It’s a frustrating scenario familiar to many gamers: you’ve invested in a premium internet plan boasting 500 Mbps or more, your router is top-of-the-line, and yet, during a crucial match, your character freezes mid-movement. Bullets miss. You’re eliminated. The kill feed rolls on—without you. High download speeds don’t always translate to smooth gameplay, and understanding why requires looking beyond the headline number on your ISP’s advertisement.
Latency, packet loss, jitter, server distance, hardware bottlenecks, and background processes all play pivotal roles in gaming performance. While bandwidth gets the spotlight, it's often not the culprit when lag strikes. Real-time online gaming demands consistency and responsiveness—not just raw throughput. This article unpacks the technical and environmental factors that can undermine even the fastest connections and offers actionable solutions to reclaim control over your gaming experience.
The Myth of Bandwidth as the Sole Performance Indicator
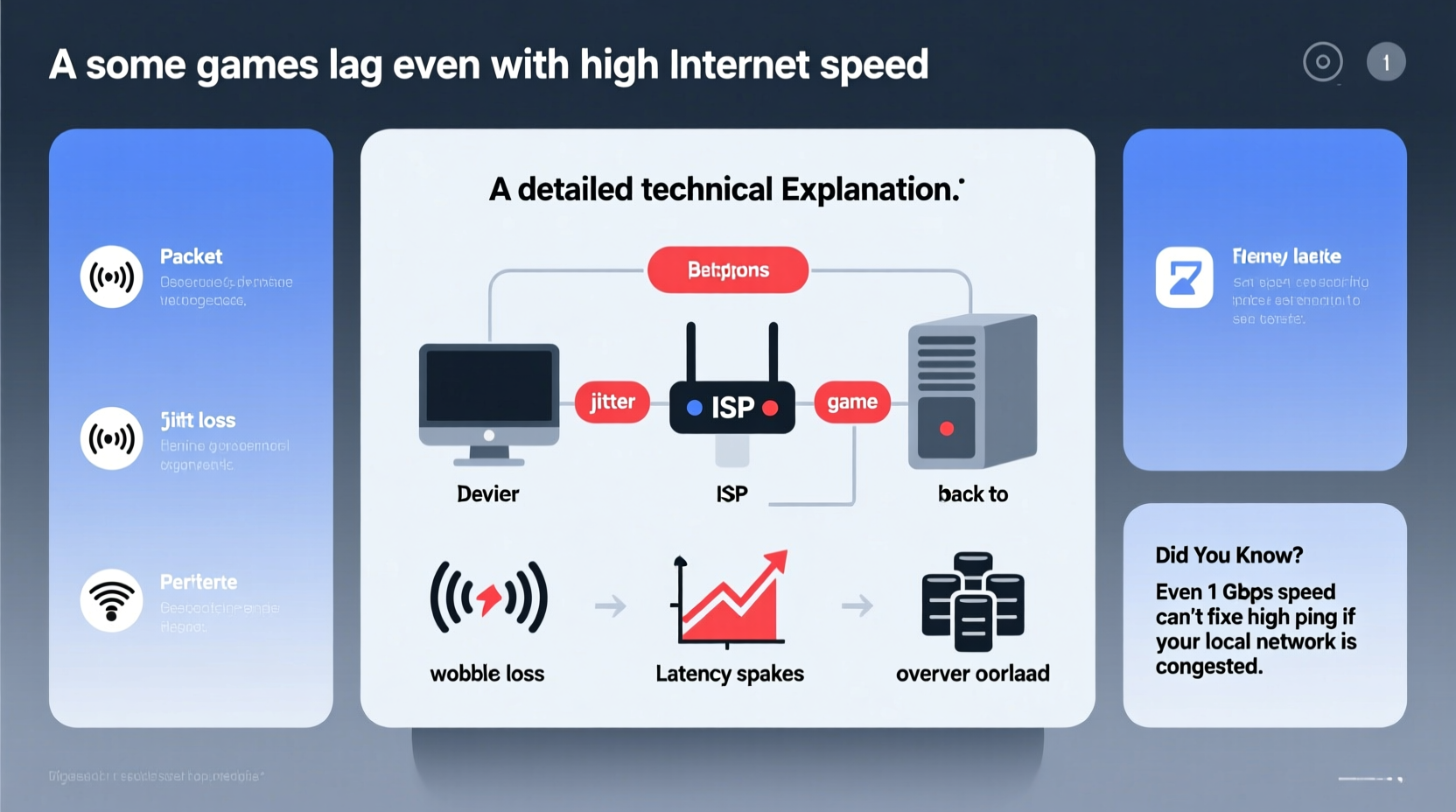
When ISPs advertise “high-speed internet,” they emphasize download and upload bandwidth—how much data can be transferred per second. For activities like streaming 4K video or downloading large files, high bandwidth is essential. But online gaming operates under different constraints. Most multiplayer games require only 3–6 Mbps for optimal performance. Once that threshold is met, additional bandwidth yields diminishing returns.
What matters more in gaming is latency, commonly referred to as \"ping.\" Latency measures the round-trip time it takes for a data packet to travel from your device to the game server and back. It’s expressed in milliseconds (ms). A ping under 50 ms is ideal; above 100 ms begins to impact responsiveness; over 150 ms results in noticeable lag. Even with gigabit speeds, high latency can make a game feel sluggish.
Consider this analogy: bandwidth is the width of a highway, while latency is the speed limit. A ten-lane highway won’t help if there’s a traffic jam at the first exit. In gaming, that “traffic jam” could be a distant server, Wi-Fi interference, or a congested home network.
Network Factors That Cause Lag Despite Fast Speeds
Several behind-the-scenes network conditions can degrade gaming performance regardless of advertised speed. These include:
- High Ping (Latency): Caused by physical distance to the game server, inefficient routing, or network congestion.
- Packet Loss: Data packets fail to reach their destination, forcing retransmission and causing stuttering or rubber-banding.
- Jitter: Variability in latency between packets disrupts real-time synchronization, making movements appear choppy.
- Network Congestion: Multiple devices streaming, downloading, or updating simultaneously consume available bandwidth and increase competition for resources.
- ISP Throttling: Some providers slow down traffic to certain services during peak hours, including gaming platforms.
These issues are often invisible to standard speed tests, which measure maximum throughput under ideal conditions but don’t simulate real-time gaming traffic patterns.
“Gamers need stability, not just speed. A connection with 30 Mbps and 20 ms ping will outperform a 1 Gbps link with 120 ms ping every time.” — Daniel Reeves, Network Engineer at GameNet Labs
Hardware and System Bottlenecks
Your internet connection is only one link in the chain. Even with flawless network performance, local hardware limitations can manifest as lag. Common culprits include:
- Outdated or Underpowered GPU/CPU: If your system struggles to render frames quickly, input delay increases, creating perceived lag.
- Insufficient RAM: Low memory leads to stuttering, especially in open-world or resource-intensive games.
- Background Processes: Automatic updates, cloud sync tools, antivirus scans, or browser tabs consuming CPU and network resources.
- Disk Speed: Slow HDDs can cause texture pop-in and loading delays, disrupting gameplay flow.
A powerful internet connection cannot compensate for a bottlenecked system. For example, if your PC delivers only 30 frames per second (FPS), even a perfect 10 ms ping won’t eliminate motion lag. Frame rate directly impacts responsiveness—higher FPS means faster visual feedback to your inputs.
Case Study: Alex’s Competitive Gaming Struggle
Alex, an avid *Valorant* player, upgraded his internet from 100 Mbps to 600 Mbps, expecting smoother gameplay. Despite the boost, he still experienced frequent freezes during matches. After testing, he discovered his Wi-Fi was operating on a crowded 2.4 GHz band, causing interference from neighboring networks. Switching to a 5 GHz channel helped slightly, but the real breakthrough came when he connected via Ethernet and closed background applications like Discord screen-sharing and Steam downloads. His in-game ping dropped from 85 ms to 32 ms, and frame pacing stabilized. The issue wasn’t speed—it was local network efficiency and system load.
Server-Side and Routing Issues
Even with optimal local conditions, you're at the mercy of the game server’s location and infrastructure. Hosting servers far from your region introduces unavoidable latency due to the laws of physics—data travels at finite speeds across fiber lines.
For instance, a player in Sydney connecting to a server in Los Angeles may experience 180+ ms ping, while a player in San Francisco sees 40 ms. No amount of local optimization can eliminate that geographical gap. Additionally, some games use peer-to-peer (P2P) networking rather than dedicated servers, meaning your connection quality depends partly on other players’ setups.
Rerouting also plays a role. ISPs don’t always send traffic along the most direct path. Suboptimal routing—sometimes caused by peering agreements or outdated network configurations—can add extra hops, increasing latency unnecessarily. Tools like traceroute or third-party apps such as PingPlotter can reveal inefficient routing paths.
| Factor | Impact on Gaming | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Distance to Server | Increases base latency | Select geographically closer servers in-game |
| Wi-Fi Interference | Causes jitter and packet loss | Use 5 GHz band or switch to Ethernet |
| Background Downloads | Consumes bandwidth and CPU | Schedule updates outside gaming sessions |
| Router Quality | Poor QoS handling affects traffic prioritization | Upgrade to a gaming router with QoS features |
| Game Optimization | Poorly coded netcode increases sensitivity to lag | Check community forums for known issues |
Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnose and Reduce Gaming Lag
Follow this systematic approach to identify and resolve the root causes of lag, even with high-speed internet:
- Test Your Actual Connection Metrics
Use tools like speedtest.net for bandwidth, but also run a ping and jitter test using ping -t google.com in Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (macOS). Look for consistent response times under 50 ms and minimal packet loss. - Switch to Wired Ethernet
Disconnect from Wi-Fi and plug directly into your router. This eliminates wireless interference and provides a stable physical connection. - Check for Background Network Usage
Open Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) and sort by “Network” usage. Identify and close apps consuming bandwidth, such as cloud backups, torrents, or streaming services. - Enable QoS (Quality of Service) on Your Router
Log into your router settings and prioritize gaming traffic. Assign higher priority to your gaming device’s IP or MAC address to ensure it gets preferential treatment during congestion. - Choose the Best Game Server Region
In multiplayer games, manually select a server closest to your physical location. Avoid auto-connect if it frequently places you on distant servers. - Update Hardware Drivers and Firmware
Ensure your GPU, network adapter, and router firmware are up to date. Outdated drivers can introduce compatibility issues and inefficiencies. - Monitor In-Game Performance Metrics
Enable FPS counters (via Steam, NVIDIA GeForce Experience, or in-game settings) and watch for dips. Pair low FPS with high ping? The issue may be local hardware, not your internet. - Test with Another Device
Borrow a friend’s laptop or use a secondary device to run the same game on your network. If lag persists, the problem is likely network-wide. If not, focus on your primary device’s configuration.
FAQ: Common Questions About Gaming Lag
Does having more bandwidth always improve gaming performance?
No. Once you exceed the minimum required bandwidth (typically 5–6 Mbps for most games), additional speed does not enhance gameplay. What matters more are latency, packet loss, and jitter—all of which are unrelated to download speed.
Can my router cause lag even with fast internet?
Yes. Older or low-end routers may lack Quality of Service (QoS) features, have poor signal management, or struggle under heavy loads. They might also use outdated Wi-Fi standards (e.g., 802.11n) that introduce latency compared to modern standards like Wi-Fi 6.
Why does my game lag only during certain times of day?
This often indicates network congestion. During peak hours (evening and weekends), more users are online, increasing demand on both your home network and your ISP’s infrastructure. It could also coincide with automatic system updates or background sync tasks on your devices.
Action Plan: Checklist to Eliminate Gaming Lag
- ✅ Test ping, jitter, and packet loss—not just download speed
- ✅ Connect via Ethernet instead of Wi-Fi
- ✅ Close unnecessary background applications
- ✅ Enable QoS on your router and prioritize gaming traffic
- ✅ Select the nearest server region in-game
- ✅ Update network drivers and router firmware
- ✅ Monitor FPS and system performance during gameplay
- ✅ Schedule large downloads outside gaming hours
- ✅ Consider upgrading to a gaming-focused router with advanced traffic management
Conclusion: Rethinking What “Fast Internet” Really Means for Gamers
High internet speed is only part of the equation. True gaming performance hinges on consistency, responsiveness, and intelligent network management. Recognizing that lag stems from a combination of factors—network quality, hardware capability, server proximity, and software efficiency—empowers you to take targeted action.
Stop chasing bandwidth numbers. Start optimizing for stability. Reconfigure your setup, audit your system, and fine-tune your connection with the precision it deserves. The difference between victory and defeat often lies not in megabits, but in milliseconds.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?