Waking up with puffy eyes is a common concern that affects people of all ages. While it’s often dismissed as a minor cosmetic issue, persistent morning puffiness can signal underlying lifestyle imbalances or even health conditions. The delicate skin around the eyes is thinner than anywhere else on the body, making it highly susceptible to fluid retention, inflammation, and visible swelling. Understanding the root causes—ranging from sleep patterns to diet and allergies—is the first step toward lasting relief.
This article explores the science behind morning eye puffiness, breaks down the most frequent triggers, and provides practical, evidence-backed strategies to reduce and prevent it. Whether your puffy eyes are occasional or a daily struggle, the insights here will help you regain clarity—both visually and physically.
The Science Behind Morning Eye Puffiness
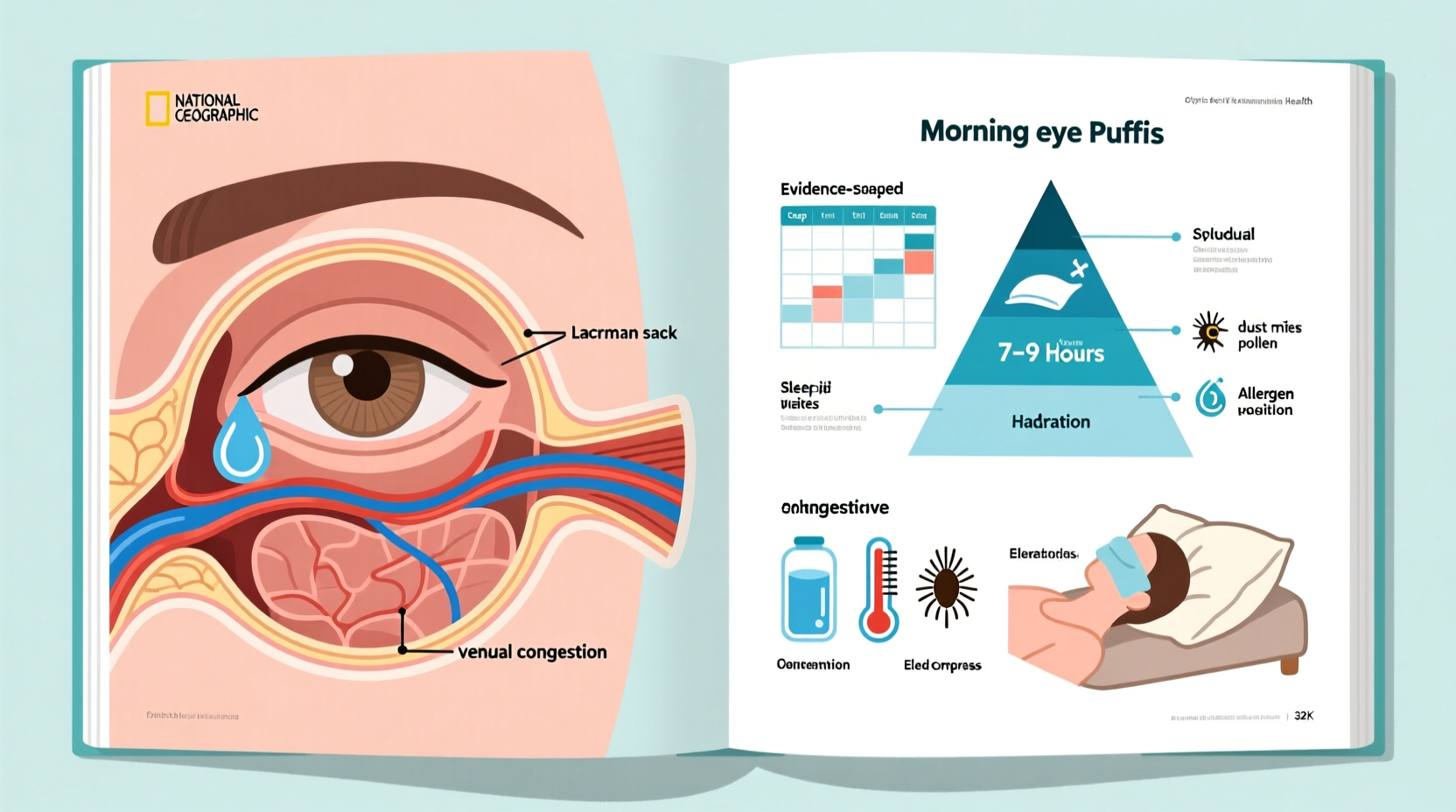
During sleep, your body undergoes numerous physiological changes. One of them involves fluid distribution. When you lie flat for several hours, gravity no longer pulls fluids downward through your body. As a result, fluid can accumulate in the face—particularly around the eyes, where tissues are more porous and less structured.
This natural process, called nocturnal fluid redistribution, explains why mild puffiness upon waking is normal. However, when swelling becomes pronounced, persistent, or accompanied by discoloration or discomfort, it may point to deeper issues such as poor lymphatic drainage, excessive sodium intake, or allergic reactions.
The periorbital area (around the eyes) contains fat pads that cushion the eyeballs. With age or chronic inflammation, these pads can shift forward, contributing to a \"bags under the eyes\" appearance. In younger individuals, temporary puffiness is more likely linked to lifestyle and environmental factors.
Common Causes of Morning Puffy Eyes
Puffy eyes aren’t always due to lack of sleep. Several interrelated factors contribute to this condition. Identifying which ones apply to you is essential for targeted treatment.
Dietary Habits
Consuming high-sodium foods—especially late at night—can lead to water retention. Sodium disrupts the balance of electrolytes in your body, prompting tissues to hold onto excess fluid. Processed snacks, canned soups, and salty condiments are major culprits.
Alcohol consumption also plays a role. It dehydrates the body while simultaneously causing blood vessels to dilate and leak fluid into surrounding tissues. This double effect often results in both puffiness and dark circles.
Allergies and Sinus Pressure
Seasonal allergies, dust mites, pet dander, or even laundry detergents can trigger an immune response that manifests around the eyes. Histamine release leads to inflammation, itching, and swelling. Rubbing your eyes worsens the condition by irritating delicate capillaries.
Chronic sinus congestion increases pressure in facial cavities, which can obstruct normal drainage pathways and cause fluid buildup beneath the eyes.
Lack of Sleep or Poor Sleep Quality
While not the sole cause, insufficient or disrupted sleep impacts circulation and hormone regulation. Cortisol levels fluctuate during poor sleep cycles, potentially increasing inflammation. Additionally, fatigue makes blood vessels more permeable, allowing plasma to seep into surrounding tissues.
Aging and Genetics
As we age, skin loses elasticity and supportive collagen. Fat pads beneath the eyes may protrude, creating a permanently swollen appearance. Some people inherit a predisposition to under-eye bags due to family genetics.
Fluid Retention from Hormonal Changes
Women may notice increased puffiness during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause due to hormonal shifts affecting fluid balance. Estrogen and progesterone influence kidney function and vascular permeability, contributing to temporary edema.
“Persistent periorbital swelling should not be ignored—especially if it's worsening over time. It could reflect systemic issues like thyroid dysfunction or kidney problems.” — Dr. Lena Torres, Ophthalmologist and Facial Rejuvenation Specialist
Solutions and Prevention Strategies
Addressing puffy eyes requires a multi-pronged approach. While quick fixes offer temporary relief, long-term improvement depends on consistent lifestyle adjustments and proper skincare.
Adjust Your Sleeping Position
Sleeping flat allows fluid to gather in the facial region. Propping yourself up with an extra pillow—or using a wedge pillow—helps drain fluids away from the eyes overnight.
Reduce Sodium Intake
Monitor your daily salt consumption. The American Heart Association recommends no more than 2,300 mg per day, ideally closer to 1,500 mg for optimal cardiovascular and fluid balance. Read labels carefully and prioritize whole, unprocessed foods.
Stay Hydrated
Paradoxically, dehydration causes the body to retain water. Drinking adequate water throughout the day supports kidney function and helps flush out excess sodium. Aim for 6–8 glasses daily, adjusting for activity level and climate.
Use Cold Compresses or Chilled Tools
Cold temperatures constrict blood vessels and reduce swelling. Apply a cold spoon, refrigerated jade roller, or damp cloth to closed eyelids for 5–10 minutes after waking. Do not press too hard—the skin is extremely thin.
Apply Eye Creams with Targeted Ingredients
Look for products containing caffeine (constricts vessels), hyaluronic acid (plumps and hydrates without swelling), peptides (support collagen), and niacinamide (reduces inflammation). Avoid heavy creams that might migrate into the eyes and cause irritation.
Treat Allergies Effectively
If allergies are suspected, consider antihistamines (after consulting a doctor) and allergen-proof bedding. Wash pillowcases weekly in hot water and keep windows closed during high pollen seasons.
Step-by-Step Morning Routine to Reduce Puffiness
Follow this simple five-step routine each morning to visibly reduce puffiness within minutes and support long-term improvements:
- Hydrate Immediately: Drink a glass of water upon waking to kickstart metabolism and rehydrate tissues.
- Cool the Area: Use chilled metal spoons or a refrigerated eye mask for 5 minutes.
- Gentle Lymphatic Massage: Using your ring finger, lightly tap from the inner corner of the eye outward along the orbital bone to encourage fluid drainage.
- Apply Eye Serum: Choose a lightweight formula with caffeine or green tea extract.
- Protect with SPF: Sun damage weakens skin structure over time. Use a mineral-based sunscreen formulated for the eye area.
Consistency matters. Performing this routine daily—even when puffiness isn't present—can strengthen microcirculation and prevent future swelling.
When to See a Doctor
Mild morning puffiness that resolves within an hour or two is typically benign. However, certain red flags warrant medical evaluation:
- Swelling persists beyond midday
- Accompanied by pain, redness, or vision changes
- Affects only one eye repeatedly
- Associated with fatigue, weight gain, or dry skin (possible hypothyroidism)
- Visible signs of kidney issues: swelling in legs, foamy urine, shortness of breath
Thyroid disorders like hypothyroidism can cause generalized edema, including periorbital puffiness. Nephrotic syndrome—a kidney condition involving protein loss—often presents with significant eye swelling upon waking.
| Symptom Pattern | Possible Cause | Action Step |
|---|---|---|
| Puffs go down within 1–2 hours | Lifestyle-related (salt, sleep, position) | Optimize hydration and sleeping posture |
| Chronic puffiness with fatigue | Hypothyroidism | Request TSH test from physician |
| Itchy, watery eyes with puffiness | Allergic reaction | Identify allergens; try antihistamine |
| Severe swelling, leg edema, foamy urine | Kidney dysfunction | Seek urgent medical assessment |
Real-Life Example: Sarah’s Journey to Clearer Mornings
Sarah, a 34-year-old marketing executive, struggled with daily puffy eyes for years. She assumed it was due to late nights, but even after improving her sleep schedule, the swelling remained. After tracking her diet, she noticed a pattern: meals high in soy sauce and processed grains consistently led to worse puffiness.
She eliminated packaged dinners, reduced added salt, and began drinking herbal teas instead of wine at dinner. Within three weeks, her morning eye swelling decreased significantly. She also started using a wedge pillow and applying a cold compress each morning. Her coworkers commented on how “well-rested” she looked—even though her workload hadn’t changed.
Sarah’s case illustrates how subtle dietary choices can have visible effects on facial appearance—and how small, sustainable changes yield real results.
Do’s and Don’ts: Quick Reference Guide
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Drink plenty of water during the day | Consume salty snacks before bed |
| Sleep with head slightly elevated | Sleep on a flat surface without support |
| Use fragrance-free eye care products | Rub or tug at puffy eyelids |
| Apply cool compresses gently | Use ice directly on skin (risk of frostbite) |
| Wash bedding weekly | Ignore persistent unilateral swelling |
Frequently Asked Questions
Can lack of sleep alone cause puffy eyes?
Yes, but it’s rarely the only factor. Poor sleep disrupts hormonal balance and circulation, contributing to puffiness. However, many people who get adequate rest still experience swelling due to diet, allergies, or fluid retention. Addressing multiple lifestyle areas yields better results than focusing solely on sleep.
Are puffy eyes the same as dark circles?
No. Puffiness refers to swelling or bulging of the lower eyelid, usually from fluid or fat displacement. Dark circles involve pigmentation, visible blood vessels, or shadowing from hollowing under the eyes. They can occur together but require different treatments.
Can eye creams really reduce puffiness?
Some can, but effectiveness depends on ingredients and consistency of use. Caffeine-based serums temporarily tighten skin by constricting blood vessels. Products with peptides may improve skin firmness over time. However, topical treatments won’t fix underlying issues like poor sleep or high sodium intake.
Take Control of Your Morning Appearance
Puffy eyes don’t have to be a daily norm. By understanding the interplay between your body’s physiology and daily habits, you can make informed choices that lead to clearer, brighter mornings. Start with small, manageable changes—like reducing evening salt intake or elevating your head during sleep—and build from there.
True improvement comes not from quick fixes, but from sustained attention to hydration, nutrition, sleep quality, and overall health. If lifestyle adjustments don’t bring results, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare provider. Sometimes, what shows up in your reflection is a message from your body worth listening to.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?