Experiencing two periods in one month can be unsettling, especially if it's out of the ordinary for your cycle. While occasional irregularities are normal, frequent or unexpected bleeding may signal an underlying condition. Understanding why this happens—and knowing when to seek help—can empower you to make informed decisions about your reproductive health.
The average menstrual cycle lasts 28 days, but anywhere between 21 and 35 days is considered within the normal range. A period typically lasts 3–7 days. When bleeding occurs more than once per cycle, it’s often not a true period but rather breakthrough bleeding, spotting, or an early onset of menstruation due to hormonal fluctuations or other factors.
Common Causes of Two Periods in One Month
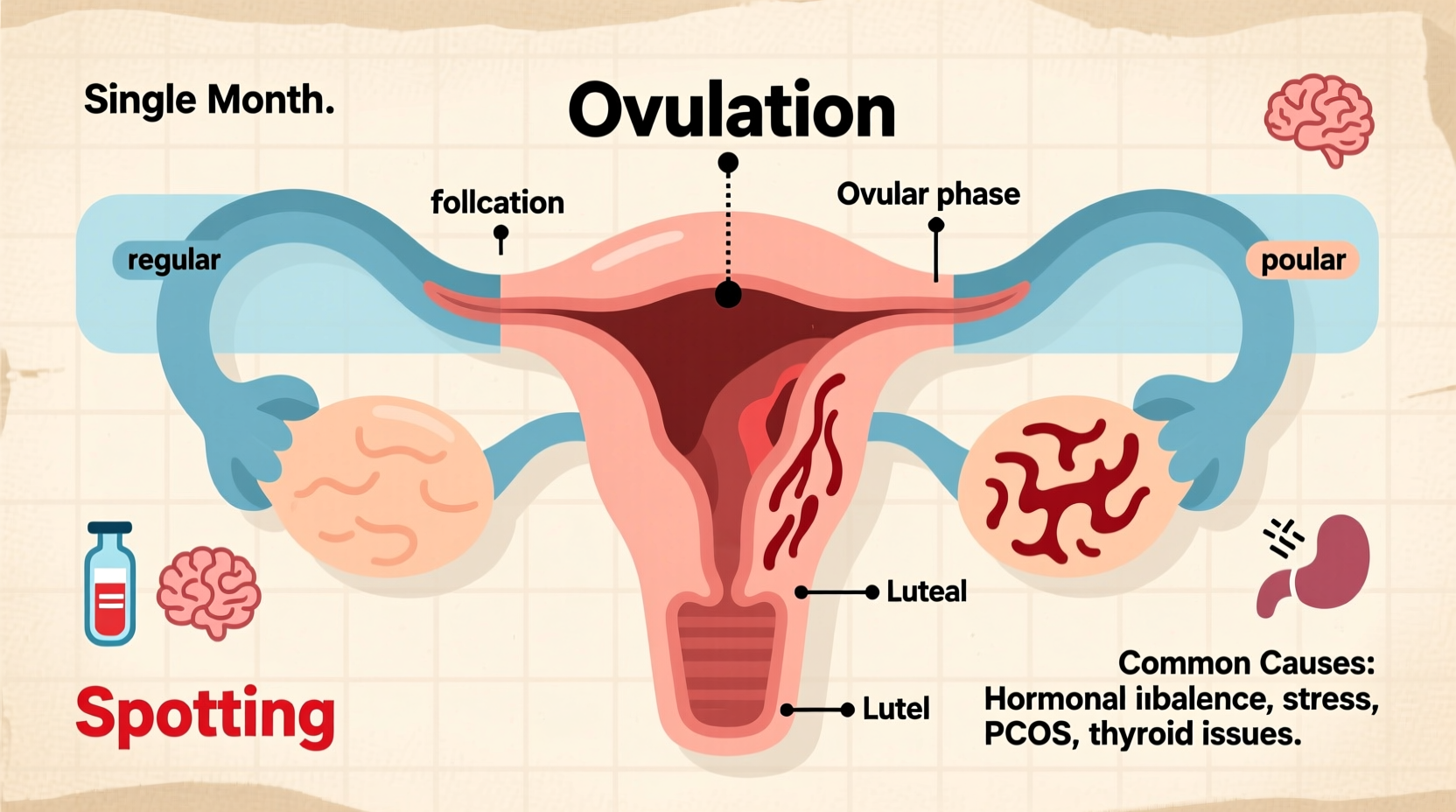
Several factors can lead to multiple bleeding episodes in a single calendar month. These range from natural hormonal shifts to medical conditions requiring attention.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels can cause the uterine lining to shed at irregular intervals. This is common during puberty, perimenopause, or after stopping hormonal birth control.
- Stress: Chronic stress affects the hypothalamus, which regulates hormones responsible for ovulation and menstruation. High cortisol levels can delay or trigger early periods.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Women with PCOS often experience irregular cycles due to elevated androgen levels and insulin resistance, sometimes leading to frequent or missed periods.
- Thyroid Disorders: Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism disrupt hormone balance and can alter menstrual patterns.
- Uterine Fibroids or Polyps: Noncancerous growths in the uterus may cause heavy or frequent bleeding, including mid-cycle spotting that resembles a second period.
- Infections: Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia or gonorrhea can lead to abnormal uterine bleeding.
- Birth Control Changes: Starting, switching, or stopping contraceptives—especially pills, IUDs, or implants—often results in irregular bleeding during the first few months.
When to Worry: 7 Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
While occasional double periods may not be serious, certain symptoms indicate the need for medical evaluation. Here are seven red flags:
- Heavy Bleeding: Soaking through a pad or tampon every hour for more than two hours.
- Prolonged Bleeding: Periods lasting longer than seven days on repeat.
- Severe Pain: Cramps that interfere with daily activities and don’t improve with over-the-counter pain relief.
- Bleeding After Sex: Postcoital bleeding can point to cervical polyps, infections, or precancerous changes.
- Foul-Smelling Discharge: May indicate infection, especially if accompanied by fever or pelvic pain.
- Sudden Onset Without Explanation: If your cycle has always been regular and now isn’t, without lifestyle changes or known stressors.
- Anemia Symptoms: Fatigue, dizziness, pale skin, or shortness of breath due to blood loss.
“Recurrent irregular bleeding should never be dismissed as ‘just stress.’ It’s your body’s way of signaling imbalance—listen to it.” — Dr. Lena Patel, OB-GYN Specialist
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
If you're experiencing two periods a month regularly—or have any of the warning signs—it’s time to consult a healthcare provider. Diagnosis usually involves:
- A detailed medical history and symptom timeline
- Physical and pelvic exam
- Blood tests (hormone levels, thyroid function, complete blood count)
- Ultrasound imaging to check for fibroids, polyps, or ovarian cysts
- In some cases, a biopsy or hysteroscopy to examine the uterine lining
Accurate diagnosis is crucial because treatment varies significantly depending on the cause. For example, PCOS might require lifestyle adjustments and medication like metformin or birth control, while fibroids could necessitate surgical intervention.
Real Example: Sarah’s Experience
Sarah, a 32-year-old teacher, noticed she had two periods in March—one on the expected date and another just 18 days later. At first, she attributed it to stress from finals week. But when it happened again in April, along with fatigue and heavier flow, she scheduled a visit with her gynecologist.
Blood work revealed mild anemia and elevated TSH levels, indicating hypothyroidism. After starting thyroid medication, her cycles normalized within three months. “I didn’t realize how much my energy and mood were tied to my hormones,” she said. “Getting tested was the best decision.”
Step-by-Step Guide to Managing Irregular Cycles
If you’re dealing with unpredictable bleeding, follow this actionable plan:
- Track Your Cycle: Use a calendar or app for at least three months to identify patterns.
- Reduce Stress: Incorporate mindfulness, yoga, or breathing exercises into your routine.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Significant weight loss or gain can disrupt hormone production.
- Evaluate Your Birth Control: Discuss side effects with your doctor; consider alternatives if needed.
- Get Tested: Request screenings for thyroid issues, STIs, and hormone imbalances.
- Rule Out Structural Issues: An ultrasound can detect fibroids or polyps.
- Follow Up: Even if initial tests are normal, revisit your doctor if symptoms persist.
| Cause | Symptoms | Common Treatments |
|---|---|---|
| Hormonal Imbalance | Irregular timing, light/heavy flow | Birth control, lifestyle changes |
| PCOS | Infrequent periods, acne, weight gain | Metformin, combined oral contraceptives |
| Uterine Fibroids | Heavy bleeding, pelvic pressure | Medication, surgery (myomectomy) |
| Thyroid Disorder | Fatigue, weight changes, hair loss | Thyroid hormone replacement |
| Birth Control Adjustment | Spotting between periods | Wait 3–6 months; switch method if persistent |
Frequently Asked Questions
Can stress really cause two periods in one month?
Yes. Stress impacts the hypothalamus-pituitary-ovarian axis, disrupting the release of hormones that regulate your cycle. This can lead to early ovulation or anovulatory cycles with breakthrough bleeding.
Is it possible to ovulate twice in one month?
No. A person cannot naturally ovulate twice in a single cycle. However, what may appear as a second period could actually be ovulation-related spotting, which is lighter and shorter than a true period.
Should I be worried if this only happened once?
Not necessarily. Isolated incidents are often due to temporary factors like travel, illness, or stress. Monitor your next few cycles. If it recurs or worsens, seek medical advice.
Conclusion: Take Charge of Your Cycle
Having two periods in one month isn't always dangerous, but it shouldn't be ignored—especially when accompanied by discomfort, heavy flow, or recurring patterns. Your menstrual cycle is a vital sign of overall health, reflecting everything from hormone balance to metabolic function.
By tracking your symptoms, recognizing warning signs, and seeking timely care, you can address issues early and maintain long-term well-being. Don’t downplay changes in your body. Whether it’s adjusting your lifestyle or consulting a specialist, small steps today can prevent bigger problems tomorrow.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?