Bluetooth speakers offer convenience and portability, but few frustrations match the sudden drop in sound when you move near a window. Whether you're hosting a backyard gathering or enjoying music by the patio, signal interruptions can ruin the experience. The issue isn't random—it's rooted in physics, materials, and environmental interference. Understanding why this happens—and how to fix it—can transform your listening experience from erratic to seamless.
The Science Behind Bluetooth Signal Disruption Near Windows
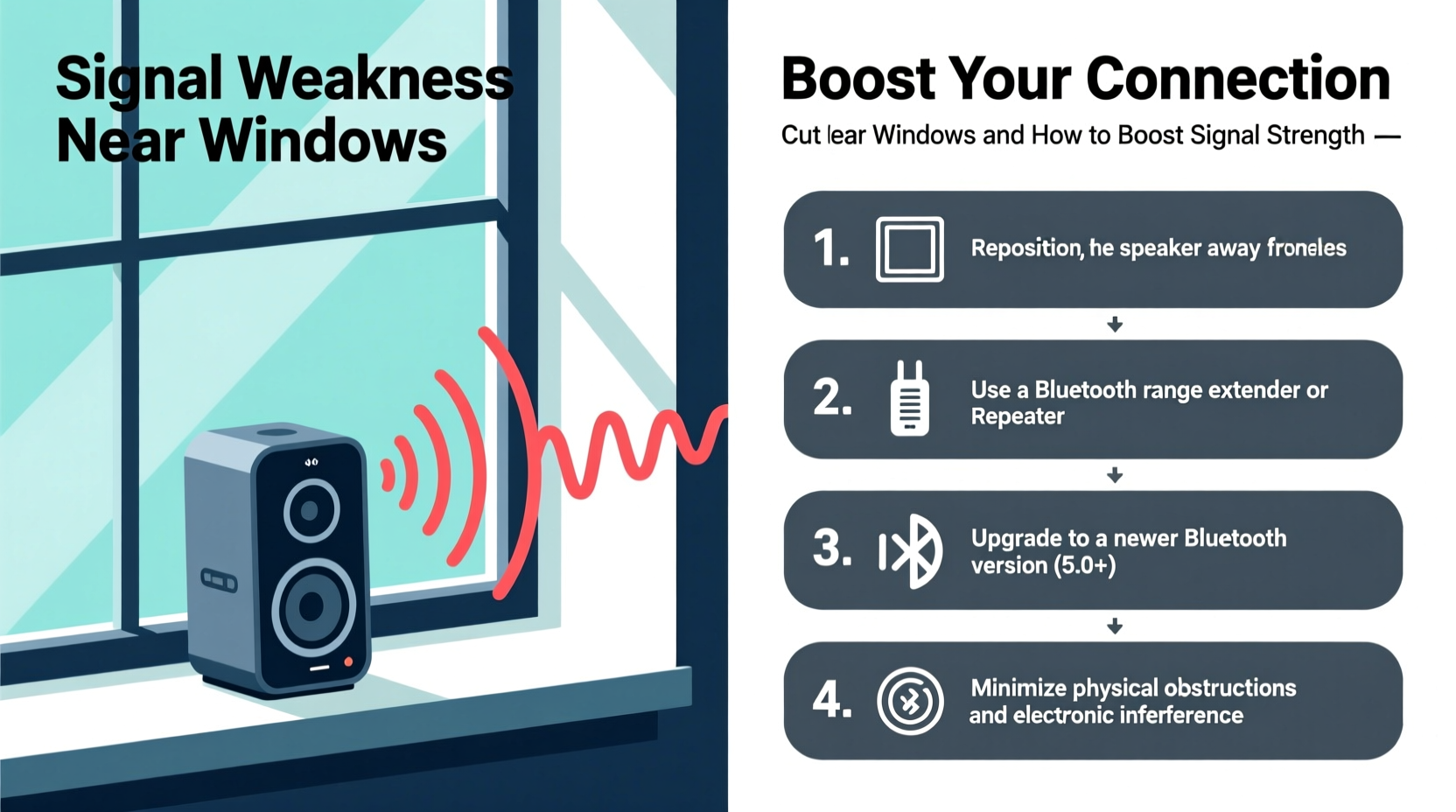
Bluetooth operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency band, the same range used by Wi-Fi routers, microwaves, and many household devices. This frequency is effective for short-range wireless communication but is highly susceptible to physical obstructions and electromagnetic interference. Windows may seem like open pathways, but modern designs often include features that block or reflect radio waves.
Many windows today are coated with low-emissivity (Low-E) films designed to improve energy efficiency by reflecting heat. Unfortunately, these metallic coatings also reflect or absorb 2.4 GHz signals, weakening or blocking Bluetooth transmission. Additionally, double- or triple-glazed windows contain layers of metal or plastic interlayers that further degrade signal penetration.
“Even seemingly transparent surfaces like energy-efficient glass can act as Faraday cages at certain frequencies, effectively shielding wireless signals.” — Dr. Lena Patel, RF Engineer and Wireless Communications Specialist
When your speaker is placed near such a window, the Bluetooth signal from your phone or tablet must pass through this barrier. Reflection, absorption, and scattering reduce signal strength, leading to latency, distortion, or complete disconnection.
Common Environmental Factors That Worsen the Problem
Beyond the window itself, several environmental conditions amplify signal loss:
- Proximity to other 2.4 GHz devices: Wi-Fi routers, cordless phones, baby monitors, and microwave ovens all operate in the same spectrum and can cause interference.
- Building materials: Metal blinds, aluminum frames, and concrete walls adjacent to windows increase signal attenuation.
- Outdoor obstacles: Trees, fences, and even weather conditions like heavy rain can scatter Bluetooth waves.
- Distance and angle: The farther your device is from the speaker, and the more oblique the signal path through the glass, the greater the chance of dropout.
How to Boost Bluetooth Signal Strength: Practical Solutions
Fixing Bluetooth dropouts near windows requires both strategic positioning and technical adjustments. Here’s a step-by-step guide to restoring reliable connectivity.
1. Reposition Your Devices Strategically
The simplest solution is often the most effective. Try moving your source device (phone, tablet) and speaker away from the window frame. Even shifting them 1–2 feet inward can bypass reflective coatings and reduce interference.
Ensure line-of-sight between devices whenever possible. If your phone is behind a metal blind or near a radiator, the signal will struggle. Keep both devices elevated and unobstructed.
2. Reduce Interference from Other Devices
Scan your environment for competing 2.4 GHz emitters. Temporarily turning off nearby Wi-Fi routers, microwaves, or smart home hubs can help isolate the problem.
If Wi-Fi must stay on, consider switching your router to the 5 GHz band (if supported), freeing up space in the 2.4 GHz spectrum for Bluetooth.
3. Use a Bluetooth Signal Booster or Repeater
While true Bluetooth repeaters are rare, some third-party devices act as range extenders by receiving and retransmitting the signal. Alternatively, use a powered USB Bluetooth adapter with enhanced antenna gain connected to a laptop or media player positioned closer to the speaker.
Note: These solutions work best in semi-permanent setups, such as patios or sunrooms.
4. Upgrade to a Speaker with Better Range and Antenna Design
Not all Bluetooth speakers are created equal. Models supporting Bluetooth 5.0 or later offer up to four times the range and improved signal resilience over older versions. Look for speakers with external antennas or MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output) technology for better performance in obstructed areas.
5. Switch Audio Transmission Methods When Possible
If Bluetooth remains unreliable, consider alternatives:
- Aux cable: A simple wired connection bypasses wireless issues entirely.
- Wi-Fi-based audio systems: Devices like Sonos or Apple AirPlay use your home network, which penetrates walls and windows more reliably than Bluetooth.
- Optical or HDMI audio transmitters: For indoor-outdoor setups, these can send audio via light or digital signals with less interference.
Checklist: How to Prevent Bluetooth Dropouts Near Windows
Follow this actionable checklist to minimize disruptions:
- ✅ Test speaker performance in different locations near the window
- ✅ Move both source device and speaker at least 1–2 feet away from the glass
- ✅ Disable or relocate nearby 2.4 GHz devices during critical playback
- ✅ Ensure your speaker supports Bluetooth 5.0 or higher
- ✅ Clean the area around devices—dust and grime don’t affect signal, but poor maintenance can mask underlying issues
- ✅ Consider using a wired connection if wireless stability remains poor
- ✅ Update firmware on both your phone and speaker—manufacturers often release fixes for connectivity bugs
Real-World Example: Solving Patio Speaker Issues
Sarah, a homeowner in Portland, struggled with her outdoor Bluetooth speaker cutting out every time she played music from her kitchen near a large energy-efficient window. She assumed the speaker was faulty and almost returned it. After researching, she realized her window had a Low-E coating. By relocating her phone from the counter (pressed against the glass) to a small table three feet inside the room, the connection stabilized instantly. She also updated her speaker’s firmware, which resolved lingering lag issues. Now, her weekend brunch playlists flow seamlessly into the garden.
This case illustrates how a combination of environmental awareness and minor adjustments can yield dramatic improvements—without spending a dime on new gear.
Do’s and Don’ts: Bluetooth Signal Management Near Windows
| Do | Don’t |
|---|---|
| Place devices away from the edge of windows | Press your phone directly against energy-efficient glass |
| Use Bluetooth 5.0+ enabled devices | Rely on outdated Bluetooth 4.0 or earlier models in high-interference zones |
| Minimize clutter and metal objects between devices | Position speakers behind metal blinds or radiators |
| Test alternative audio methods (wired, Wi-Fi) | Assume the speaker is defective without testing variables |
| Keep software and firmware updated | Ignore manufacturer updates that improve connectivity |
Frequently Asked Questions
Can window tint cause Bluetooth signal loss?
Yes. Many window tints contain metallic particles designed to block UV and infrared radiation. These same particles reflect or absorb 2.4 GHz signals, including Bluetooth. Ceramic or non-metallic tints are less likely to interfere.
Does weather affect Bluetooth performance near windows?
Indirectly, yes. Rain, fog, or high humidity can slightly attenuate wireless signals. More importantly, wet glass increases surface reflection, making it harder for signals to pass through. Cold temperatures may also reduce battery efficiency in portable speakers, indirectly affecting transmission power.
Is there a way to test if my window is blocking Bluetooth?
Yes. Perform a simple test: play audio from your phone to the speaker with both devices indoors, away from the window. Note the volume and clarity. Then, slowly move your phone toward the window while maintaining playback. If the sound cuts out or distorts only when near the glass—while distance and orientation remain consistent—the window is likely the culprit.
Expert Tips for Long-Term Signal Reliability
For those using Bluetooth speakers regularly near windows—such as in sunrooms, conservatories, or open-plan living spaces—long-term planning pays off.
- Designate a signal-friendly zone: Identify a spot where both speaker and source maintain stable connection and mark it for regular use.
- Invest in dual-mode audio systems: Some modern speakers support both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, allowing you to switch protocols depending on location.
- Use a Bluetooth extender with directional antenna: Though niche, products like the Sennheiser BTD 500 USB can extend range by focusing signal directionally, useful for indoor-to-outdoor setups.
- Monitor signal strength apps: On Android, apps like “Bluetooth Scanner” or “WiFi Analyzer” can show real-time signal quality, helping you pinpoint dead zones.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Wireless Audio Experience
Bluetooth dropouts near windows are not inevitable—they’re predictable and fixable. By understanding how building materials, signal physics, and device capabilities interact, you can make informed choices that ensure smooth, uninterrupted sound. Whether it’s repositioning your phone, upgrading to a newer speaker, or switching to a more robust audio protocol, the tools are within reach.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?