Bluetooth speakers offer unmatched convenience, letting you enjoy music wirelessly from smartphones, tablets, or laptops. But nothing disrupts the experience like sudden dropouts—mid-song silence, erratic volume changes, or complete disconnection. While frustrating, these issues are rarely random. They stem from specific technical, environmental, or usage-related causes. Understanding why your Bluetooth speaker disconnects—and how to fix it—is essential for consistent, high-quality audio. This guide breaks down the root causes, provides actionable solutions, and shares real-world insights to help you stabilize your Bluetooth pairing for good.
Common Causes of Bluetooth Speaker Disconnections
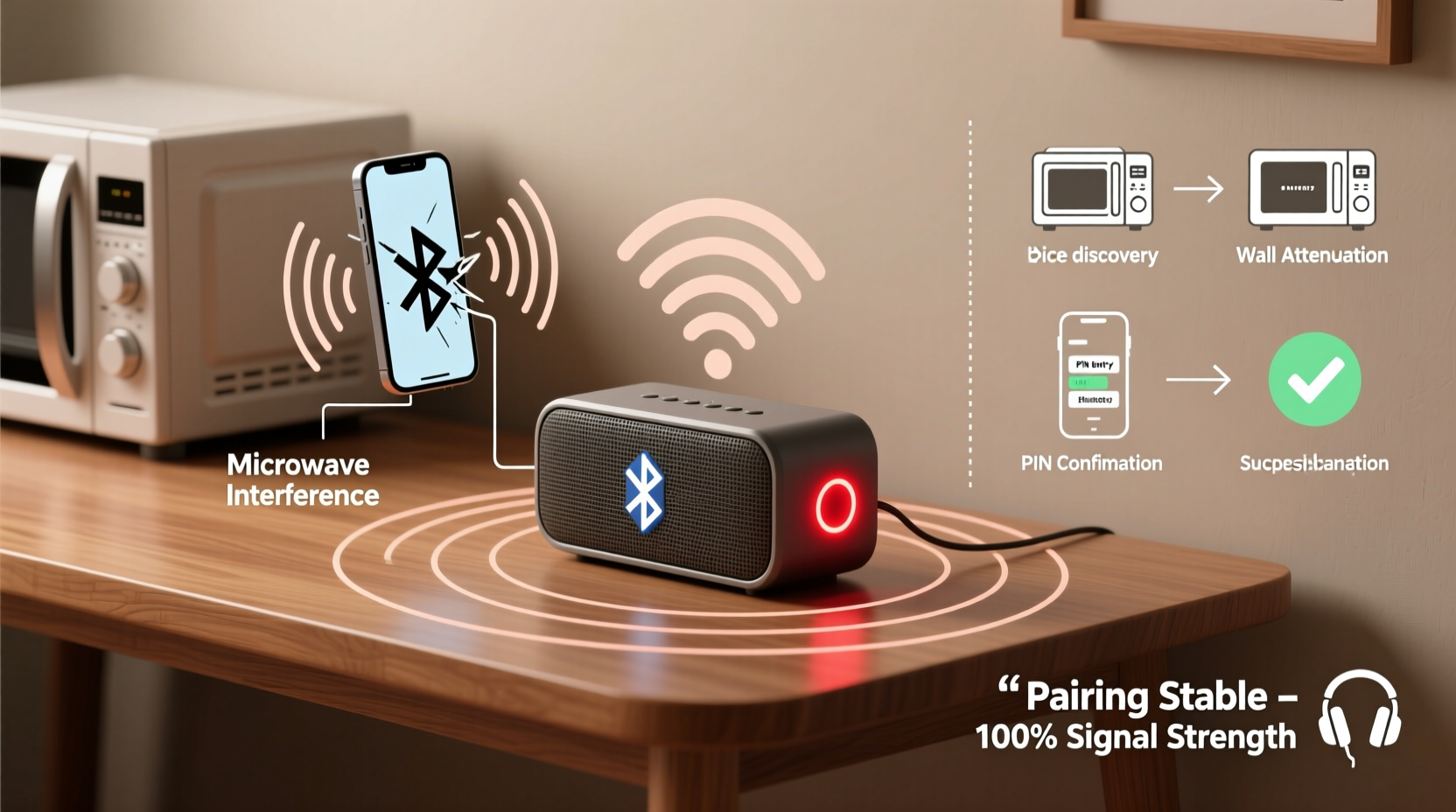
Before attempting fixes, it's crucial to identify what’s triggering the instability. Bluetooth relies on a 2.4 GHz radio frequency band, which is shared with Wi-Fi routers, microwaves, cordless phones, and other wireless devices. Interference in this crowded spectrum is one of the leading causes of signal disruption.
- Signal interference: Nearby electronics emit electromagnetic noise that can degrade or block Bluetooth signals.
- Distance and obstacles: Walls, furniture, and even human bodies absorb or reflect Bluetooth waves, weakening the connection beyond 30 feet (10 meters).
- Low battery: A weak power source affects both the speaker and the connected device’s ability to maintain stable transmission.
- Outdated firmware: Older software may lack bug fixes or compatibility updates needed for modern devices.
- Pairing conflicts: Multiple paired devices trying to connect simultaneously cause confusion in the Bluetooth stack.
- Device memory overload: Some speakers store up to eight previous pairings; exceeding this limit leads to unstable switching.
Step-by-Step Guide to Stabilize Bluetooth Pairing
Fixing disconnection problems requires a methodical approach. Follow this sequence to eliminate common issues and lock in a reliable connection.
- Power cycle both devices: Turn off the speaker and the connected device (phone, tablet, etc.). Wait 30 seconds, then power them back on. This clears temporary glitches in the Bluetooth module.
- Forget and re-pair the device: Go to your phone’s Bluetooth settings, select the speaker, and choose “Forget.” Then turn the speaker into pairing mode and reconnect it as if setting it up for the first time.
- Reduce wireless congestion: Move away from Wi-Fi routers, microwaves, or USB 3.0 ports, which emit strong 2.4 GHz interference. If using Wi-Fi, consider switching your router to the 5 GHz band to free up space.
- Update firmware: Check the manufacturer’s website or app (e.g., Bose Connect, JBL Portable, Sony | Music Center) for available firmware updates. These often include stability improvements.
- Clear old pairings: Access the speaker’s pairing menu (via buttons or app) and delete unused devices to prevent auto-switching conflicts.
- Test with another source device: Connect the speaker to a different phone or tablet. If the issue persists, the problem lies with the speaker. If it works smoothly, the original device may need troubleshooting.
- Check battery levels: Charge both the speaker and the source device above 50% before testing again. Low power can throttle wireless performance.
Environmental Factors That Impact Signal Stability
Even with perfect hardware, your surroundings play a major role in Bluetooth reliability. Materials like concrete, metal, and water (including the human body) significantly weaken radio signals. For example, placing a speaker behind a bookshelf or across the room through a kitchen wall can reduce effective range by more than half.
Additionally, large gatherings or public spaces introduce dozens of competing Bluetooth signals—from headphones to smartwatches—creating a phenomenon known as \"Bluetooth saturation.\" In such environments, connections become unstable due to channel contention.
| Environment | Impact on Bluetooth | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Open outdoor area | Minimal interference; optimal range (~30 ft) | Ensure both devices have full battery and updated software |
| Indoor with drywall walls | Moderate signal loss (~15–20 ft effective range) | Avoid placing speaker behind furniture or appliances |
| Kitchen or bathroom | High interference (microwave, metal fixtures, humidity) | Relocate speaker during use; avoid operation near active microwave |
| Crowded public space | Poor stability due to multiple Bluetooth signals | Use wired alternatives or noise-canceling modes if available |
“Bluetooth isn’t just about proximity—it’s about path clarity. Even a few feet of distance through a metal door can be worse than 20 feet in open air.” — Dr. Alan Reyes, Wireless Communication Engineer
Tips to Permanently Improve Connection Reliability
Once you’ve resolved immediate disconnection issues, implement long-term habits to prevent recurrence. These practices go beyond basic troubleshooting and focus on sustainable performance.
- Limit multi-device switching: Avoid enabling “multi-point pairing” unless necessary. While convenient, connecting to two devices at once splits resources and increases latency and dropout risk.
- Use Bluetooth 5.0+ devices: Newer Bluetooth standards offer longer range, higher speed, and better interference resistance. Upgrade both your speaker and source device if they’re below version 5.0.
- Disable unused wireless features: Turn off NFC, Wi-Fi, or location services on your phone when not needed—they can interfere with Bluetooth stability.
- Position strategically: Place the speaker on an elevated surface, centered in the room, and facing the listener. Avoid corners or enclosed shelves.
- Minimize cable clutter: USB hubs, extension cords, and power strips generate electromagnetic fields that disrupt 2.4 GHz signals. Keep them at least 1–2 feet away from the speaker.
Mini Case Study: Fixing Dropouts at a Home Office Setup
Mark, a remote worker in Chicago, experienced frequent Bluetooth disconnections between his laptop and a popular portable speaker during video calls and background music playback. The speaker was placed across the room, behind a metal filing cabinet, and near a Wi-Fi router.
He followed the stabilization steps: moved the speaker to his desk, updated its firmware via the companion app, forgot and re-paired the laptop, and switched his router to 5 GHz Wi-Fi. He also disabled automatic switching to his smartphone, which had previously interrupted the laptop connection.
The result? No dropouts over the next three weeks. Audio remained crisp during meetings, and music played uninterrupted throughout work hours. Mark noted that simply relocating the speaker made the biggest difference—proving that placement often outweighs technical upgrades.
Bluetooth Best Practices Checklist
Use this checklist monthly—or whenever you notice instability—to keep your Bluetooth speaker running smoothly.
- ✅ Re-pair the speaker with your main device every 4–6 weeks to refresh the connection.
- ✅ Update firmware on both the speaker and connected devices quarterly.
- ✅ Delete old or unused pairings from the speaker’s memory.
- ✅ Charge the speaker fully at least once per month, even if not in use.
- ✅ Test connectivity weekly under normal usage conditions.
- ✅ Keep the speaker clean—dust buildup around ports and vents can affect internal electronics.
- ✅ Avoid exposing the speaker to extreme temperatures or moisture, which damage internal antennas.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does my Bluetooth speaker disconnect when I move around the house?
Bluetooth has a limited effective range, typically 30 feet in ideal conditions. Moving through walls, especially those containing metal, concrete, or pipes, weakens the signal. Additionally, transitioning between rooms may place you near interfering devices like microwaves or cordless phones. To maintain connection, stay within 15–20 feet of the speaker with minimal obstructions.
Can a phone case cause Bluetooth disconnection?
Most standard cases do not interfere. However, heavy-duty metal cases or magnetic mounts can partially block the phone’s internal antenna, reducing signal strength. If you suspect interference, test the connection without the case or switch to a non-metallic alternative.
Does turning off Bluetooth on other devices help?
Yes. While passive Bluetooth devices don’t actively transmit, having many enabled devices nearby increases background noise in the 2.4 GHz band. Turning off Bluetooth on unused phones, earbuds, or watches reduces congestion and improves overall network stability.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Wireless Experience
Bluetooth speaker disconnections are not inevitable—they’re solvable with the right knowledge and habits. From managing interference to optimizing placement and maintaining firmware, every factor contributes to a seamless listening experience. Technology should enhance your life, not interrupt it. By applying these proven strategies, you reclaim control over your audio environment and enjoy uninterrupted sound whether you're working, relaxing, or entertaining.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?