Bluetooth speakers offer convenience and portability, making them a favorite for indoor and outdoor listening. But if you’ve noticed your speaker cutting out when placed near a window, you’re not alone. This frustrating issue often stems from signal interference caused by the environment around the glass. Understanding the science behind this disruption—and knowing how to fix it—can restore seamless audio and improve your overall listening experience.
Windows may seem like passive architectural features, but they can actively interfere with wireless signals. Whether you're hosting a patio party, enjoying morning coffee with music, or working from home with background tunes, consistent audio performance matters. This guide breaks down the technical causes of Bluetooth dropouts near windows and provides actionable, real-world solutions to keep your sound clear and uninterrupted.
The Science Behind Bluetooth Signal Interference Near Windows
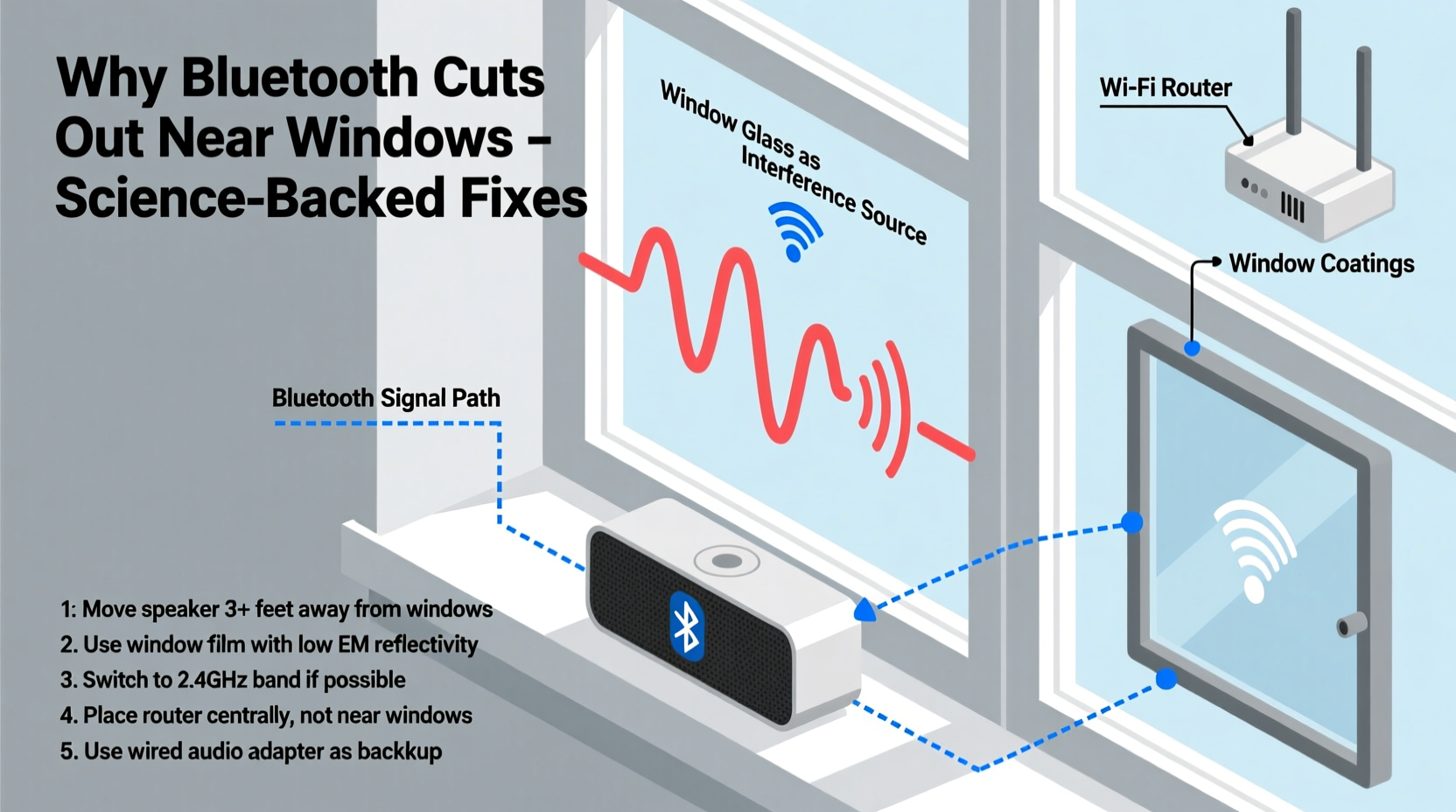
Bluetooth operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency band, which is shared with many household devices including Wi-Fi routers, microwaves, cordless phones, and baby monitors. While this frequency allows for reliable short-range communication, it's also prone to congestion and interference. When a Bluetooth speaker is placed near a window, several factors can degrade the signal between your device (phone, tablet, laptop) and the speaker.
Modern windows often contain metallic coatings or films designed to improve insulation and block UV rays. These materials, especially low-emissivity (Low-E) glass, are engineered to reflect heat and light—but they also reflect or absorb radio frequencies, including Bluetooth signals. As a result, the connection becomes unstable, leading to audio stuttering, lag, or complete disconnection.
In addition to the glass itself, nearby external sources can contribute to interference. Urban environments are saturated with wireless signals—from neighboring Wi-Fi networks to cellular towers. When your speaker is near a window facing the street or another building, it may be exposed to higher levels of electromagnetic noise that disrupt the 2.4 GHz band.
“Signal reflection and absorption from coated glass can reduce Bluetooth range by up to 70% in some cases.” — Dr. Alan Reyes, Wireless Communication Engineer
Common Causes of Bluetooth Disruptions Near Windows
To effectively solve the problem, it’s important to identify the root cause. Here are the most common culprits behind Bluetooth speaker dropouts near windows:
- Metallic window coatings: Low-E glass contains thin metallic layers that block infrared and ultraviolet light but also interfere with RF signals.
- Wi-Fi congestion: If your router is near the same window, overlapping signals on the 2.4 GHz band can cause interference.
- Physical obstructions: Even though windows are transparent to light, they can still attenuate radio waves, especially if double- or triple-paned.
- External signal noise: Nearby cell towers, security systems, or public Wi-Fi can flood the airwaves near exterior walls.
- Distance and angle: Placing the speaker directly against the glass reduces signal strength due to reflection and scattering.
Proven Solutions to Prevent Bluetooth Cutouts
Fortunately, there are several effective strategies to minimize or eliminate Bluetooth interference near windows. These solutions range from simple repositioning to hardware upgrades, depending on your setup and environment.
1. Reposition Your Speaker and Source Device
The easiest fix is adjusting placement. Move the speaker a few feet away from the window, ideally toward the center of the room. Similarly, ensure your phone or tablet isn’t sitting right next to the glass. The goal is to create a clearer line of sight between devices and reduce exposure to reflective surfaces.
2. Use the 5 GHz Band for Wi-Fi (If Applicable)
If you have a dual-band Wi-Fi router, switch your primary devices to the 5 GHz network. This frees up the 2.4 GHz band for Bluetooth use, reducing competition for bandwidth. Note that while Bluetooth cannot use 5 GHz, minimizing traffic on 2.4 GHz improves its reliability.
3. Install a Bluetooth Signal Extender or Repeater
For larger rooms or challenging layouts, consider using a Bluetooth extender. These devices receive the original signal and rebroadcast it, effectively bridging the gap between your source and speaker. Place the repeater between your phone and the speaker, away from the window, to maintain a stable connection.
4. Switch to Wired Audio When Possible
In persistent interference zones, abandon wireless altogether. Use an auxiliary cable (3.5mm or USB-C, depending on your speaker) to connect directly. While this sacrifices portability, it guarantees zero dropouts and often delivers higher audio quality.
5. Upgrade to a Speaker with Better Antenna Design
Not all Bluetooth speakers are created equal. Higher-end models feature advanced antenna systems, multipoint pairing, and support for newer Bluetooth versions (like 5.0 or 5.3), which offer improved range, stability, and interference resistance. Look for speakers marketed as “long-range” or “outdoor-grade” if you frequently use them near windows or patios.
Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnose and Fix the Issue
Follow this systematic approach to identify and resolve Bluetooth interference near windows:
- Test the speaker away from the window: Move it to the center of the room. If the audio stabilizes, the window is likely the culprit.
- Check for active Wi-Fi devices nearby: Temporarily turn off your router or switch to 5 GHz to see if performance improves.
- Minimize other 2.4 GHz devices: Turn off microwaves, cordless phones, or smart home gadgets during testing.
- Change the orientation of the speaker: Rotate it so the antenna side (usually the control panel) faces your device.
- Update firmware: Check the manufacturer’s app or website for Bluetooth speaker updates that may improve connectivity.
- Use a non-metallic stand: Elevate the speaker on wood or plastic instead of metal surfaces, which can further distort signals.
- Conduct a long-term test: Play audio for 10–15 minutes in different positions to confirm a lasting fix.
Comparison: Effective vs. Ineffective Fixes
| Approach | Effectiveness | Why It Works (or Doesn’t) |
|---|---|---|
| Move speaker 3+ feet from window | High | Reduces exposure to reflective glass and external interference. |
| Switch Wi-Fi to 5 GHz | High | Frees up 2.4 GHz spectrum for Bluetooth use. |
| Use a Bluetooth repeater | Medium-High | Extends range but adds complexity and cost. |
| Cover window with thick curtain | Low-Medium | May block some external noise but doesn’t address internal reflection. |
| Place speaker directly on windowsill | Low | Maximizes signal reflection and interference risk. |
| Use AUX cable instead of Bluetooth | Very High | Eliminates wireless dependency entirely. |
Real-World Example: Solving Dropouts in a Sunroom Setup
Sarah, a remote worker in Chicago, loved playing ambient music through her Bluetooth speaker in her sunroom. However, she constantly experienced audio cutouts every time she moved her phone across the room. After testing various positions, she realized the speaker—placed on a metal windowsill—was directly affected by her Low-E insulated windows and a nearby Wi-Fi router.
She followed the diagnostic steps: first moving the speaker inward by five feet, then switching her laptop to the 5 GHz Wi-Fi network. She also updated the speaker’s firmware via the companion app. The result? A stable connection throughout the day, even during video calls with background music.
Sarah’s case highlights how multiple small adjustments can collectively resolve what seems like a persistent technical flaw. No single fix worked alone—it was the combination of repositioning, network management, and software updates that made the difference.
Checklist: How to Prevent Bluetooth Speaker Cutouts Near Windows
Use this checklist to quickly troubleshoot and prevent future disruptions:
- ✅ Move speaker at least 3 feet away from the window
- ✅ Ensure your phone/tablet isn’t near the glass
- ✅ Switch Wi-Fi to 5 GHz if using a dual-band router
- ✅ Update speaker firmware regularly
- ✅ Avoid placing speaker on metal surfaces
- ✅ Test with a wired connection to confirm interference
- ✅ Consider a Bluetooth repeater for large or signal-heavy spaces
- ✅ Choose Bluetooth 5.0+ speakers for better performance
Frequently Asked Questions
Can window tint cause Bluetooth interference?
Yes, especially metallic or ceramic-based tints. These contain conductive materials that block or weaken radio signals, including Bluetooth. Non-metallic dyes are less likely to interfere.
Does double-pane glass affect Bluetooth more than single-pane?
Generally, yes. Double- and triple-pane windows often include insulating gases and additional coatings that increase signal attenuation. The more layers and reflective materials, the greater the interference.
Will a Bluetooth speaker work better on a balcony than near a window?
It depends. Outdoors, there’s less signal reflection from walls, but you may face stronger interference from public Wi-Fi or cellular networks. Also, weatherproof speakers tend to have better antennas, improving performance in open areas.
Final Thoughts and Next Steps
Bluetooth speaker cutouts near windows are a common but solvable issue. The key lies in understanding how building materials and wireless ecosystems interact. Modern energy-efficient windows, while beneficial for climate control, inadvertently create dead zones for Bluetooth signals. By adjusting placement, optimizing your wireless environment, and upgrading hardware when necessary, you can enjoy uninterrupted audio—even in the sunniest corner of your home.
Don’t accept poor performance as inevitable. Small changes often yield dramatic improvements. Start with repositioning your speaker and reviewing your Wi-Fi setup. If problems persist, explore extenders or wired alternatives. With the right strategy, your music should flow as freely as the view outside your window.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?