USB ports are essential for connecting peripherals like keyboards, mice, external drives, and smartphones. When a USB port stops functioning, it can disrupt workflows, data transfers, and device charging. The issue may stem from hardware failure, outdated drivers, incorrect power settings, or operating system glitches. Resolving USB problems requires a methodical approach—starting with simple checks and progressing to advanced diagnostics. This guide walks through proven solutions to restore functionality across Windows, macOS, and Linux systems.
Initial Diagnosis: Is It the Port, Cable, or Device?
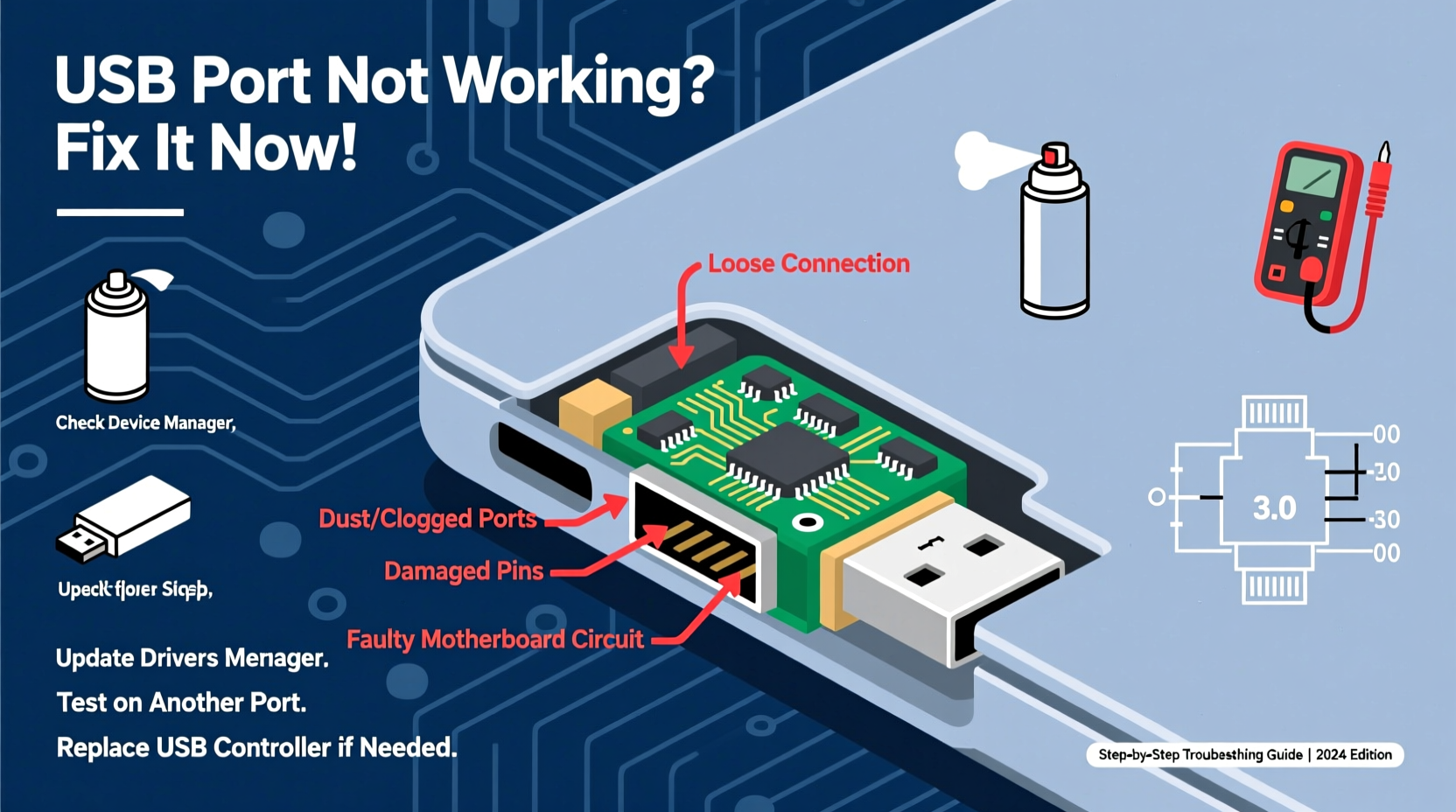
Before diving into complex fixes, confirm whether the issue lies with the USB port itself. Plug in multiple known-working devices—a flash drive, mouse, or phone—to see if any respond. Try different cables, as damaged or low-quality ones often mimic port failure. If none of the connected devices work in a specific port but function elsewhere, the port is likely at fault. Conversely, if one device fails across multiple ports, the problem may be with the device or cable.
Check for physical damage: bent pins, debris, or looseness inside the port. Use compressed air to gently clean dust or lint. Avoid metal tools, which could cause short circuits. On laptops, inspect for signs of liquid damage near the ports, which can corrode internal connections over time.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Process
Follow this structured sequence to identify and resolve the root cause efficiently:
- Reboot the system – A simple restart can clear temporary software glitches affecting USB recognition.
- Try another USB port – Determine if the issue is isolated to one port or affects multiple ports.
- Test on another computer – Verify device and cable functionality outside the current environment.
- Check Device Manager (Windows) – Look for unrecognized or disabled USB controllers.
- Update or reinstall USB drivers – Outdated or corrupted drivers frequently cause connectivity issues.
- Disable selective suspend settings – Power-saving features may disable USB ports during sleep.
- Reset SMC and NVRAM (Mac) – Critical for resolving power and peripheral detection problems on Apple hardware.
- Inspect kernel logs (Linux) – Use
dmesg | grep -i usbto detect errors during device insertion.
Common Software Fixes by Operating System
Windows: Reinstalling USB Controllers
In Device Manager, expand \"Universal Serial Bus controllers.\" Right-click each entry labeled \"USB Root Hub\" or similar and select \"Uninstall device.\" After removing all, restart the PC. Windows will automatically redetect and reinstall the USB drivers upon boot. This refreshes the driver stack and resolves many silent failures.
macOS: Resetting System Management Controller (SMC)
The SMC manages power delivery, including USB ports. For Intel-based Macs, shut down, then press Shift+Control+Option+Power for 10 seconds. Release and power on. For Apple Silicon Macs, no manual reset is needed—the system handles it internally during shutdown cycles. However, resetting NVRAM (Option+Command+P+R at startup) can help restore default hardware settings.
Linux: Reload USB Kernel Modules
Open a terminal and run:
sudo modprobe -r xhci_hcd && sudo modprobe xhci_hcd
This unloads and reloads the USB 3.0 (xHCI) controller module. If using older USB 2.0 systems, replace xhci_hcd with ehci_hcd. Monitor output via dmesg to verify successful reinitialization.
Hardware-Level Issues and Solutions
Sometimes, the problem isn’t software-related. Internal USB headers on desktop motherboards can become loose or misaligned. Open the case and ensure front-panel USB connectors are securely seated on the motherboard pins. Consult your motherboard manual for correct pin layout—reversed connections won't damage components but will prevent operation.
Laptops present greater challenges. If multiple ports fail simultaneously, especially after an impact or spill, internal flex cables or the USB controller chip may be damaged. These require professional repair. In some models, such as certain Dell or Lenovo business laptops, USB functionality is managed by firmware-level settings in BIOS. Ensure USB ports are enabled under \"Integrated Peripherals\" or similar sections.
“Over 40% of reported USB failures we see in service centers are actually caused by power management bugs or driver corruption—not hardware defects.” — Rajiv Mehta, Senior Technician at TechCare Repair Labs
Do’s and Don’ts When Fixing USB Ports
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Use compressed air to clean ports gently | Insert sharp objects like paperclips into USB ports |
| Keep operating system and drivers updated | Ignore repeated disconnection warnings |
| Test with certified, high-quality cables | Force a plug if it doesn’t fit smoothly |
| Check BIOS/UEFI settings for disabled ports | Assume a dead port means the whole machine is failing |
| Back up data before major system resets | Apply liquid cleaners directly into ports |
Real-World Example: Recovering a Non-Functional External Drive Connection
A freelance photographer was unable to access her backup SSD via USB-C on her Windows 10 laptop. The drive appeared intermittently in File Explorer but disconnected during file transfers. Initial tests showed the same behavior on another computer, suggesting a hardware fault. However, she tried a different USB-C cable—previously dismissed as “working fine” for charging—and the drive mounted instantly and remained stable.
Further inspection revealed the original cable lacked full data-transfer capabilities despite its appearance. The lesson? Not all USB-C cables support high-speed data. Always use cables rated for your device's protocol (e.g., USB 3.2 Gen 2, Thunderbolt 3). This single change saved her from unnecessary drive recovery costs and downtime.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does my USB device work sometimes but disconnect randomly?
Intermittent disconnections often point to insufficient power supply, especially with bus-powered devices like external hard drives. Try using a powered USB hub or connect the device to a rear motherboard port (on desktops), which typically delivers more stable power. Also, check for outdated chipset drivers or enable “Disable selective suspension” in Windows Power Options.
Can I fix a physically damaged USB port myself?
Soldering a broken USB port requires precision equipment and micro-soldering skills. For desktops, replacing the entire motherboard header bracket is feasible. On laptops, unless you have experience with board-level repair, seek professional help. Attempting DIY fixes without proper tools risks permanent damage.
My USB ports stopped working after a Windows update. What should I do?
This is common. First, roll back recent updates via Settings > Update & Security > Recovery > \"Go back to the previous version.\" Alternatively, enter Safe Mode and uninstall recently updated USB or chipset drivers. Reinstall them after rebooting normally. You can also use System Restore to revert to a point before the update.
Preventive Maintenance Checklist
- ✅ Regularly clean USB ports with compressed air every 3–6 months
- ✅ Keep OS and chipset drivers up to date
- ✅ Use surge protectors to prevent voltage spikes damaging USB controllers
- ✅ Avoid hot-plugging high-power devices repeatedly
- ✅ Disable USB selective suspend in power plans for mission-critical setups
- ✅ Store spare cables in labeled containers by capability (data vs. charge-only)
Final Thoughts and Next Steps
USB port issues are rarely insurmountable. Most cases stem from easily correctable software, driver, or cabling problems rather than irreversible hardware damage. By following a logical diagnostic path—from basic plug tests to driver reinstalls and BIOS checks—you can resolve the majority of connectivity failures without technical assistance.
For persistent problems, consider consulting manufacturer support or authorized repair services, particularly when dealing with soldered ports or internal flex cables. Remember, prevention matters: treat USB ports with care, use quality accessories, and maintain your system proactively.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?