High-speed internet is no longer a luxury—it’s a standard in most homes. Yet, many gamers still experience frustrating lag during online matches, even when their ISP promises blazing-fast speeds. You might have 500 Mbps download and low advertised ping, but if your character freezes mid-fight or your shots register too late, the connection isn’t truly optimized for real-time gameplay. The truth is, internet speed and gaming performance are not the same thing. Latency, routing inefficiencies, hardware bottlenecks, and server distance all play critical roles in how smoothly your game runs—regardless of bandwidth.
This article breaks down the hidden causes behind gaming lag despite a fast connection and provides actionable strategies to minimize ping and enhance responsiveness across competitive titles like Fortnite, Valorant, Call of Duty, and others.
Understanding the Difference Between Speed and Latency
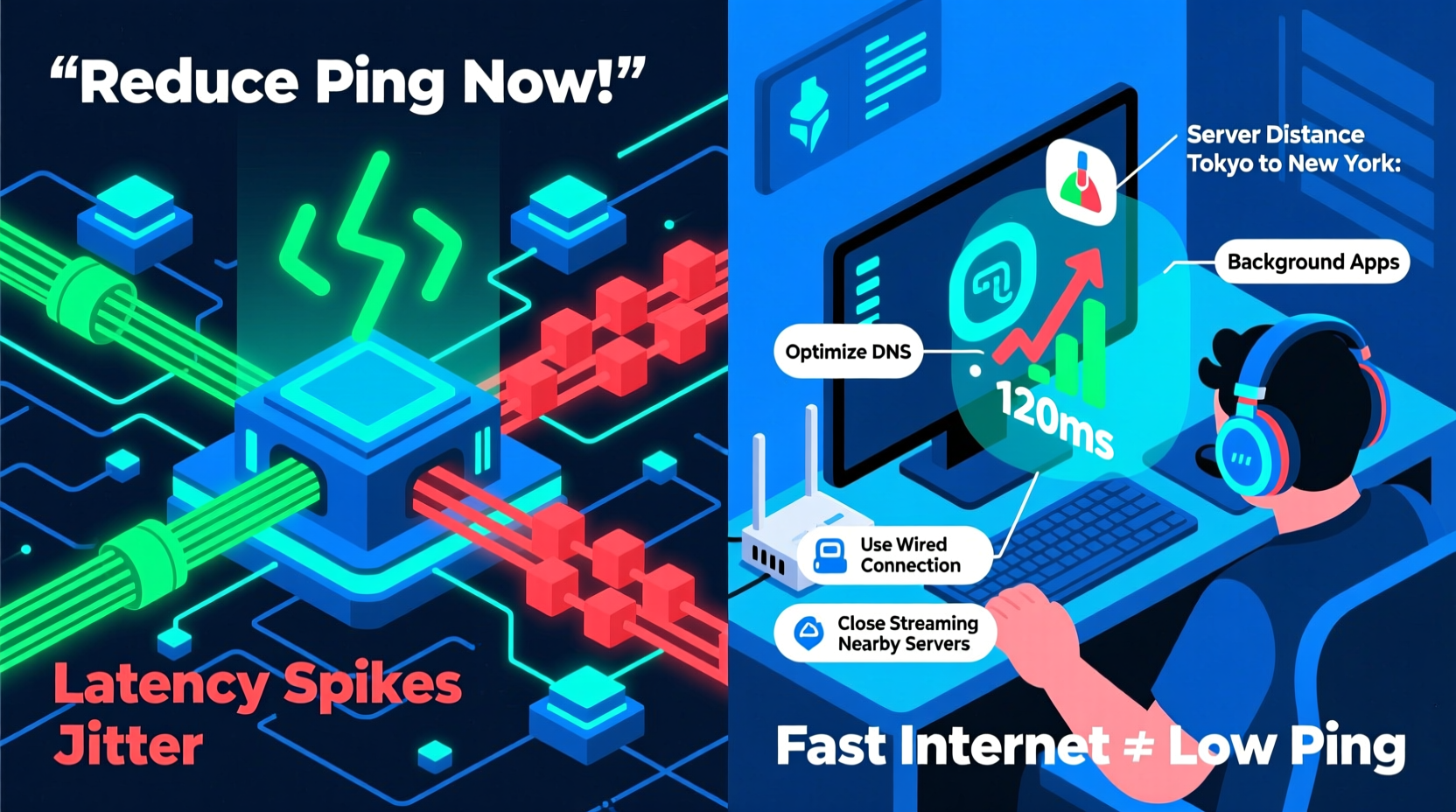
One of the most common misconceptions among gamers is equating high download/upload speeds with low latency. While both are important, they serve different functions:
- Bandwidth (Speed): Measures how much data can be transferred per second—useful for downloading updates or streaming video.
- Latency (Ping): Refers to the time it takes for a data packet to travel from your device to the game server and back, measured in milliseconds (ms).
In online gaming, latency is king. A 30 ms ping feels snappy; anything above 100 ms introduces noticeable delay. Even with gigabit fiber, poor routing or network congestion can spike your ping unpredictably. Think of it like driving on a wide highway (high bandwidth) that suddenly hits a traffic jam at an off-ramp (high latency). Your car has plenty of room, but you’re still delayed reaching your destination.
“Gamers often blame their ISP when the real culprit is last-mile routing inefficiency or Wi-Fi interference.” — David Lin, Network Engineer at CloudShield Technologies
Common Causes of Lag Despite Fast Internet
Even with a premium internet plan, several factors can sabotage your gaming experience. Here's what typically goes wrong:
1. Wi-Fi Interference and Signal Degradation
Wireless connections are inherently less stable than wired ones. Walls, appliances, neighboring networks, and even Bluetooth devices can interfere with your signal. This leads to packet loss, jitter, and fluctuating ping—even if your base speed test looks good.
2. Suboptimal Routing Paths
Your data doesn’t take a direct route to the game server. It hops through multiple intermediate nodes controlled by ISPs and transit providers. Sometimes, these paths are inefficient due to peering disputes, outdated infrastructure, or geographical detours. For example, your traffic might go from New York to London before reaching a server in Los Angeles.
3. Background Bandwidth Consumption
Other devices or applications on your network—like cloud backups, streaming services, or automatic updates—can consume bandwidth and introduce contention. Even if total usage is below your cap, bursty activity can cause micro-lags that disrupt real-time gameplay.
4. Server-Side Congestion or Distance
No matter how optimized your home network is, you're limited by the game server’s location and load. Playing on a server thousands of miles away adds unavoidable latency. During peak hours, overloaded servers increase processing delays, making your connection feel sluggish regardless of your setup.
5. Outdated or Underpowered Hardware
Your router, modem, or PC may not be capable of handling modern gaming demands efficiently. Older routers lack Quality of Service (QoS) features, while insufficient RAM or CPU power can cause frame drops that mimic network lag.
How to Reduce Ping and Improve Game Responsiveness
Reducing ping isn’t just about upgrading your internet plan. It requires a holistic approach to network optimization. Below are practical steps you can implement today.
Step-by-Step Guide to Lowering Your Ping
- Switch to a Wired Ethernet Connection
Replace Wi-Fi with a physical Ethernet cable between your gaming device and router. This eliminates wireless interference and reduces jitter significantly. - Restart Your Router and Modem Regularly
Firmware glitches accumulate over time. A weekly reboot clears memory leaks and resets unstable connections. - Enable QoS (Quality of Service) Settings
Access your router’s admin panel and prioritize gaming traffic. Assign higher priority to your console or PC so it gets first access to bandwidth during congestion. - Close Background Applications
Shut down torrents, streaming apps, cloud sync tools, and any software using the internet in the background. - Choose Closer Game Servers
Select servers geographically nearest to you. In games without auto-selection, manually pick regions like “US East” instead of “Europe” if you’re based in New York. - Upgrade to a Gaming-Optimized Router
Modern gaming routers (e.g., ASUS ROG, Netgear Nighthawk) include advanced QoS, MU-MIMO, and traffic shaping tailored for low-latency performance. - Use a DNS Optimizer
Change your DNS to faster alternatives like Google DNS (8.8.8.8), Cloudflare (1.1.1.1), or OpenDNS. This speeds up domain resolution times, reducing initial connection delays. - Consider a Gaming VPN (Selectively)
While most traditional VPNs increase latency, specialized services like ExitLag or WTFast optimize routing by using private peering channels to bypass congested public routes.
Do’s and Don’ts: Managing Your Gaming Network
| Do | Don't |
|---|---|
| Use Ethernet cables for critical gaming sessions | Rely solely on Wi-Fi for competitive play |
| Update router firmware monthly | Ignore firmware updates or use default passwords |
| Limit number of active devices during gameplay | Allow automatic Windows/Mac updates during matches |
| Test ping using command-line tools (ping -t) | Trust only third-party speed tests without checking actual latency |
| Invest in a mesh system if Wi-Fi is unavoidable | Place your router near microwaves or metal objects |
Real-World Example: Fixing Persistent Lag in Competitive Play
Take the case of Marcus, a ranked Valorant player in Chicago. Despite having a 300 Mbps cable connection, he consistently experienced 140+ ms ping and rubberbanding during crucial duels. Initial troubleshooting showed no obvious issues—Wi-Fi signal was strong, no downloads were running.
After running a traceroute, Marcus discovered his traffic was being routed through Dallas before reaching the East Coast-based game server—a detour adding ~60 ms unnecessarily. He contacted his ISP, who acknowledged known routing inefficiencies. Switching to a DOCSIS 3.1 modem and enabling IPv6 reduced the hop count. Additionally, Marcus connected via Ethernet and enabled QoS on his new ASUS GT-AX11000 router. Within days, his average ping dropped to 42 ms with near-zero packet loss. His in-game K/D ratio improved noticeably within two weeks, proving that technical optimization directly impacts performance.
Checklist: Optimize Your Setup in Under 30 Minutes
- ✅ Connect your gaming device directly to the router via Ethernet
- ✅ Restart your modem and router
- ✅ Close all non-essential apps (Spotify, Discord streams, browsers)
- ✅ Change DNS to 1.1.1.1 (Cloudflare) or 8.8.8.8 (Google)
- ✅ Log into your router settings and enable QoS for gaming
- ✅ Select the closest available game server
- ✅ Run a continuous ping test to the game server (
ping -t [server IP]) - ✅ Schedule heavy downloads outside gaming hours
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a better internet plan fix high ping?
Not necessarily. Upgrading bandwidth helps only if your current plan is saturated. High ping is usually caused by routing, distance, or local network issues—not raw speed. Focus on optimizing your existing connection before paying for more Mbps.
Is it possible to have zero ping?
No. Due to the laws of physics, data travels at roughly two-thirds the speed of light through fiber. Even locally hosted servers have minimum round-trip delays of 5–10 ms. Anything under 30 ms is considered excellent for consumer-grade connections.
Does a gaming PC affect ping?
Not directly. However, a slow PC can cause frame rate drops that make network lag more apparent. Input delay from poor hardware can also create the illusion of high ping. Ensure your system meets or exceeds recommended specs for smooth rendering.
Final Thoughts: Winning Starts Before the Match Begins
Gaming success isn’t determined solely by reflexes and strategy—network precision matters just as much. A well-tuned connection gives you a tangible edge: faster shot registration, smoother movement, and consistent performance under pressure. While fast internet is a good foundation, true optimization comes from understanding how data moves from your machine to the server and back again.
By addressing hidden culprits like suboptimal routing, Wi-Fi instability, and background traffic, you can dramatically reduce ping—even without changing ISPs. The difference between victory and defeat often lies in milliseconds. Take control of your network environment, apply the steps outlined here, and enter every match with confidence that your connection won’t hold you back.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?