Waking up with a puffy, bloated face is a common experience that can be both frustrating and confusing. You go to bed looking like yourself, only to find your cheeks fuller, eyes sunken yet swollen, and jawline blurred by fluid retention. While occasional morning facial swelling is usually harmless, frequent puffiness may point to lifestyle habits, sleep quality, or underlying health factors. The good news: most causes are manageable with simple changes. Understanding the root reasons behind this condition is the first step toward reducing it—naturally, effectively, and consistently.
The Science Behind Morning Facial Swelling
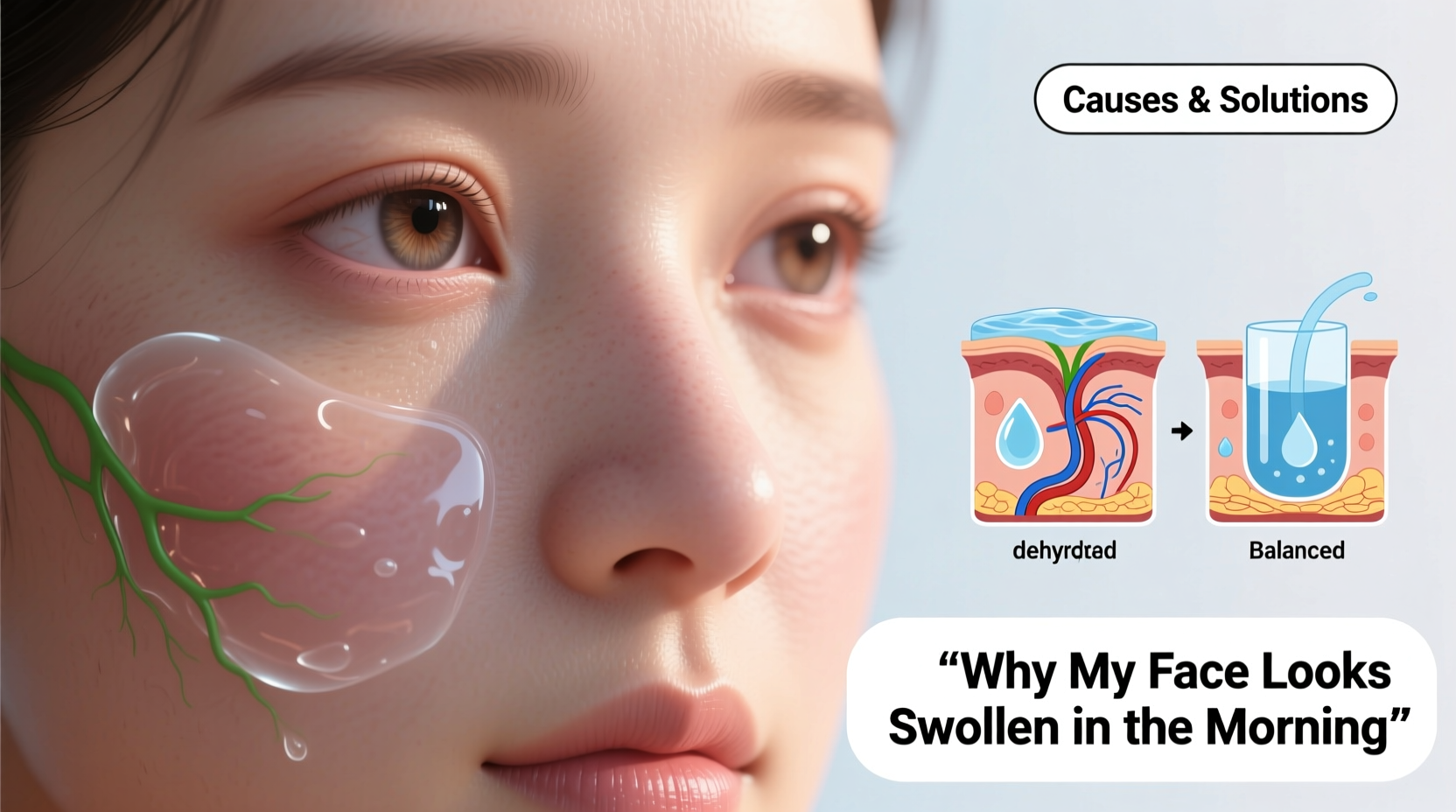
Facial puffiness upon waking is primarily due to fluid accumulation, also known as edema. When you lie flat during sleep, gravity redistributes bodily fluids more evenly than when upright. This allows fluid to pool in the soft tissues of the face—particularly around the eyes, cheeks, and jawline. As circulation slows overnight, lymphatic drainage becomes less efficient, contributing to temporary swelling.
Additionally, hormonal fluctuations play a role. Cortisol, the stress hormone, typically peaks in the early morning hours, which can influence water retention. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) levels also rise at night, signaling the kidneys to conserve water rather than excrete it—another reason you might wake up feeling \"bloated,\" including in the face.
“Morning facial puffiness is often a sign of suboptimal fluid regulation. It’s not just about salt—it’s about sleep posture, hydration rhythm, and circulatory health.” — Dr. Lena Torres, Board-Certified Dermatologist & Skin Physiologist
Common Causes of Morning Facial Swelling
While some degree of mild puffiness is normal, persistent or severe swelling should be investigated. Below are the most frequent contributors:
- Sleep Position: Sleeping flat on your back encourages fluid to settle in the face. Elevating your head slightly can minimize this effect.
- Dietary Sodium Intake: Consuming high-sodium meals late in the day—such as processed snacks, canned soups, or takeout—can lead to water retention.
- Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol dehydrates the body while triggering inflammation and dilation of blood vessels, increasing facial swelling.
- Allergies: Undiagnosed allergies to dust mites, laundry detergents, or skincare products can cause low-grade inflammation, especially noticeable after prolonged skin contact during sleep.
- Dehydration: Ironically, not drinking enough water prompts the body to hold onto existing fluids, worsening puffiness.
- Poor Sleep Quality: Fragmented sleep disrupts hormonal balance and impairs lymphatic clearance, both of which contribute to facial edema.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Thyroid disorders (like hypothyroidism), kidney dysfunction, or chronic sinus issues may manifest as recurrent facial swelling.
Natural and Effective Ways to Reduce Morning Facial Puffiness
Reducing facial swelling doesn’t require expensive creams or invasive treatments. Most solutions involve adjusting daily routines and being mindful of physiological signals. Here are proven strategies backed by dermatologists and wellness experts.
1. Optimize Your Sleep Environment
Your sleeping position significantly impacts fluid distribution. Lying completely flat allows gravity to pool fluid in facial tissues. To counteract this:
- Use an extra pillow or an adjustable bed to elevate your head slightly (about 30 degrees).
- Avoid sleeping on your stomach, which presses the face into the pillow and restricts lymphatic flow.
- Choose hypoallergenic bedding if allergies are suspected—dust mites thrive in standard pillows and comforters.
2. Adjust Evening Hydration Habits
Hydration timing matters. Drinking large amounts of water right before bed floods the system when circulation is slow, increasing overnight retention. Instead:
- Front-load your water intake earlier in the day.
- Limit liquids 60–90 minutes before bedtime to reduce nighttime fluid buildup.
- Include potassium-rich foods (bananas, spinach, avocados) in your dinner—they help balance sodium levels and promote natural diuresis.
3. Revise Your Nighttime Diet
What you eat—and when—directly affects morning appearance. Avoid:
- Processed foods high in sodium (chips, frozen meals, cured meats).
- Alcohol, especially within three hours of bedtime.
- Heavy, spicy, or inflammatory meals late at night.
Instead, opt for light dinners rich in antioxidants and lean proteins—think grilled salmon with steamed broccoli or a quinoa salad with leafy greens.
4. Incorporate Lymphatic Drainage Techniques
The lymphatic system removes waste and excess fluid from tissues but relies on muscle movement and manual stimulation. Since it slows during rest, jumpstarting it in the morning helps.
- Begin with clean hands and a slightly damp face.
- Using gentle pressure, massage from the center of the face outward along the jawline, under the eyes, and up the forehead.
- Spend 60 seconds focusing on each area, using upward strokes to encourage fluid movement toward lymph nodes near the ears and neck.
- Follow with a cool rinse or chilled jade roller for added vasoconstriction.
5. Use Cold Therapy Upon Waking
Cold temperatures constrict blood vessels and reduce inflammation. Applying cold therapy within 10 minutes of waking can visibly decrease puffiness.
Step-by-Step Morning Routine to Reduce Facial Swelling
Follow this five-minute routine every morning to combat puffiness effectively:
- Wake Up & Drink Water (1 min): Start with a glass of room-temperature water to kickstart metabolism and rehydrate after hours without fluids.
- Facial Massage (2 min): Perform a light lymphatic drainage massage using fingertips or a chilled tool.
- Cool Compress (1 min): Apply a cold washcloth or refrigerated eye mask to constrict capillaries and soothe tissues.
- Light Exercise (3–5 min): Do quick movements like jumping jacks or brisk walking to increase circulation and stimulate lymph flow.
- Skincare Application (1 min): Use a lightweight eye cream containing caffeine or peptides to further tighten and brighten.
This sequence leverages physiology—activating circulation, supporting detoxification, and reducing inflammation—to deliver visible results in days.
Do’s and Don’ts: Managing Facial Puffiness
| Do | Don’t |
|---|---|
| Drink most of your water between 7 AM and 6 PM | Chug water right before bed |
| Eat potassium-rich foods daily | Consume salty snacks at night |
| Elevate your head with an extra pillow | Sleep flat on your back without support |
| Practice facial massage regularly | Rub your eyes aggressively when puffy |
| Limit alcohol and processed foods | Drink wine or cocktails late in the evening |
Real-Life Example: How Sarah Reduced Chronic Morning Puffiness
Sarah, a 34-year-old project manager, struggled with persistent facial swelling for over a year. She initially blamed her genetics, assuming she simply “woke up puffy.” After trying countless serums and face rollers with little improvement, she consulted a dermatologist who asked detailed questions about her habits.
It turned out Sarah routinely ate frozen meals high in sodium, drank wine three nights a week, and slept on two flat pillows. She also admitted to staying up late scrolling, often falling asleep with minimal water intake after dinner.
With guidance, she made targeted changes: switching to homemade dinners, stopping alcohol three days before important meetings, elevating her head with a wedge pillow, and drinking 70% of her daily water before 7 PM. Within two weeks, her morning puffiness decreased dramatically. By week four, coworkers noticed her “more awake” appearance—even before coffee.
Her transformation wasn’t due to a miracle product, but consistent, science-aligned adjustments.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is morning facial swelling a sign of a serious health problem?
Occasional puffiness is normal. However, if swelling is persistent, painful, asymmetric, or accompanied by fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, or voice changes, consult a healthcare provider. These could indicate thyroid disease, kidney issues, or autoimmune conditions.
Can drinking more water really reduce facial puffiness?
Yes—chronic dehydration tricks the body into hoarding water. Consistent hydration throughout the day supports kidney function and reduces compensatory fluid retention, including in the face.
How long does it take to see results from lifestyle changes?
Many people notice improvement within 3–5 days of reducing sodium, improving sleep posture, and optimizing hydration. Lasting change typically stabilizes within two to four weeks of consistent practice.
Final Thoughts: Take Control of Your Morning Appearance
Facial swelling upon waking isn't inevitable. It's a signal—one that reflects your hydration patterns, diet, sleep quality, and overall internal balance. Rather than masking it with filters or makeup, address the root causes with intention and consistency. Small shifts in behavior compound into significant improvements in how you look and feel each morning.
You don’t need extreme diets or costly treatments. Focus on sustainable habits: hydrate wisely, reduce dietary sodium, elevate your head, and support your body’s natural detox systems. Over time, you’ll likely find not only reduced puffiness but improved energy, clearer skin, and better overall well-being.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?