Streaming platforms like Netflix, Hulu, Disney+, and BBC iPlayer have transformed how we consume entertainment. But geographic restrictions limit access based on your location. Enter virtual private networks (VPNs)—a tool many use to bypass these barriers and unlock global content. Yet, a pressing question remains: Do VPNs for streaming actually work? The answer isn’t a simple yes or no. While some VPNs reliably unblock content, others fail due to aggressive detection systems employed by streaming services.
The reality is a constant digital tug-of-war. Streaming platforms invest heavily in identifying and blocking traffic from known VPN servers, while premium VPN providers counter with advanced obfuscation techniques and dynamic IP rotation. Understanding this dynamic is key to making an informed decision about whether—and how—a VPN can serve your streaming needs.
How Streaming Services Detect and Block VPN Traffic
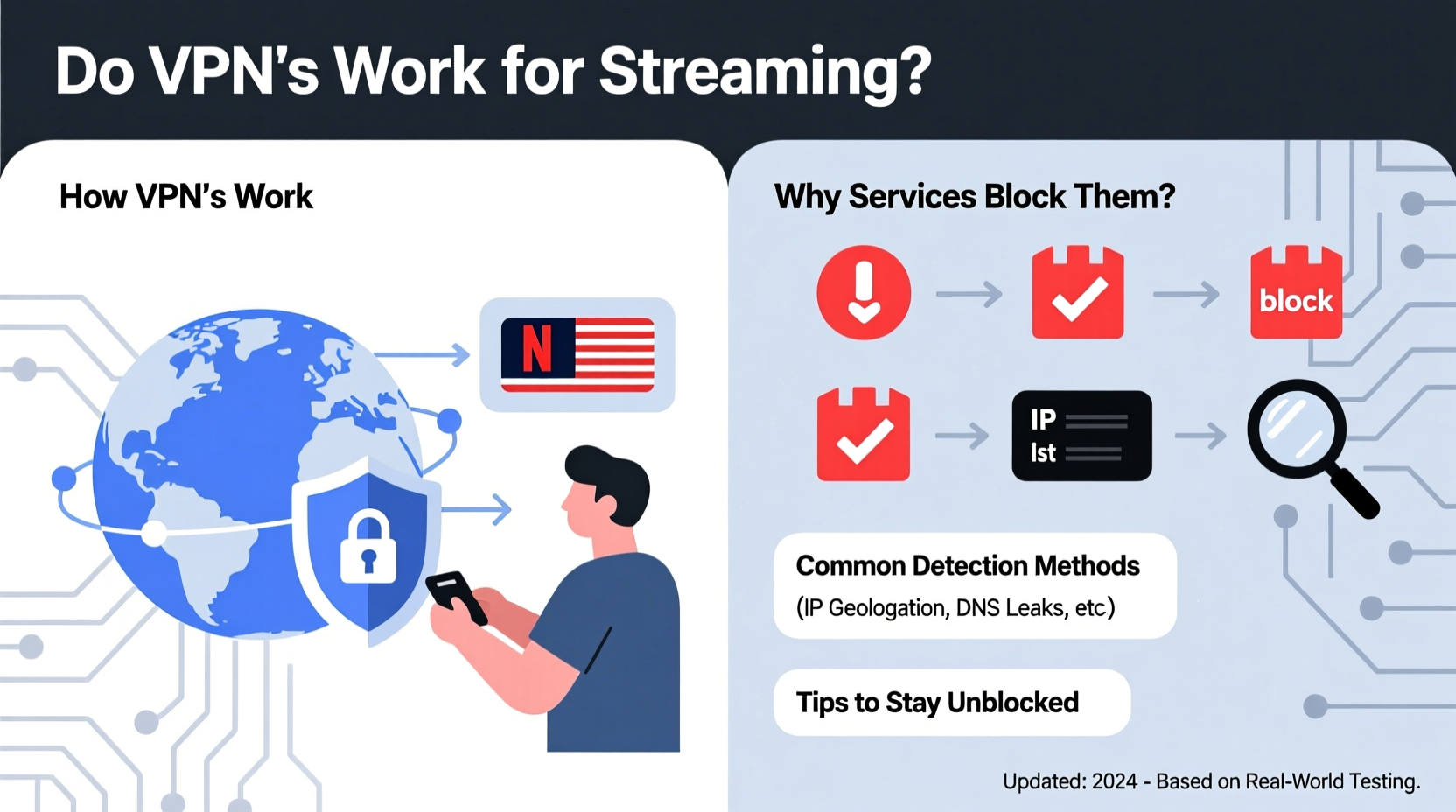
Streaming platforms enforce regional licensing agreements. When you connect from outside a licensed region, they’re legally obligated to restrict access. To achieve this, they don’t just rely on basic IP geolocation. Instead, they deploy sophisticated detection mechanisms designed to identify patterns associated with commercial VPN usage.
One primary method is maintaining blacklists of IP addresses known to belong to data centers rather than residential ISPs. Since most VPNs operate servers in data centers, their IPs are easily flagged. For example, if thousands of users suddenly appear to be accessing Netflix from the same IP address in Amsterdam—but claiming to be in the U.S.—the platform flags that as suspicious behavior.
Beyond IP analysis, streaming services use:
- Deep packet inspection (DPI): Analyzes network traffic patterns to detect encrypted tunnels typical of VPNs.
- Behavioral analytics: Monitors login frequency, device types, and viewing habits inconsistent with normal user behavior.
- Port and protocol identification: Identifies non-standard ports or protocols commonly used by OpenVPN or WireGuard connections.
Platforms like Netflix have become particularly adept at this. In 2016, they began aggressively cracking down on VPN access, leading to widespread failures among budget providers. Today, only a handful of high-end services consistently maintain access.
“Netflix spends millions annually refining its geo-blocking infrastructure. It’s not just about location—it’s about identifying anomalies in connection behavior.” — David Chen, Cybersecurity Analyst at StreamGuard Labs
Which VPNs Still Work for Streaming in 2024?
Not all VPNs are created equal when it comes to bypassing streaming blocks. The most effective ones combine technical innovation with operational agility. They rotate IP addresses frequently, use residential-like proxies, and offer specialized servers optimized for media access.
Based on independent testing and user reports, the following providers currently demonstrate reliable performance across major platforms:
| VPN Provider | Netflix (US) | Hulu | Disney+ | BBC iPlayer | Special Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NordVPN | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | Double encryption, SmartPlay technology |
| ExpressVPN | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | Lightway protocol, TrustedServer tech |
| Surfshark | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | Unlimited devices, CleanWeb ad blocker |
| CyberGhost | ✅ Yes | ⚠️ Occasionally | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | Dedicated streaming profiles |
| Private Internet Access | ❌ No | ❌ No | ⚠️ Limited | ❌ No | Open-source apps, strong privacy focus |
Note that performance can vary over time. A provider working today may face blocks tomorrow. This volatility underscores the importance of choosing a service committed to ongoing anti-detection development.
Real-World Example: Bypassing Regional Restrictions Abroad
Consider Sarah, a U.S.-based professional temporarily relocating to Japan for work. She wanted to continue watching her favorite shows on Hulu, which doesn’t offer service outside the United States. After trying two low-cost VPNs—both blocked immediately—she switched to ExpressVPN.
Upon connecting to a New York-based server, Hulu loaded without issue. Over six months, she maintained consistent access. The difference? ExpressVPN uses obfuscated servers that mask traffic to resemble regular HTTPS activity, evading DPI filters. Additionally, its frequent IP rotation prevented blacklisting.
This case illustrates a critical point: success depends less on using any VPN and more on selecting one engineered specifically for streaming circumvention.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a VPN for Streaming
If you're new to using a VPN for streaming, follow this practical sequence to maximize your chances of success:
- Choose a reputable provider: Prioritize services known for streaming compatibility (e.g., NordVPN, ExpressVPN).
- Download and install the app: Use official sources only—avoid third-party stores.
- Log in and select a server: Pick one located in the country whose content you want to access (e.g., Los Angeles for Hulu).
- Clear browser cache or app data: Residual location data can trigger blocks even after switching IPs.
- Test connectivity: Visit the streaming site or open the app. If blocked, try another server in the same region.
- Enable split tunneling (if available): Route only your streaming app through the VPN to improve speed.
- Monitor performance: Reconnect periodically if buffering occurs or access drops.
Some platforms require additional steps. For instance, BBC iPlayer often demands JavaScript execution and cookie acceptance—so avoid minimal browsers or ad blockers during setup.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Many users assume that once connected to a VPN, all geo-restrictions will vanish. This misconception leads to frustration. Here are common mistakes and how to sidestep them:
- Using free or outdated VPNs: These typically lack the resources to maintain unblocked IPs and often throttle bandwidth.
- Connecting to crowded servers: High user volume slows speeds and increases detection risk. Opt for less popular locations within the same country.
- Ignoring DNS leaks: Even with a secure tunnel, misconfigured DNS settings can expose your real location. Run a leak test via sites like dnsleaktest.com.
- Expecting 100% uptime: Blocks happen. Premium services restore access quickly, but temporary outages are normal.
“We see spikes in support tickets every time Netflix updates its firewall rules. The best providers resolve issues within hours, not days.” — Lena Park, Customer Experience Lead at NordVPN
Checklist: Choosing a Streaming-Friendly VPN
Before committing to a subscription, verify the following features:
- ✅ Proven ability to unblock top platforms (Netflix, Hulu, etc.)
- ✅ Servers in multiple countries (U.S., U.K., Canada, Australia, Japan)
- ✅ Fast connection speeds (minimum 10 Mbps for HD streaming)
- ✅ Obfuscation or stealth mode to bypass deep packet inspection
- ✅ Regular IP address rotation
- ✅ Apps for all your devices (smart TVs, Fire Stick, mobile, desktop)
- ✅ 24/7 customer support with live chat
- ✅ Money-back guarantee (ideally 30 days or longer)
Avoid providers that promise “anonymous streaming” without concrete evidence of functionality. Transparency matters—look for detailed blog posts or status pages showing current server performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I get banned from Netflix for using a VPN?
No, Netflix does not ban user accounts for attempting to use a VPN. However, you’ll encounter an error message (such as M7111-5059) indicating that proxy usage is detected. Once you disconnect the VPN, normal service resumes immediately.
Why does my VPN work with Netflix but not Hulu?
Different platforms employ varying levels of detection sophistication. Hulu, for example, has tightened its security in recent years and now blocks many previously functional IP ranges. You may need to switch servers or upgrade to a more capable provider.
Are there legal risks to using a VPN for streaming?
In most Western countries—including the U.S., Canada, and the U.K.—using a VPN is legal. However, it violates the terms of service of many streaming platforms. While enforcement is rare, it could theoretically lead to account suspension. The primary risk is loss of access, not legal action.
Conclusion: Yes, It Works—But Only With the Right Tools
A VPN for streaming absolutely works—but not universally or permanently. Success hinges on choosing a provider built for the challenge: one that actively combats detection, maintains fast and stable servers, and adapts quickly to new blocks. The cat-and-mouse game between streamers and platforms continues, but with the right strategy, viewers can stay ahead.
Investing in a premium, streaming-optimized service pays off in reliability, speed, and peace of mind. Don’t settle for promises—demand proof. Test rigorously, monitor performance, and switch if needed. In a world where content is increasingly fragmented by borders, a capable VPN isn’t just a convenience; it’s a gateway to the full breadth of digital entertainment.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?