It’s a common kitchen scare: you press start on your microwave, step away for a moment, and return to see bright flashes inside—sparks dancing around your food like tiny lightning bolts. While it might seem dramatic, microwave sparking (also known as arcing) is more common than many realize. In most cases, it’s not an appliance malfunction but a reaction between microwave energy and specific materials or foods. Understanding the science behind this phenomenon and knowing what to avoid can prevent damage to your microwave and reduce fire risks.
Microwaves work by emitting electromagnetic waves that excite water molecules in food, generating heat through friction. However, these waves can also interact with conductive materials—like metal or dense mineral deposits—causing electrical discharges. When these discharges become visible as sparks, it's a sign something in or on your food is reflecting or concentrating the microwave energy unpredictably.
What Causes Microwave Sparking?
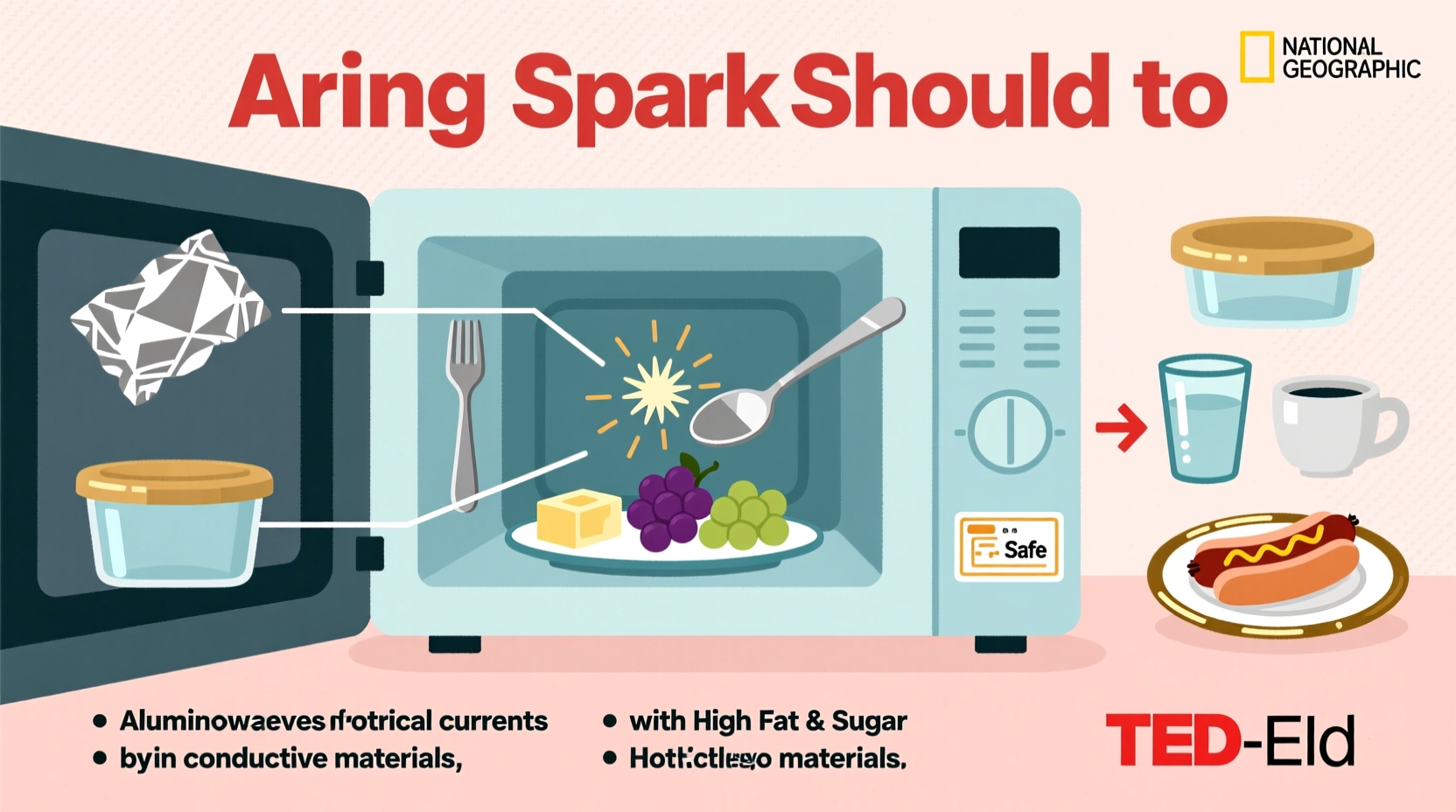
Sparking occurs when microwave energy is concentrated in a small area or encounters a material that conducts electricity. The magnetron—the component that generates microwaves—emits radiation at a frequency designed to be absorbed by water, fats, and sugars. But when this energy hits something metallic or highly conductive, it induces electric currents. If the current jumps across a gap—such as between two pieces of foil or within a damaged interior coating—it creates a spark.
The interior walls of microwaves are designed to reflect microwaves safely, but only because they’re made of smooth, grounded metal. Introducing foreign conductive objects disrupts this balance. Even foods with high mineral content or unusual textures can act as unintentional conductors under the right conditions.
Foods That Commonly Cause Sparking
Not all sparking is due to metal utensils or aluminum foil. Some foods naturally contain elements that react poorly in microwaves. These include:
- Grapes and cherry tomatoes: Their size and high ion content create plasma when cut in half or placed close together. The skin traps microwaves between the halves, forming a conductive bridge that ionizes the air, producing sparks and sometimes flames.
- Carrots and hot dogs: Often contaminated with microscopic mineral deposits (like iron or magnesium) from soil. These minerals can concentrate microwave energy and cause localized sparking, especially if the food has been stored for long periods.
- Processed meats with additives: Cured meats such as bacon or deli slices may contain metal-based preservatives (e.g., sodium nitrite with trace iron). Overheating can lead to small arcs along the edges.
- Foods with thick skins or membranes: Egg yolks, potatoes, and sausages can build up internal steam pressure. If not pierced, they may burst violently—but more subtly, the tension in the membrane can create micro-arcing points when heated unevenly.
“Grape plasma formation is one of the most well-documented microwave phenomena. It’s not magic—it’s physics meeting fruit.” — Dr. Aaron Persad, Applied Physicist, McGill University
Non-Food Items That Trigger Arcing
Beyond food, everyday kitchen items can turn your microwave into a hazard zone if used incorrectly:
| Item | Why It Sparks | Safer Alternative |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum foil | Thin metal reflects microwaves; sharp edges concentrate charge | Use microwave-safe lids or parchment paper |
| Gold-trimmed dishes | Metallic paint contains conductive particles | Ceramic or glass without metallic accents |
| Takeout containers with foil lining | Hidden metal layers trap and reflect energy | Transfer food to microwave-safe bowl |
| Twist ties or staples | Metal wire creates arc points | Remove packaging completely |
| Damaged microwave interior | Chipped enamel exposes underlying metal | Replace or repair unit immediately |
Even seemingly harmless items like ceramic mugs with decorative glaze can pose risks. Some older or imported dishware uses metal-based pigments that glow or spark under microwave exposure. If you notice flickering light or popping sounds, stop the microwave immediately.
Real Example: The Case of the Exploding Grapes
A homeowner in Portland reported seeing flames shoot from her microwave after reheating halved grapes for her child’s snack. She had read online that cutting grapes makes them easier to eat, but didn’t know the physics behind the danger. After the incident, she contacted a local university extension office, where researchers explained that the grape’s diameter is nearly ideal for focusing microwave energy. When two halves remain connected by a thin strip of skin, the point of contact becomes a hotspot, ionizing sodium and potassium ions and creating plasma.
This case prompted widespread awareness campaigns, including videos from science educators demonstrating how even blueberries and olives can behave similarly under certain conditions. The takeaway? Size, composition, and proximity matter just as much as material type.
How to Prevent Microwave Sparking: A Step-by-Step Guide
Preventing sparking isn’t complicated, but it requires consistent attention to detail. Follow this sequence every time you use your microwave:
- Inspect the cavity: Look for signs of damage—chipped paint, rust, or burn marks—especially on the ceiling and walls. Any exposed metal should prompt immediate discontinuation of use until repaired.
- Check the container: Only use labeled “microwave-safe” cookware. Avoid anything with metallic trim, recycled paper (which may contain metal fragments), or foam trays with foil seals.
- Prepare food properly: Pierce skins of potatoes, egg yolks, sausages, and squash. Cut grapes, cherries, and cherry tomatoes into quarters rather than halves to eliminate plasma risk.
- Remove hidden metals: Check frozen meal trays for foil linings. Discard twist ties, staples, or takeout boxes with metal handles.
- Start with shorter intervals: Heat food in 30-second bursts, stirring in between. This reduces overheating risks and allows you to catch early signs of arcing.
- Monitor during operation: Stay nearby during microwaving, especially with unfamiliar foods or containers. If sparking occurs, stop the microwave immediately—do not open the door until the activity stops.
What to Do If Your Microwave Sparks
If you see sparks while your microwave is running, follow these steps without delay:
- Stop the microwave immediately. Do not wait for the cycle to finish.
- Do not open the door right away. Wait 10–15 seconds to ensure no residual arcing continues.
- Unplug the unit before inspecting further to eliminate electrical hazards.
- Remove the item carefully using oven mitts—some containers may be superheated.
- Inspect both the food and the microwave interior. Look for scorch marks, melted spots, or lingering metallic debris.
- Clean thoroughly with mild soap and water. Avoid abrasive pads that could scratch the enamel coating.
If sparking persists with different foods or clean containers, the issue may lie within the microwave itself—such as a faulty waveguide cover (a mica sheet that protects the magnetron outlet). Replacing this component often resolves recurring arcing issues and costs less than $20.
Essential Microwave Safety Checklist
Use this checklist before every microwave session to minimize risks:
- ✅ Container is labeled microwave-safe
- ✅ No metal parts, foil, or metallic paint present
- ✅ Food with skin or membrane has been pierced
- ✅ Grapes, tomatoes, berries are cut into small pieces
- ✅ Takeout packaging has been removed entirely
- ✅ Interior walls and ceiling show no damage
- ✅ Waveguide cover (behind stirrer fan) is clean and intact
- ✅ You will monitor the microwave during use
Frequently Asked Questions
Can sparking damage my microwave permanently?
Yes. Repeated arcing can burn holes in the waveguide cover, degrade the magnetron, or pit the interior lining. Over time, this reduces efficiency and increases fire risk. One or two minor incidents may not ruin the unit, but ongoing sparking should never be ignored.
Is it safe to continue using a microwave after it sparks?
Only if the cause was clearly identified and removed—such as a piece of foil or a grape—and the interior shows no damage. If sparking happens again with safe materials, stop using the appliance and consult a technician or consider replacement.
Are some microwaves more prone to sparking than others?
All microwaves operate on the same principles, but older models or those with worn interiors are more vulnerable. Compact or low-wattage units may also heat unevenly, increasing the chance of hotspots and accidental arcing. Regular maintenance significantly reduces risk regardless of brand.
Final Thoughts: Safe Heating Starts with Awareness
Microwave sparking isn’t just alarming—it’s a warning sign. Whether caused by a forgotten spoon, a slice of processed meat, or a misunderstood grape, each incident reveals a gap in kitchen safety knowledge. The good news is that prevention is simple, cost-effective, and largely habitual.
By understanding how microwaves interact with food and materials, you gain control over one of the most used—and often misused—appliances in the home. Replace guesswork with informed choices: inspect containers, prepare food mindfully, and maintain your unit regularly. These small actions protect not only your microwave but also your household.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?