Smart lighting offers convenience, ambiance control, and energy savings—but nothing undermines the experience like flickering lights, especially when dimming. If your smart bulbs flicker at low brightness levels, you're not alone. This common issue affects many homeowners using LED-based smart lighting systems. The root causes range from incompatible hardware to firmware glitches and electrical interference. More importantly, persistent flickering isn’t just annoying—it can shorten bulb lifespan and indicate deeper compatibility or safety concerns.
Understanding why flickering occurs is the first step toward a stable, flicker-free lighting environment. With the right knowledge and adjustments, most issues can be resolved without replacing your entire setup. This guide breaks down the technical reasons behind dimming-related flicker and provides actionable steps to diagnose and fix the problem for good.
Understanding How Smart Lights Dim
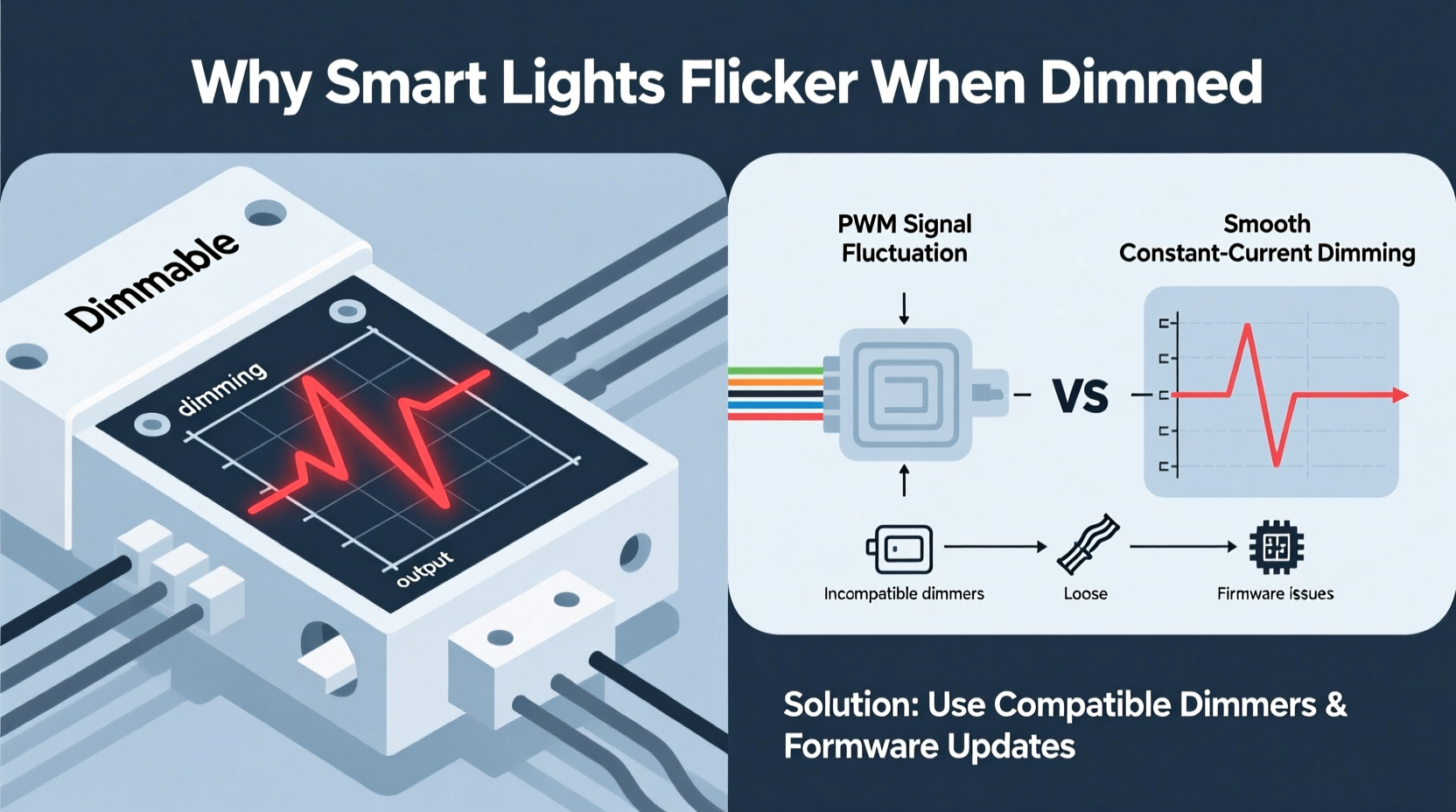
Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs that dim smoothly by reducing voltage, most smart LEDs use pulse-width modulation (PWM) or constant current reduction (CCR) to simulate dimming. PWM rapidly turns the light on and off—so fast the human eye perceives it as a steady, lower brightness. CCR adjusts the actual current flowing through the LED, offering smoother results but requiring more sophisticated drivers.
Many smart bulbs rely on internal drivers to manage this process. When these drivers are poorly designed, mismatched with dimming commands, or subjected to unstable power, they can produce visible flicker—especially at lower brightness levels where the margin for error is smallest.
“Flicker in dimmed LEDs often stems from driver instability or protocol mismatches—not necessarily the bulb quality.” — Dr. Alan Reeves, Lighting Systems Engineer, IEEE Member
Common Causes of Flickering During Dimming
Flickering doesn’t always mean faulty bulbs. In fact, it’s often a symptom of broader system incompatibilities or configuration issues. Below are the most frequent culprits:
1. Incompatible Dimming Method
Not all smart lights support the same dimming protocols. Some respond best to app-based dimming via Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, while others may conflict with physical wall dimmers. Using a traditional triac dimmer switch with non-dimmable or digitally controlled smart bulbs is a leading cause of flickering.
2. Poor Power Supply or Voltage Fluctuations
LEDs require stable, low-voltage DC power. If the AC-to-DC conversion inside the bulb or fixture is inconsistent—due to aging components or electrical noise—flickering can occur during dimming. Homes with older wiring or shared circuits may experience micro-fluctuations that trigger instability.
3. Firmware Bugs or Outdated Software
Smart bulbs depend on firmware to interpret dimming signals. Bugs in early firmware versions may misread commands or fail to maintain consistent output at low levels. Manufacturers frequently release updates to improve dimming behavior—ignoring these leaves users vulnerable to known issues.
4. Wireless Interference
Bulbs relying on Zigbee, Z-Wave, or Wi-Fi can experience signal dropouts if routers or hubs are overloaded or too distant. A lost dimming command mid-transition can result in abrupt changes or flicker as the bulb reverts to default settings.
5. Overloaded Circuits or Shared Neutrals
When multiple high-load devices share a circuit, the resulting electrical noise can interfere with sensitive LED drivers. Similarly, shared neutral wires in multi-way circuits can create backfeed issues that destabilize low-power operation.
How to Diagnose the Source of Flicker
Before applying fixes, isolate the root cause. Follow this diagnostic approach:
- Test one bulb at a time in a simple setup—directly screwed into a lamp plugged into a known stable outlet.
- Dim using only the app—bypass any wall switches or third-party automation.
- Observe at different brightness levels, especially between 5% and 20%, where flicker is most common.
- Check for patterns: Does flickering happen only when other appliances turn on? Only at night? Only with certain scenes?
- Update firmware on all bulbs and the controlling hub or bridge.
If the bulb flickers even in isolation, the issue is likely internal—either a defective unit or inherent design limitation. If it works fine alone but flickers in your ceiling fixture, the problem may lie in the fixture, circuit, or control method.
Step-by-Step Guide to Stabilize Your Smart Lights
Follow this sequence to eliminate flickering systematically:
Step 1: Remove Physical Dimmers (If Present)
Most smart bulbs are designed to be dimmed via software, not mechanical switches. Traditional dimmers reduce voltage using phase-cut methods (leading or trailing edge), which confuse LED drivers.
- Turn off power at the breaker.
- Remove the wall dimmer switch and replace it with a standard toggle switch or smart switch designed for LED loads.
- Alternatively, bypass the switch entirely and leave it in the \"on\" position, controlling brightness solely through the app.
Step 2: Ensure Firmware Is Up to Date
Manufacturers regularly patch dimming performance. For example, Philips Hue released firmware updates specifically to smooth out flicker in their White Ambiance line below 10% brightness.
- Open your smart lighting app (e.g., Hue, LIFX, Nanoleaf).
- Navigate to device settings and check for updates.
- Restart the hub if prompted after installation.
Step 3: Optimize Network Stability
Wi-Fi congestion or weak Zigbee mesh networks lead to delayed or missed commands.
- Place your hub centrally, away from metal objects and large appliances.
- Add Zigbee repeaters (like smart plugs) to strengthen signal paths.
- Switch to a 2.4 GHz band if using Wi-Fi bulbs—5 GHz has faster speeds but shorter range and poorer wall penetration.
Step 4: Use Compatible Fixtures and Drivers
Enclosed fixtures trap heat, which degrades LED performance over time. Similarly, old magnetic transformers in low-voltage setups can interfere with electronic drivers.
- Ensure fixtures are rated for enclosed use if applicable.
- Avoid daisy-chaining too many bulbs on a single circuit.
- For integrated LED fixtures, verify the built-in driver supports smooth dimming down to 1%.
Step 5: Adjust Dimming Curves (Advanced)
Some platforms allow customization of the dimming curve—the relationship between slider position and actual brightness output. A linear curve may make tiny adjustments at low levels too drastic.
- In Hue Bridge settings, enable “Adjust light brightness based on room” or manually tweak curves via third-party apps like Hue Essentials.
- LIFX bulbs allow curve adjustments through their API for smoother fade-ins.
Do’s and Don’ts: Smart Light Dimming Best Practices
| Action | Do | Don’t |
|---|---|---|
| Dimming Control | Use app or voice commands for dimming | Use traditional triac dimmers with smart bulbs |
| Fixture Type | Use open or ventilated fixtures | Install in tightly enclosed, unventilated housings |
| Network Setup | Use dedicated Zigbee/Z-Wave hubs | Overload Wi-Fi with dozens of smart bulbs |
| Maintenance | Update firmware monthly | Ignore update notifications |
| Installation | Match bulb specs with fixture requirements | Mix different brands/models on the same dimmed circuit |
Mini Case Study: Resolving Flicker in a Living Room Setup
Mark installed four Philips Hue White Ambiance bulbs in his living room ceiling fixture, controlled by a Hue Bridge. He noticed persistent flickering when dimming below 15%, especially when turning on the air conditioner.
He followed the stabilization steps:
- Confirmed no wall dimmer was present—switch was standard toggle.
- Updated all bulbs and bridge firmware—resolved minor lag but not flicker.
- Discovered the AC unit and lights shared a circuit. Used a plug-in EMI filter on the AC to reduce electrical noise.
- Added a Hue Repeatable Power Outlet nearby to strengthen Zigbee signal.
After these changes, flickering ceased. Mark also adjusted the dimming curve so 10% on the slider equaled a stable 8% output, avoiding the problematic lower threshold.
FAQ
Can flickering smart lights be dangerous?
Occasional flicker due to software glitches is typically not hazardous. However, persistent flickering caused by overheating, poor wiring, or incompatible dimmers can increase fire risk or damage drivers over time. If flickering is accompanied by buzzing, burning smells, or heat buildup, disconnect the fixture and consult an electrician.
Why do only some of my smart bulbs flicker when dimmed?
This often points to batch variation, age differences, or placement in areas with weaker wireless signals. Older bulbs may have outdated drivers less capable of handling low-level dimming. Replace suspect units or ensure all are updated to the latest firmware version.
Are there smart bulbs known for flicker-free dimming?
Yes. High-end models like Philips Hue, LIFX Z, and Nanoleaf Shapes are engineered for smooth dimming down to 1%. Look for bulbs advertising “flicker-free” operation or compliance with IEEE 1789 standards for low-risk LED modulation.
Checklist: Eliminate Smart Light Flicker
- ☐ Remove traditional dimmer switches
- ☐ Update all bulb and hub firmware
- ☐ Test bulbs in isolation to identify faulty units
- ☐ Strengthen wireless network (add repeaters if needed)
- ☐ Verify circuit load and avoid sharing with high-draw appliances
- ☐ Adjust dimming curves or set minimum brightness
- ☐ Replace bulbs not rated for dimming or enclosed fixtures
- ☐ Consult an electrician if flickering persists across multiple brands
Conclusion
Flickering smart lights when dimmed are a solvable problem—not an inevitable flaw. By understanding the interplay between dimming technology, electrical environment, and wireless reliability, you can create a lighting system that performs smoothly at every brightness level. The key lies in matching the right control method to your bulbs, maintaining updated firmware, and ensuring clean power and strong signals.
Start with the basics: eliminate incompatible dimmers, update software, and test individual components. Most flicker disappears with small, logical adjustments. Once stabilized, your smart lights will deliver the seamless, ambient experience they were designed for—without the distraction of erratic flashes.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?