YouTube is the most widely used video platform on the internet, and embedding its content into websites, blogs, or learning management systems is a common practice. However, many users encounter issues when trying to embed videos—whether the iframe fails to load, displays an error, or simply doesn’t appear. These problems can frustrate content creators, educators, and developers alike. The good news is that most embedding issues stem from predictable causes and can be resolved with targeted troubleshooting.
This comprehensive guide breaks down the most frequent reasons YouTube videos fail to embed, provides practical solutions, and equips you with tools to diagnose and fix problems quickly across different platforms and environments.
Common Causes of YouTube Embedding Failures
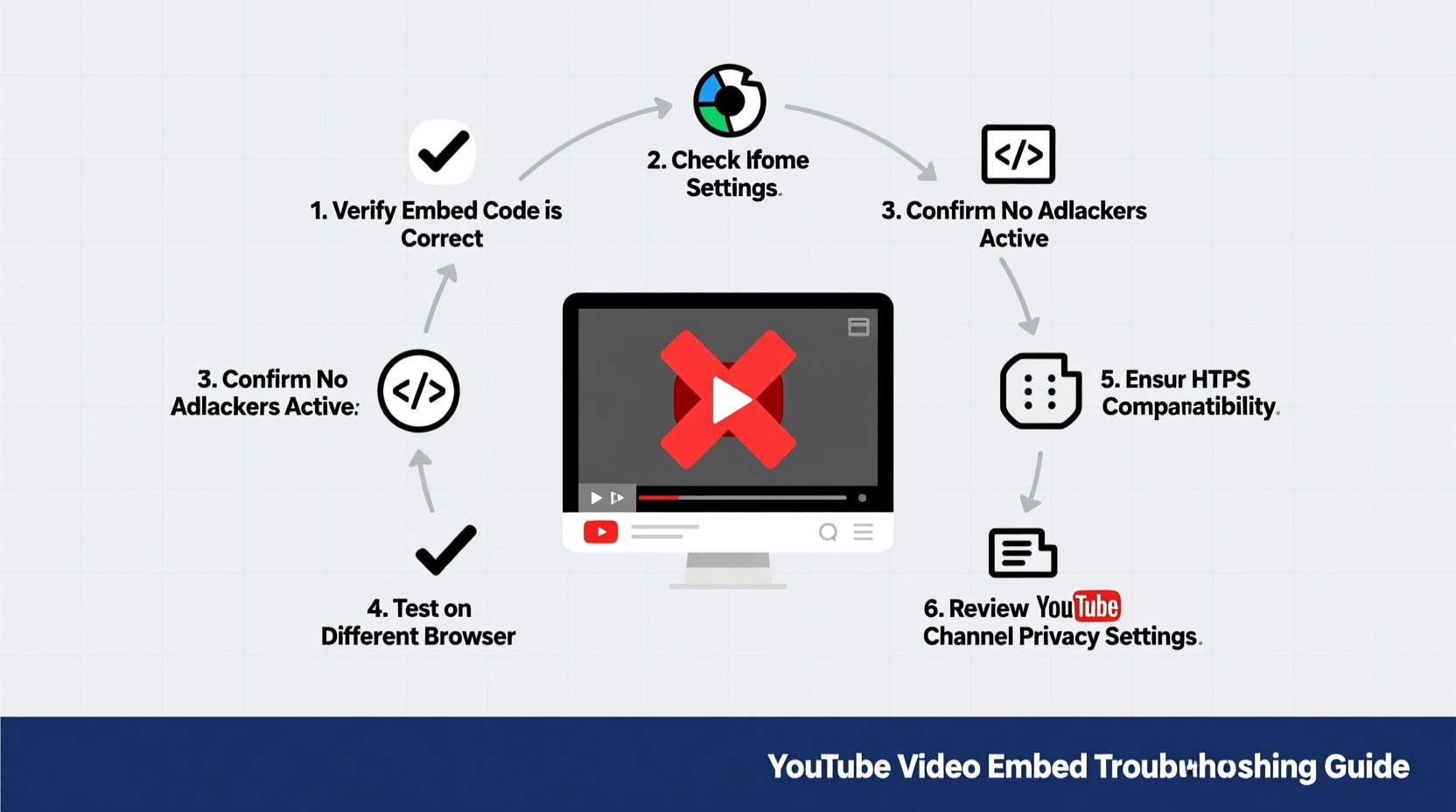
Before jumping into fixes, it's essential to understand what might be preventing a YouTube video from embedding properly. The root cause often falls into one of these categories:
- Incorrect embed code: Using outdated or malformed iframe syntax.
- Privacy settings on YouTube: Videos set to \"Unlisted\" or \"Private\" may not embed on external sites.
- Content Security Policy (CSP) restrictions: Website security headers blocking external scripts.
- Ad blockers or browser extensions: Interfering with iframe loading.
- Platform-specific limitations: WordPress, Wix, or Shopify may modify or strip embed codes.
- Network or regional restrictions: Some videos are blocked in certain countries.
Identifying which category your issue belongs to is the first step toward resolution.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fix Embedding Issues
Follow this structured approach to systematically eliminate possible causes and restore proper video functionality.
- Verify the Video’s Embedding Permissions
Log in to YouTube Studio, navigate to the video, and check under \"Visibility\" settings. Ensure \"Allow embedding\" is enabled. If the video is private or unlisted without embedding allowed, it won’t display on external sites. - Use the Correct Embed Code
Always obtain the embed code directly from YouTube:- Go to the video page.
- Click “Share” → “Embed.”
- Copy the provided iframe code.
https://www.youtube.com/embed/VIDEO_ID - Check for HTML Sanitization
Content Management Systems like WordPress or Drupal sometimes strip iframe tags for security. Use trusted plugins (e.g., WP YouTube Lyte, Embed Plus) or switch to a full HTML block (in Gutenberg) instead of a paragraph or custom HTML block that may sanitize input. - Test in Multiple Browsers and Devices
Open the page in Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. If the video loads in one but not another, the issue likely lies with browser settings, extensions, or cached data. - Inspect Console Errors
Right-click the page → “Inspect” → go to the “Console” tab. Look for errors like:Refused to frame 'https://www.youtube.com/' because it violates the Content Security Policy.Blocked by extension
- Disable Browser Extensions Temporarily
Ad blockers (like uBlock Origin), privacy tools (such as Privacy Badger), or script blockers can prevent YouTube iframes from loading. Disable them temporarily to test.
Content Security Policy (CSP) Conflicts
Modern websites use CSP headers to enhance security by restricting which external resources can load. If your site has a strict CSP, YouTube’s domain must be explicitly whitelisted.
For example, a typical CSP header might look like:
Content-Security-Policy: frame-src 'self';
This blocks all external frames, including YouTube. To allow embedding, update the header:
Content-Security-Policy: frame-src 'self' https://www.youtube.com https://youtube.com https://*.ytimg.com;
If you're using a hosting platform (e.g., Netlify, Cloudflare), CSP settings may be configured at the server or CDN level. Consult your provider’s documentation or developer team to adjust these policies safely.
“Overly restrictive CSP rules are among the top hidden causes of failed YouTube embeds in enterprise environments.” — Lena Park, Web Security Engineer at DevSecure Labs
Platform-Specific Fixes
Different platforms handle embeds differently. Below is a comparison of common platforms and their known quirks.
| Platform | Common Issue | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| WordPress | Classic Editor strips iframe tags | Use a Custom HTML block or install a trusted embed plugin |
| Wix | Auto-resizes or crops videos incorrectly | Adjust container size manually; use Wix’s native YouTube element |
| Shopify | Theme filters remove iframe code | Paste embed in HTML editor mode; avoid rich text fields |
| Medium | Doesn’t support raw iframe | Paste the YouTube URL on its own line—Medium auto-embeds it |
| Notion | Limited iframe support | Use /youtube command or paste link directly |
Mini Case Study: Corporate Training Portal Fails to Load Videos
A mid-sized tech company launched an internal training portal using React and hosted on Netlify. Employees reported that YouTube videos used in modules were not loading, showing only a blank space. The development team confirmed the embed code was correct and functional in isolated tests.
Upon inspecting browser console logs, they discovered a CSP violation: Refused to frame 'https://www.youtube.com/'. The issue traced back to a default Netlify security header that blocked all external frames. The fix involved adding YouTube domains to the frame-src directive in the _headers file:
/* Content-Security-Policy: frame-src 'self' https://www.youtube.com;
After deployment, videos loaded instantly across all user devices. This case highlights how backend security policies can silently disrupt frontend features.
Troubleshooting Checklist
Use this checklist to methodically resolve embedding issues:
- ✅ Confirm the YouTube video allows embedding (via YouTube Studio)
- ✅ Copy the latest embed code from YouTube’s “Share > Embed” option
- ✅ Paste the iframe into a clean HTML page to test isolation
- ✅ Check browser console for CSP or script errors
- ✅ Disable ad blockers and test in incognito mode
- ✅ Verify your website’s Content Security Policy includes YouTube domains
- ✅ Ensure your CMS or platform hasn’t stripped the iframe code
- ✅ Test responsiveness: use
width=\"100%\"andheight=\"auto\"for mobile compatibility
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does my embedded video show “Video unavailable”?
This message usually means one of three things: the video has been deleted, set to private, or restricted by region. Double-check the video’s visibility settings on YouTube and ensure it hasn’t been age-restricted in your country.
Can I embed a playlist instead of a single video?
Yes. In the YouTube embed tool, toggle the option to “Show playlist.” The iframe src will change to include &list= and &index= parameters. Make sure the playlist is public or unlisted with embedding enabled.
Do embedded videos work offline?
No. Embedded YouTube videos require an active internet connection and access to YouTube’s servers. They cannot be viewed offline, even if cached.
Final Thoughts and Next Steps
YouTube embedding failures are rarely due to a single factor. They often result from a combination of permissions, platform behavior, and security configurations. By following a structured diagnostic process—starting with the video settings and moving through code, browser, and server-level checks—you can identify and resolve nearly any embedding issue.
Remember, prevention is easier than repair. When publishing content, always preview embedded videos across devices and browsers. Implement monitoring tools that alert you if embedded resources fail to load over time.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?