If your smartphone hotspot starts strong but slows to a crawl after just a few minutes of use, you're not imagining things—and you're certainly not alone. Many users experience this frustrating drop in speed when tethering their laptops, tablets, or other devices to their phone's data connection. The culprit? More often than not, it's carrier-imposed bandwidth throttling. This isn't a glitch in your device or poor signal strength; it’s a deliberate policy enforced by mobile providers to manage network congestion and prioritize certain types of usage.
Understanding why carriers throttle hotspot data—and how they do it—can help you make smarter decisions about your data plan, device usage, and even provider selection. This article breaks down the mechanics of hotspot throttling, explains how carriers justify it, and provides actionable steps to reduce its impact on your daily connectivity needs.
What Is Carrier Throttling?
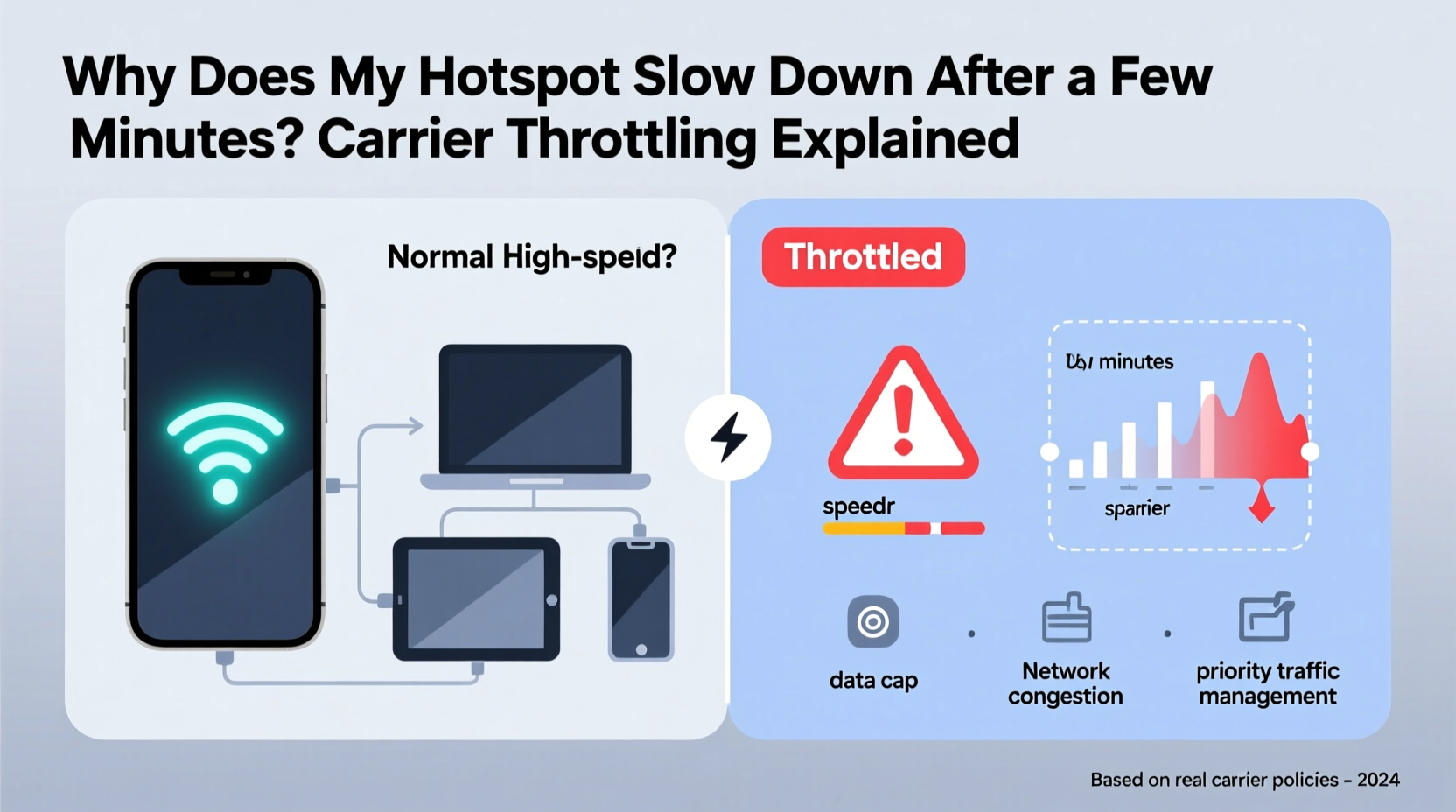
Carrier throttling refers to the intentional slowing down of internet speeds by a mobile service provider. This practice is typically applied after a user reaches a certain threshold of high-speed data consumption. While some throttling affects all data equally, hotspot (or tethering) throttling is often more aggressive and occurs earlier than regular cellular data slowdowns.
Carriers argue that throttling helps maintain network stability during peak hours and ensures fair access for all users. However, from a consumer perspective, it can feel deceptive—especially when marketed \"unlimited\" plans come with fine-print limitations that kick in precisely when you need consistent performance most.
Throttling doesn’t disconnect you from the internet. Instead, your download and upload speeds may drop dramatically—from 20+ Mbps to as low as 1–3 Mbps—making video calls, streaming, and large downloads nearly impossible.
Why Hotspot Data Gets Targeted First
Mobile carriers treat hotspot usage differently from standard phone browsing for several technical and business reasons:
- Higher Bandwidth Demand: When you use your phone as a hotspot, multiple devices may connect simultaneously, consuming far more data than typical app usage.
- Network Congestion Risk: A single hotspot user can generate traffic comparable to several regular users, increasing strain on local cell towers.
- Different Usage Patterns: Carriers assume hotspot users are doing heavier tasks like streaming HD video, downloading files, or working remotely—all of which require sustained throughput.
- Plan Tier Differentiation: By limiting hotspot speeds, carriers encourage customers to upgrade to more expensive plans that offer higher or unlimited tethering allowances.
In essence, hotspot data is seen as “premium” usage. Even if your main data plan is labeled “unlimited,” your tethering privileges might be capped at 10GB, 30GB, or even lower before throttling begins.
“Carriers don’t throttle because they can’t handle the load—they do it because it drives revenue through tiered pricing.” — David Lin, Senior Analyst at Mobile Infrastructure Group
How Carriers Implement Throttling: Methods and Triggers
Each major carrier uses slightly different rules to determine when and how much to throttle your hotspot connection. Here’s a breakdown of common practices across top U.S. providers:
| Carrier | High-Speed Hotspot Allowance | Post-Throttle Speed | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verizon | 15–75 GB (varies by plan) | ~600 Kbps | Limited speed makes browsing difficult; video calling unusable. |
| AT&T | 15–50 GB (depending on plan) | 1.5–3 Mbps | Lower-tier plans throttle faster; prepaid plans often have no hotspot. |
| T-Mobile | 50 GB (Magenta), Unlimited (Magenta MAX) | 3G-level speeds (~1 Mbps) | Magenta MAX offers full-speed tethering; others deprioritized after cap. |
| Visible (Verizon MVNO) | Unlimited but deprioritized | Varies widely | No hard cap, but speeds drop during congestion after heavy use. |
The key trigger for throttling is usually cumulative data usage over a billing cycle. Once you exceed your plan’s allocated high-speed hotspot allowance, throttling activates immediately—even if your total data usage is still within limits.
Some carriers also use “deprioritization” rather than strict speed caps. This means your hotspot remains technically fast, but during times of network congestion, your connection is pushed to the back of the queue behind higher-tier users.
Real-World Example: Remote Worker Struggles with Midday Slowdowns
Consider Sarah, a freelance graphic designer who works remotely while traveling. She relies on her smartphone hotspot to attend Zoom meetings, upload design files, and collaborate via cloud tools. Her carrier advertises an “unlimited” plan with 30GB of high-speed hotspot data.
For the first two weeks of her billing cycle, everything runs smoothly. But starting around day 18, she notices her video calls freezing, file uploads timing out, and websites loading slowly—even though her phone shows full signal bars. After checking her data usage, she realizes she’s used 32GB of hotspot data. Despite having plenty of general data left, her tethering has been throttled to 1.5 Mbps.
This real-life scenario illustrates how easily users can hit invisible thresholds. Without clear alerts or proactive notifications, many only discover throttling after productivity suffers.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Diagnose and Reduce Hotspot Throttling
You can’t always prevent throttling, but you can take control of your usage patterns and minimize its impact. Follow these steps:
- Check Your Plan Details: Log into your carrier account or review your contract to find your exact hotspot allowance and throttling policy. Don’t rely on marketing slogans like “unlimited.”
- Monitor Data Usage Weekly: Use built-in tools (iOS Settings > Cellular > Current Period or Android Settings > Network & Internet > Data Usage) to track hotspot consumption separately from phone data.
- Set Up Alerts: Enable data warnings at 50%, 80%, and 100% of your hotspot limit to avoid surprises.
- Test Speeds Before and After Slowdown: Run a speed test (using apps like Ookla Speedtest) when your hotspot feels fast and again when it slows. Compare results to confirm throttling.
- Switch to Wi-Fi Whenever Possible: At cafes, hotels, or coworking spaces, disable hotspot mode and connect directly to available networks.
- Use a Secondary SIM or eSIM: Consider a second line with a different carrier or a dedicated mobile broadband plan for heavy tethering days.
- Upgrade Your Plan Temporarily: Some carriers allow short-term upgrades to unlock additional hotspot data—useful for travel or urgent projects.
Workarounds and Alternatives to Carrier Throttling
While you can’t completely eliminate throttling under most consumer plans, there are strategies to work around it:
- Use a VPN (With Caveats): Some users report temporary relief using a mobile-friendly VPN, which encrypts traffic and may obscure usage patterns. However, modern carrier systems detect volume regardless of encryption, so this is unreliable and not a long-term fix.
- Switch Carriers Based on Tethering Needs: If you regularly exceed 15–30GB of hotspot use, consider switching to a provider like T-Mobile Magenta MAX or AT&T Unlimited Premium, which offer higher or truly unlimited tethering.
- Invest in a Dedicated Mobile Hotspot Device: Devices like the Netgear Nighthawk or Alcatel LinkZone often come with better data terms or business-tier plans that include higher prioritization.
- Leverage Wi-Fi Calling and Offline Modes: Configure your laptop apps (Google Docs, Outlook, etc.) to work offline and sync later. Use Wi-Fi calling on your phone to preserve hotspot bandwidth.
One emerging option is fixed wireless home internet (e.g., T-Mobile Home Internet), which operates on the same network but doesn’t count against mobile data. For remote workers in supported areas, this can replace the need for constant hotspot reliance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does 5G affect hotspot throttling?
Not significantly. While 5G offers faster peak speeds, throttling policies are based on data volume and plan tier, not network generation. You’ll still be throttled once you exceed your hotspot allowance, even on ultra-fast mmWave 5G.
Can I appeal or reverse throttling once it starts?
Generally, no. Throttling resets automatically at the start of your next billing cycle. In rare cases, contacting customer service may result in a one-time data boost, especially if you’re a long-term customer, but this isn’t guaranteed.
Is hotspot throttling legal?
Yes. As long as carriers clearly disclose their throttling policies in the terms of service, the FCC considers it a permissible network management practice. However, advocacy groups continue to push for clearer labeling of “unlimited” claims.
Final Thoughts: Taking Control of Your Connection
Hotspot throttling isn’t going away anytime soon. It’s embedded in the economics of mobile data, where carriers balance infrastructure costs with competitive pricing. But awareness is power. Knowing when, why, and how your connection will slow down allows you to plan accordingly—whether that means upgrading your plan, switching providers, or adjusting your workflow to stay within safe usage zones.
The best defense against throttling is proactive management. Track your data, understand your plan’s true limitations, and don’t hesitate to explore alternatives when your needs outgrow what mainstream unlimited plans actually deliver.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?