alerts and rainfall compensation features that pause irrigation after storms.
Do float indicators require calibration?
Not in the traditional sense, but they should be inspected monthly for debris, algae buildup, or mechanical jamming. A stuck float can give false “full” readings even when the tank is empty.
Are there privacy concerns with sensor apps?
Most reputable brands encrypt data and allow offline modes. To minimize exposure, choose apps that store data locally or offer opt-out cloud syncing. Avoid devices requiring social media logins.
Checklist: Selecting the Right Tool for Your Needs
- ☐ Identify primary goal: prevent under-watering, reduce waste, or monitor remotely?
- ☐ Confirm access to power and internet at the site.
- ☐ Determine number of trees to monitor—single unit or scalable network?
- ☐ Check compatibility with existing irrigation controllers.
- ☐ Evaluate battery life and replacement ease.
- ☐ Prioritize weather integration if evaporation spikes are common in your region.
- ☐ Consider hybrid setups: use a float as backup with a sensor as primary.
Conclusion: Act Before the Spike
Evaporation doesn’t wait for symptoms to appear—and neither should your warning system. While physical float indicators serve a role in basic water management, they fall short when anticipating sudden environmental changes. Tree water level sensor apps, by contrast, transform reactive gardening into proactive stewardship. They provide context-aware alerts, leverage predictive modeling, and integrate seamlessly into modern smart ecosystems.
For anyone responsible for trees where health, yield, or aesthetics matter—from backyard gardeners to commercial growers—the investment in intelligent monitoring pays dividends in resilience, efficiency, and peace of mind. Don’t wait for leaves to curl. Detect the threat before it emerges.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?