Bluetooth speakers offer unmatched convenience for enjoying music wirelessly, whether at home, in the backyard, or on a hike. But nothing disrupts the experience faster than sudden audio dropouts—especially when you simply step a few feet away from your device. If your speaker consistently cuts out as you move, you're not dealing with faulty hardware in most cases. Instead, you're encountering the limitations of wireless technology interacting with physical space, interference, and design constraints. Understanding the root causes and practical solutions can dramatically improve your listening experience.
The Science Behind Bluetooth Signal Loss
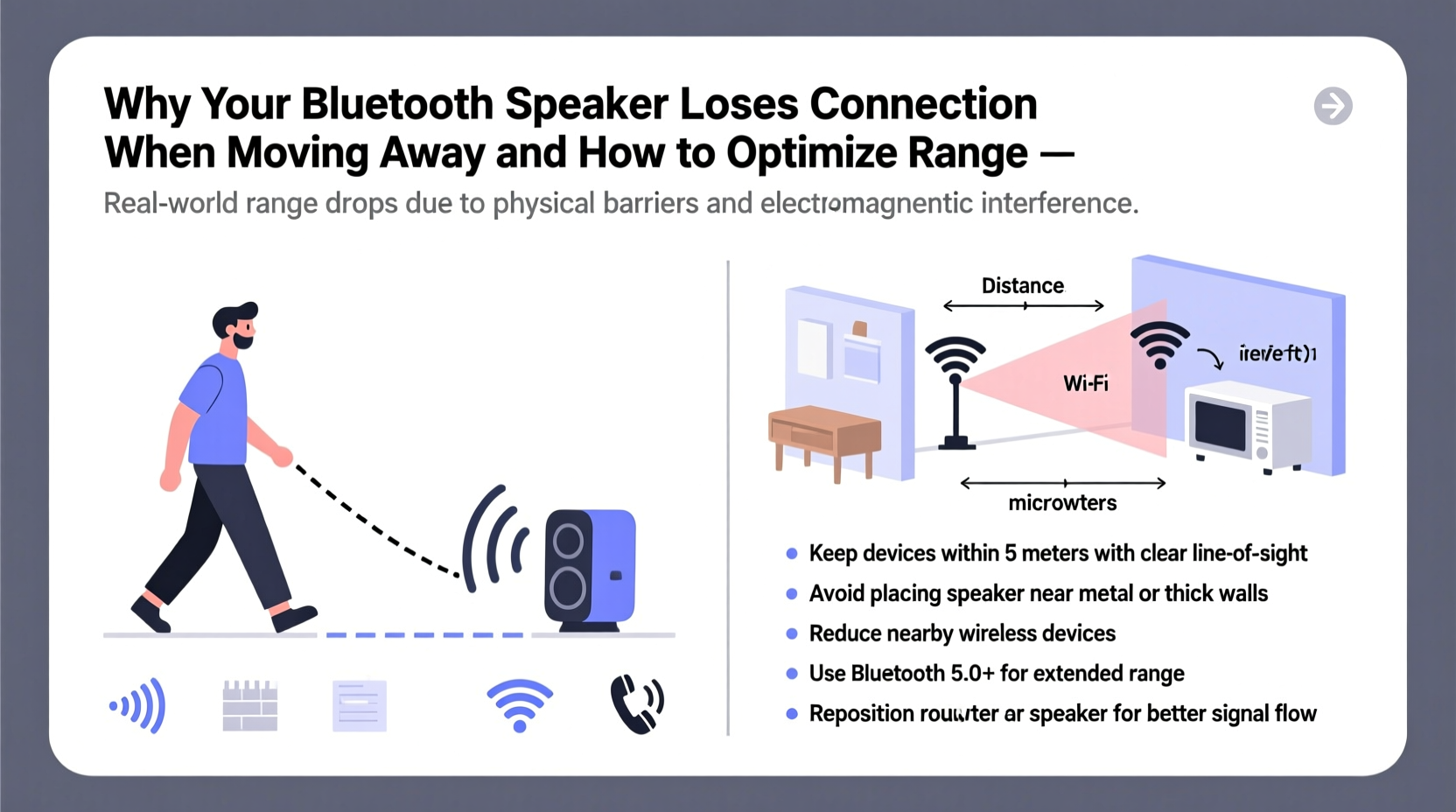
Bluetooth operates using short-range radio waves in the 2.4 GHz frequency band—the same spectrum used by Wi-Fi routers, microwaves, and many smart home devices. This frequency is effective for low-power, close-proximity communication but has inherent limitations in range and penetration through solid objects. Most Bluetooth speakers use Class 2 transmitters, which have a standard range of about 33 feet (10 meters) under ideal conditions. However, real-world environments rarely match lab-perfect scenarios.
When you walk away from your speaker, especially beyond this threshold, the signal strength weakens. Walls, furniture, appliances, and even people absorb or reflect radio waves, further reducing effective range. The farther you move, the more likely the connection becomes unstable, leading to intermittent sound, stuttering, or complete disconnection.
“Bluetooth was designed for personal area networks—not whole-home coverage. Its strength lies in efficiency and low power, not long-distance performance.” — Dr. Alan Zhou, Wireless Communications Researcher, MIT Media Lab
Common Causes of Bluetooth Speaker Dropouts
Signal loss isn’t random. It follows predictable patterns influenced by environment, device quality, and usage habits. Below are the most frequent culprits behind Bluetooth speaker cutouts:
- Physical Obstacles: Walls, floors, metal furniture, and large appliances block or scatter Bluetooth signals. Concrete and brick walls are particularly disruptive.
- Distance Beyond Effective Range: Even within the rated 33-foot range, obstacles reduce usable distance. Moving past corners or into adjacent rooms often exceeds reliable connectivity.
- Electromagnetic Interference: Wi-Fi networks, cordless phones, baby monitors, and microwave ovens operate in the same 2.4 GHz band and can cause signal congestion.
- Low Battery on Either Device: A weakening battery in either the speaker or source device (phone, tablet) reduces transmission power and stability.
- Outdated Bluetooth Version: Older Bluetooth standards (like 3.0 or 4.0) have shorter ranges and slower data transfer compared to newer versions such as 5.0 and 5.3.
- Poor Antenna Design: Some compact or budget speakers sacrifice internal antenna quality to save space or cost, limiting their ability to maintain connections.
How to Improve Bluetooth Speaker Range and Stability
You don’t need expensive gear to fix most Bluetooth issues. With a few strategic adjustments, you can significantly extend usable range and minimize interruptions.
1. Optimize Placement for Line-of-Sight
Position your speaker and source device so they have a clear, unobstructed path between them. Avoid placing either behind cabinets, inside bags, or near large metal objects. Elevating the speaker slightly off the floor can also help, as ground-level clutter absorbs signals.
2. Reduce Interference from Other Devices
Identify nearby electronics that may be causing interference. Turn off unused Wi-Fi extenders, move microwaves away from entertainment areas, or switch your router to the 5 GHz band (if supported) to free up the 2.4 GHz spectrum for Bluetooth.
3. Upgrade to Bluetooth 5.0 or Higher
If your current speaker uses an older Bluetooth version, consider upgrading. Bluetooth 5.0 doubles the theoretical range (up to 800 feet in open spaces), improves data speed, and enhances signal resilience. While real-world indoor performance won't reach those extremes, the improvement over Bluetooth 4.2 is noticeable.
4. Use a Bluetooth Range Extender or Repeater
These small devices receive and rebroadcast the Bluetooth signal, effectively acting as a relay. Place one midway between your audio source and speaker to bridge dead zones. Note: Not all repeaters support high-quality audio streaming, so choose models specifically designed for A2DP (stereo audio) profiles.
5. Switch Audio Sources Strategically
Sometimes the issue isn’t the speaker—it’s the transmitting device. iPhones and some Android phones vary in Bluetooth output strength. Try pairing with a different phone or tablet to test performance. Also, ensure your device’s OS is updated, as firmware improvements often include better Bluetooth management.
6. Minimize Background App Activity
Background apps can interfere with Bluetooth stability by consuming system resources or triggering location-based services that disrupt wireless modules. Close unnecessary apps and disable features like Bluetooth scanning in location settings.
Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnose and Fix Bluetooth Cutouts
- Test in an Open Space: Move both devices into a wide-open area with no walls or electronics nearby. Walk away slowly while playing audio to determine the true maximum range.
- Note Where Dropouts Begin: Mark the distance and direction where sound starts breaking up. Is it consistent? Does turning change the outcome?
- Introduce One Obstacle at a Time: Add a wall, door, or appliance between devices to isolate what’s causing signal loss.
- Check for Interference: Temporarily turn off Wi-Fi, cordless phones, and other 2.4 GHz devices. Retest the connection.
- Update Firmware: Visit the manufacturer’s website or app to check for speaker or phone updates.
- Reset Bluetooth Settings: On your phone, “forget” the speaker, restart both devices, then re-pair them.
- Try a Different Source Device: Rule out hardware issues by testing with another phone or tablet.
- Evaluate Upgrade Options: If problems persist despite optimization, consider a speaker with Bluetooth 5.0+ and stronger antenna design.
Do’s and Don’ts of Bluetooth Speaker Use
| Do | Don’t |
|---|---|
| Keep devices charged during use | Use a low-battery phone as a primary audio source |
| Place speaker in central, elevated position | Hide speaker inside drawers or behind furniture |
| Limit active Bluetooth devices nearby | Run multiple Bluetooth speakers and headphones simultaneously without testing stability |
| Update firmware regularly | Ignore manufacturer software updates |
| Use wired alternatives for critical applications | Rely solely on Bluetooth for outdoor events beyond 30 feet |
Real-World Example: Fixing Backyard Audio Issues
Mark bought a popular portable Bluetooth speaker for his patio gatherings. Indoors, it worked flawlessly. But when guests moved into the backyard—just 25 feet away through a sliding glass door—the audio would cut out every few minutes. Frustrated, he assumed the speaker was defective.
After reading about Bluetooth limitations, he tested the setup systematically. He discovered that the aluminum frame of the glass door was blocking the signal. By moving the speaker six inches forward onto a side table—clear of the frame—and placing his phone on a patio shelf facing outward, the connection stabilized. He also turned off his Wi-Fi extender temporarily during parties, reducing interference. These simple changes eliminated dropouts entirely, transforming his outdoor experience.
Checklist: Maximize Your Bluetooth Speaker Performance
- ✅ Test range in open space to establish baseline performance
- ✅ Ensure both speaker and source device are fully charged
- ✅ Position devices with clear line-of-sight whenever possible
- ✅ Update firmware on both speaker and smartphone
- ✅ Minimize nearby sources of 2.4 GHz interference
- ✅ Reset Bluetooth pairing if connection feels sluggish
- ✅ Consider upgrading to a Bluetooth 5.0+ model for larger spaces
- ✅ Use a wired auxiliary connection as backup for stationary setups
Frequently Asked Questions
Can walls really block Bluetooth signals?
Yes. Drywall causes minor attenuation, but materials like concrete, brick, metal, and insulated glass significantly weaken Bluetooth signals. Each wall can reduce effective range by 30–70%, depending on composition.
Does Bluetooth range improve with volume level?
No. Volume level does not affect transmission range. However, higher audio bitrates (used in high-quality codecs like aptX) require more stable connections, which may make dropouts more noticeable at louder volumes.
Is there a way to extend Bluetooth range beyond 100 feet reliably?
For consistent performance beyond 100 feet, Bluetooth alone is not reliable. Consider using a Wi-Fi-based audio system (like Sonos), a dedicated RF transmitter, or a directional Bluetooth repeater designed for long-range use.
Final Thoughts: Enjoy Seamless Wireless Audio
Bluetooth speaker cutouts aren’t inevitable—they’re usually the result of environmental factors and suboptimal setup. By understanding how wireless signals behave and applying targeted fixes, you can reclaim stable audio throughout your home or outdoor space. Small changes in placement, device management, and awareness of interference can yield dramatic improvements. And when it’s time to upgrade, prioritize models with Bluetooth 5.0 or later and strong user reviews regarding range performance.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?