Waking up with a swollen, hard bump on your skin can be alarming—especially when you're certain it wasn't there the night before. More often than not, this is the aftermath of a bug bite. While most insect bites cause only mild irritation, some result in firm, raised areas that can linger for days or even weeks. Understanding why bug bites turn hard, what symptoms to expect, and how to treat them effectively can help you respond quickly and prevent complications.
Why Bug Bites Become Hard: The Science Behind the Swelling
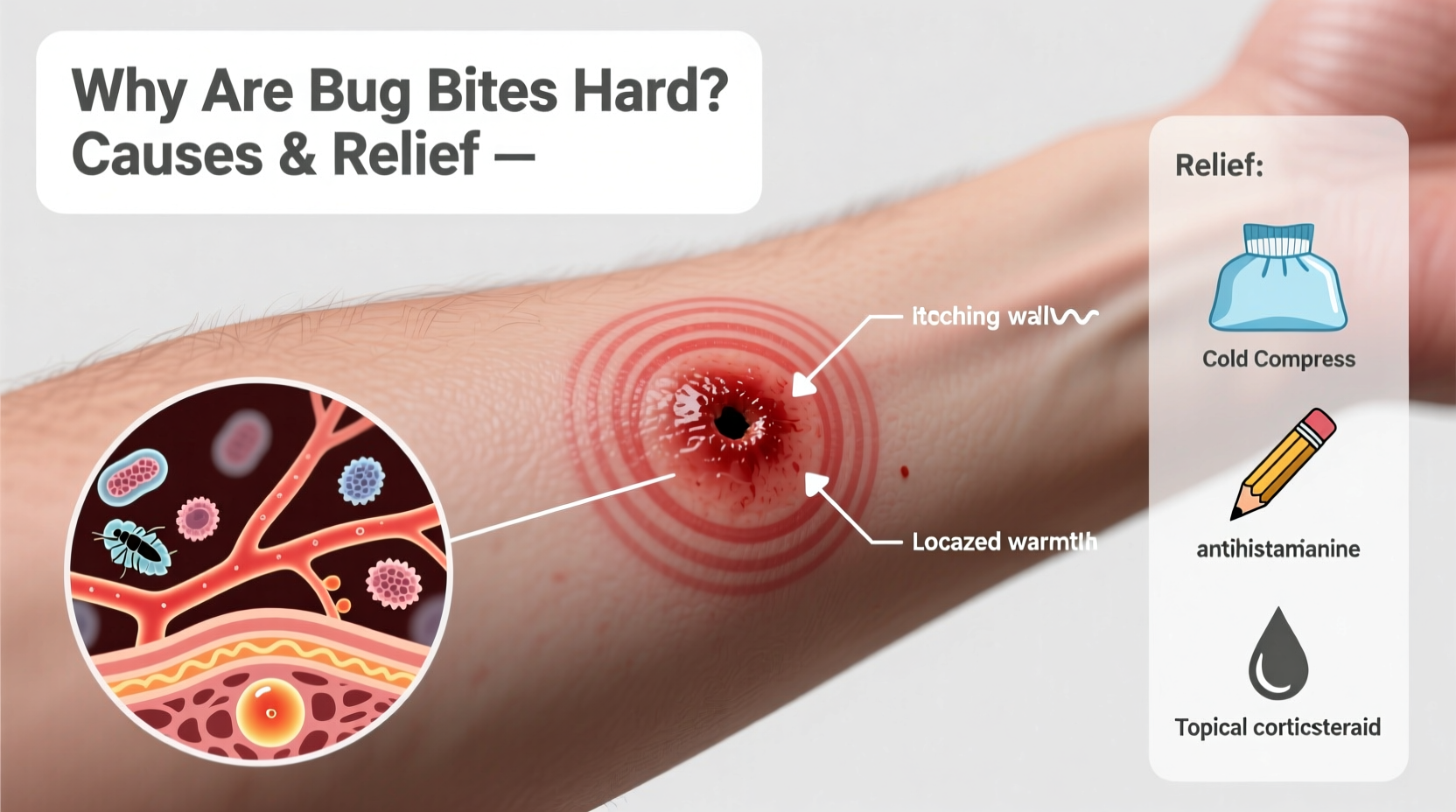
When an insect bites, it injects saliva into your skin to prevent blood from clotting during feeding. Your immune system recognizes these foreign proteins as invaders and responds by releasing histamines and other inflammatory chemicals. This immune reaction causes localized swelling, redness, and itching.
In some cases, the body's response intensifies, leading to hardened tissue around the bite site. This firmness occurs due to:
- Inflammatory cell buildup: White blood cells accumulate at the site to fight off perceived threats, causing firm swelling.
- Fluid retention: Plasma leaks from capillaries into surrounding tissues, contributing to edema and a bumpy texture.
- Fibrous tissue formation: In prolonged reactions, the body may lay down collagen fibers, making the area feel tough or rubbery.
Certain insects are more likely to provoke this type of reaction. Mosquitoes, fleas, bed bugs, and biting flies commonly cause hard bumps, especially in individuals with sensitive immune systems.
“Repeated exposure to insect saliva can sensitize the immune system, making subsequent bites trigger stronger local reactions—even if they weren’t problematic before.” — Dr. Lena Patel, Allergy & Immunology Specialist
Symptoms Associated with Hard Bug Bites
A hard bug bite isn’t just about texture—it often comes with a cluster of symptoms that vary in severity. Recognizing these signs helps differentiate a normal immune response from something more serious.
| Symptom | Description | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Firm, raised lump under the skin, sometimes warm to touch | 3–14 days |
| Itching | Mild to intense urge to scratch; may worsen at night | 1–7 days |
| Redness | Localized inflammation around the bite center | 2–5 days |
| Swelling | Puffiness extending beyond the bite site | Up to 1 week |
| Pain or tenderness | Soreness when pressed or moved (common with spider bites) | Varies; longer if infected |
In rare cases, people experience exaggerated reactions known as “papular urticaria,” where bites evolve into large, hive-like nodules that persist for weeks. Children and those with eczema are particularly prone to this condition.
Common Causes of Hard Bug Bites
Not all bugs produce the same reaction. Some species are notorious for leaving behind stubborn, hard welts. Here’s a breakdown of the usual suspects:
- Bed Bugs: Often bite in clusters or lines, causing delayed but intense reactions. The bites swell and harden over 24–48 hours.
- Fleas: Prefer ankles and lower legs. Their bites are small but surrounded by a red halo and significant hardness.
- Mosquitoes: Typically soft at first but can harden in allergic individuals, forming itchy, coin-sized bumps.
- Spiders: Some venomous species (like the brown recluse) cause necrotic lesions, but even non-venomous spiders can induce firm, inflamed areas.
- No-See-Ums (biting midges): Tiny but painful. Their bites often blister and remain hard for over a week.
Environmental factors also play a role. Humidity, heat, and perspiration can exacerbate inflammation, making bites appear larger and firmer than they would otherwise.
Effective Relief Strategies for Hard Bug Bites
Treating a hard bug bite involves reducing inflammation, relieving discomfort, and preventing secondary issues like infection. Start with conservative home care and escalate only if needed.
- Clean the area: Wash with mild soap and water to remove bacteria and residual insect saliva.
- Apply a cold compress: Use ice wrapped in cloth for 10 minutes at a time to reduce swelling and numb itching.
- Use topical treatments: Calamine lotion, hydrocortisone cream (1%), or antihistamine gels can soothe irritation.
- Take oral antihistamines: Non-drowsy options like loratadine (Claritin) or cetirizine (Zyrtec) help control immune overreaction.
- Elevate if swollen: If bites are on limbs, elevate to reduce fluid buildup.
For persistent hardness lasting more than two weeks, consider using a gentle exfoliating agent (like salicylic acid) to encourage skin turnover—just ensure no open sores are present.
When to See a Doctor
Most bug bites resolve on their own. However, seek medical attention if you notice any of the following:
- Expanding redness with streaks (sign of cellulitis)
- Pus or yellow crusting (indicates infection)
- Increasing pain or warmth around the bite
- Fever, chills, or fatigue accompanying the bite
- Bite located near eyes, mouth, or genitals
“If a bite continues to harden and grow after 72 hours, it’s worth getting evaluated. What starts as a simple reaction could progress to an abscess or systemic issue.” — Dr. Marcus Tran, Emergency Medicine Physician
Mini Case Study: Sarah’s Reaction to Flea Bites
Sarah, a 34-year-old pet owner, returned from vacation to find her dog excessively scratching. Within days, she began noticing itchy, hard bumps on her ankles and arms. Initially dismissing them as mosquito bites, she was alarmed when the welts grew larger and didn’t fade after a week.
After inspecting her home, she discovered flea droppings in her carpet. A pest control service confirmed an infestation. Sarah treated her home and pets, then applied hydrocortisone cream and took daily antihistamines. The hardness subsided within ten days, though one bite left a temporary dark spot.
Her experience highlights the importance of identifying the source. Without addressing the root cause—fleas—the bites would have continued regardless of treatment.
Checklist: How to Respond to a Hard Bug Bite
Follow this step-by-step checklist to manage symptoms safely and effectively:
- ✅ Wash the bite with soap and water
- ✅ Apply a cold pack for 10-minute intervals
- ✅ Use over-the-counter anti-itch cream or lotion
- ✅ Take an oral antihistamine if itching is severe
- ✅ Monitor the area for changes over the next 3–5 days
- ✅ Avoid scratching—keep nails short or wear gloves at night
- ✅ Seek medical advice if signs of infection develop
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a hard bug bite be a sign of an allergy?
Yes. Large, hard reactions—especially those exceeding 4 inches in diameter or lasting over a week—are often classified as \"large local reactions,\" indicating immune hypersensitivity. While not life-threatening like anaphylaxis, they suggest your body is strongly reacting to insect saliva.
How long should a bug bite stay hard?
Most hard bites begin softening within 3–5 days and fully resolve in 7–14 days. If hardness persists beyond two weeks without improvement, consult a healthcare provider to rule out infection or granuloma formation.
Are natural remedies effective for hard bug bites?
Some natural options like aloe vera, oatmeal paste, or diluted tea tree oil may offer mild relief. However, avoid unproven treatments such as banana peels or vinegar soaks, which lack clinical backing and may irritate sensitive skin.
Prevention: Stopping Bites Before They Start
The best way to avoid hard bug bites is to prevent them altogether. Integrate these habits into your routine:
- Use EPA-approved repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus.
- Wear long sleeves and pants in wooded or grassy areas.
- Inspect hotel rooms and rental properties for signs of bed bugs.
- Treat pets regularly for fleas and ticks.
- Install window screens and repair tears promptly.
For those with recurrent reactions, keeping a bite journal can help identify patterns—such as specific locations, times of day, or associated activities—that increase exposure risk.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Skin’s Response
Hard bug bites are more than just a nuisance—they’re a signal from your body that it’s fighting off foreign substances. By understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms early, and applying targeted relief, you can minimize discomfort and speed recovery. Most importantly, don’t ignore persistent or worsening reactions. With the right knowledge and proactive care, you can protect yourself and your family from unnecessary suffering.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?