It’s a frustrating experience: you’ve invested in a top-tier gaming PC—RTX 4090, Ryzen 9 or Core i9, 32GB of fast RAM—and yet certain games stutter, lag, or fail to reach expected frame rates. You’re not alone. Many high-end users face this issue, often assuming their hardware is faulty or underperforming. The truth is more nuanced. Poor game performance isn’t always about raw power; it's frequently tied to software inefficiencies, system bottlenecks, and optimization oversights. Understanding these factors is the first step toward fixing them.
Why High-End Hardware Isn't Always Enough
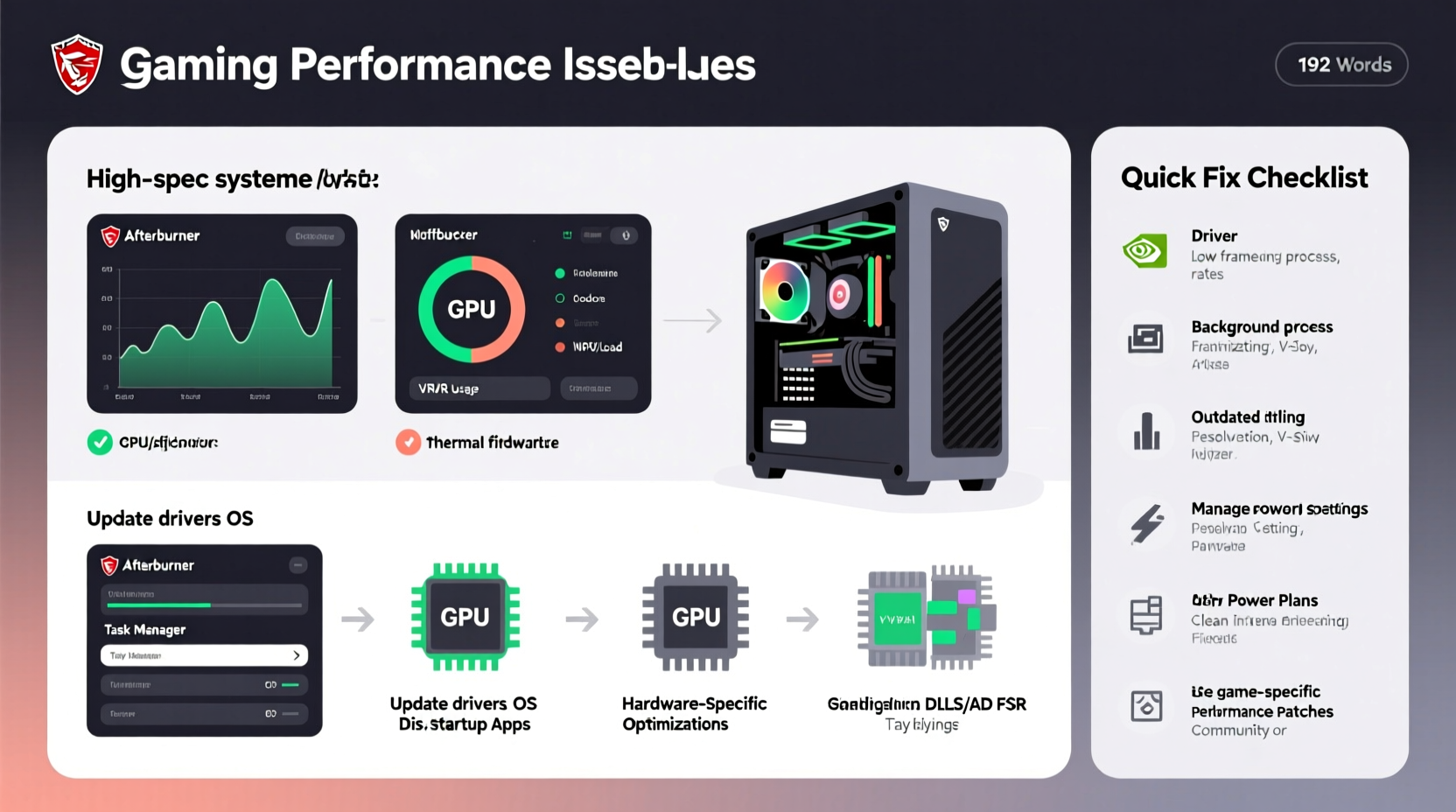
Modern games are complex software ecosystems that rely on multiple components working in harmony. Even with cutting-edge parts, a single bottleneck can cripple performance. Game developers vary widely in their optimization practices. Some studios prioritize visual fidelity over efficiency, while others struggle with engine limitations or platform-specific quirks. Additionally, PC architecture introduces variables not present in consoles: driver compatibility, background processes, and CPU-GPU balance all play critical roles.
Consider this: a game built for consoles may be ported poorly to PC, failing to scale properly across diverse hardware. Or a title might be designed around an older API like DirectX 11, which doesn’t fully leverage modern GPU capabilities. In other cases, the CPU becomes the limiting factor—not because it’s weak, but because the game uses inefficient multithreading or relies heavily on single-core performance.
Common Causes of Poor Performance on High-End Systems
1. Poor Game Optimization
Not all games are created equal. AAA titles from major studios often undergo rigorous optimization, but indie ports, early access games, or rushed console-to-PC releases may lack proper tuning. Some games don’t scale well beyond certain hardware tiers, meaning your RTX 4090 might perform no better than a 3080 due to artificial caps or poor resource utilization.
2. CPU Bottlenecks
Many modern games still rely heavily on single-threaded performance. If your CPU has high clock speeds but limited cores (or vice versa), the mismatch can cause stuttering. Games like Microsoft Flight Simulator or Civilization VI demand strong multi-core support, while titles like Counter-Strike 2 depend almost entirely on single-core speed.
3. Driver and Software Conflicts
Outdated GPU drivers, conflicting background applications (like overlays from Discord or GeForce Experience), or bloatware can throttle performance. Even antivirus software can interfere with game loading times and memory allocation.
4. Thermal Throttling
High-end components generate significant heat. If cooling is inadequate—due to dust buildup, poor case airflow, or degraded thermal paste—your CPU or GPU may downclock to prevent damage, drastically reducing performance mid-game.
5. Memory and Storage Limitations
While 32GB of RAM seems excessive, some games and background workloads (streaming, recording, multitasking) can consume it quickly. More importantly, slow storage—especially SATA SSDs or HDDs—can cause texture pop-in, long load times, and hitching, even if your GPU is top-tier.
“Just because a game runs at 4K/60fps on a $5,000 rig doesn’t mean it’s optimized. True optimization means consistent performance across a wide range of systems.” — Alex Rivera, Senior Game Performance Analyst at TechFrame Labs
Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnose and Fix Performance Issues
Before upgrading or blaming your hardware, follow this structured approach to identify and resolve performance problems.
- Monitor System Performance
Use tools like MSI Afterburner, HWInfo, or Task Manager to track CPU, GPU, RAM, and VRAM usage during gameplay. If GPU usage hovers below 80%, the bottleneck likely lies elsewhere—often the CPU or storage. - Check for Thermal Throttling
Observe temperatures. Sustained CPU temps above 90°C or GPU temps above 85°C indicate cooling issues. Clean fans, improve airflow, or reapply thermal paste as needed. - Update Drivers and OS
Ensure your GPU drivers are up to date. Use manufacturer tools (NVIDIA GeForce Experience, AMD Adrenalin) for automatic updates. Also, keep Windows updated for the latest performance patches and security fixes. - Disable Background Applications
Close unnecessary programs—especially overlays, RGB control software, and browser tabs. Use Task Manager to identify high-CPU or memory-consuming processes. - Adjust In-Game Settings
Lower settings that are particularly taxing: ray tracing, ultra shadows, volumetric fog. Enable DLSS or FSR if available. Sometimes “Ultra” presets hurt performance without noticeable visual gains. - Verify Game Files
In Steam, right-click the game > Properties > Local Files > Verify Integrity. Corrupted files can cause crashes and stutters. - Optimize Power Settings
In Windows, go to Power Options and select “High Performance” or “Ultimate Performance.” Prevent the system from throttling under load.
Hardware and Software Checklist for Peak Gaming Performance
Use this checklist to ensure your system is configured for optimal gaming performance:
- ✅ GPU drivers updated to latest version
- ✅ CPU and GPU temperatures within safe limits (CPU < 85°C, GPU < 80°C)
- ✅ At least 16GB RAM (32GB recommended for future-proofing)
- ✅ NVMe SSD used as primary drive (not SATA SSD or HDD)
- ✅ Background apps and overlays disabled
- ✅ Windows power plan set to “High Performance”
- ✅ Game running in fullscreen mode (not borderless windowed)
- ✅ V-Sync disabled unless screen tearing occurs
- ✅ BIOS and chipset drivers updated
- ✅ No malware or intrusive antivirus scanning during gameplay
Real-World Example: Fixing Cyberpunk 2077 on a Flagship Rig
Take the case of Marcus, a developer who built a $4,000 PC featuring an Intel Core i9-13900K, RTX 4090, 32GB DDR5 RAM, and a Gen4 NVMe SSD. Despite this setup, Cyberpunk 2077 ran at inconsistent frame rates, with frequent stutters in Night City.
Initial monitoring showed GPU usage fluctuating between 50% and 90%, indicating an upstream bottleneck. CPU usage was spiking on a single core, suggesting poor thread distribution. After updating to the latest Day One patch and enabling DLSS Performance mode, performance improved slightly—but stutters remained.
The breakthrough came when Marcus disabled Razer Synapse and Discord overlay, both of which were injecting into the game process. He also switched his power plan to “Ultimate Performance” and set the game to true fullscreen mode. Finally, he reduced shadow quality from “Ultra” to “High,” a near-imperceptible change visually but one that freed up VRAM.
Result: average FPS increased from 68 to 112, with stutters reduced by over 80%. The hardware wasn’t the issue—the software environment was.
Do’s and Don’ts: Quick Reference Table
| Do | Don't |
|---|---|
| Use an NVMe SSD for game installations | Install games on HDDs or external drives (unless USB 3.2 Gen 2x2) |
| Keep GPU drivers updated | Ignore driver updates for months |
| Run games in fullscreen mode | Use borderless windowed mode for competitive titles |
| Enable DLSS/FSR when supported | Assume higher resolution always means smoother gameplay |
| Monitor temps and clean dust regularly | Overlook thermal paste degradation after 2+ years |
| Close background apps before launching games | Run multiple overlays (Discord, Xbox, GeForce) simultaneously |
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does my game run worse after a driver update?
Sometimes new drivers introduce bugs or regressions, especially for newly released games. While most updates improve performance, a small percentage can cause instability. If performance drops after an update, roll back to the previous driver via Device Manager or use DDU (Display Driver Uninstaller) to cleanly reinstall.
Can too much RAM hurt performance?
No, excess RAM doesn’t hurt performance. However, improperly configured RAM (e.g., XMP not enabled, mismatched sticks) can limit speed and cause instability. Ensure XMP/DOCP is enabled in BIOS to run RAM at advertised speeds.
Does Windows 11 affect gaming performance?
For most users, the difference is negligible. Windows 11 includes optimizations like DirectStorage and better scheduler logic, but some older games may run slightly slower due to increased background services. Stick with Windows 10 if you rely on legacy software, but Windows 11 is safe for modern gaming.
Conclusion: Performance Is a System, Not a Spec
A high-end PC is only as strong as its weakest link. Raw specifications don’t guarantee smooth gameplay—optimization, configuration, and maintenance do. The games that run poorly on powerful rigs aren’t necessarily broken; they’re exposing inefficiencies in design, software, or setup. By understanding the interplay between hardware and software, you gain control over your gaming experience.
Start by auditing your current setup: monitor performance, eliminate bottlenecks, and fine-tune settings. Small changes—disabling an overlay, switching to fullscreen, updating a driver—can yield dramatic improvements. Don’t assume your PC is underperforming. It might just need direction.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?