It’s a common frustration: you connect your phone to Wi-Fi expecting better performance and longer battery life, only to notice the opposite. Instead of lasting longer, your battery seems to deplete faster than when using cellular data. This counterintuitive behavior baffles many users, but it's not imaginary — there are real technical and behavioral reasons behind it. The good news? Most causes are fixable with simple adjustments. From background app activity to weak signal strength, several factors can turn your Wi-Fi connection into a hidden battery drain. Understanding these causes empowers you to take control and optimize both connectivity and power efficiency.
Why Wi-Fi Might Be Draining Your Battery Faster
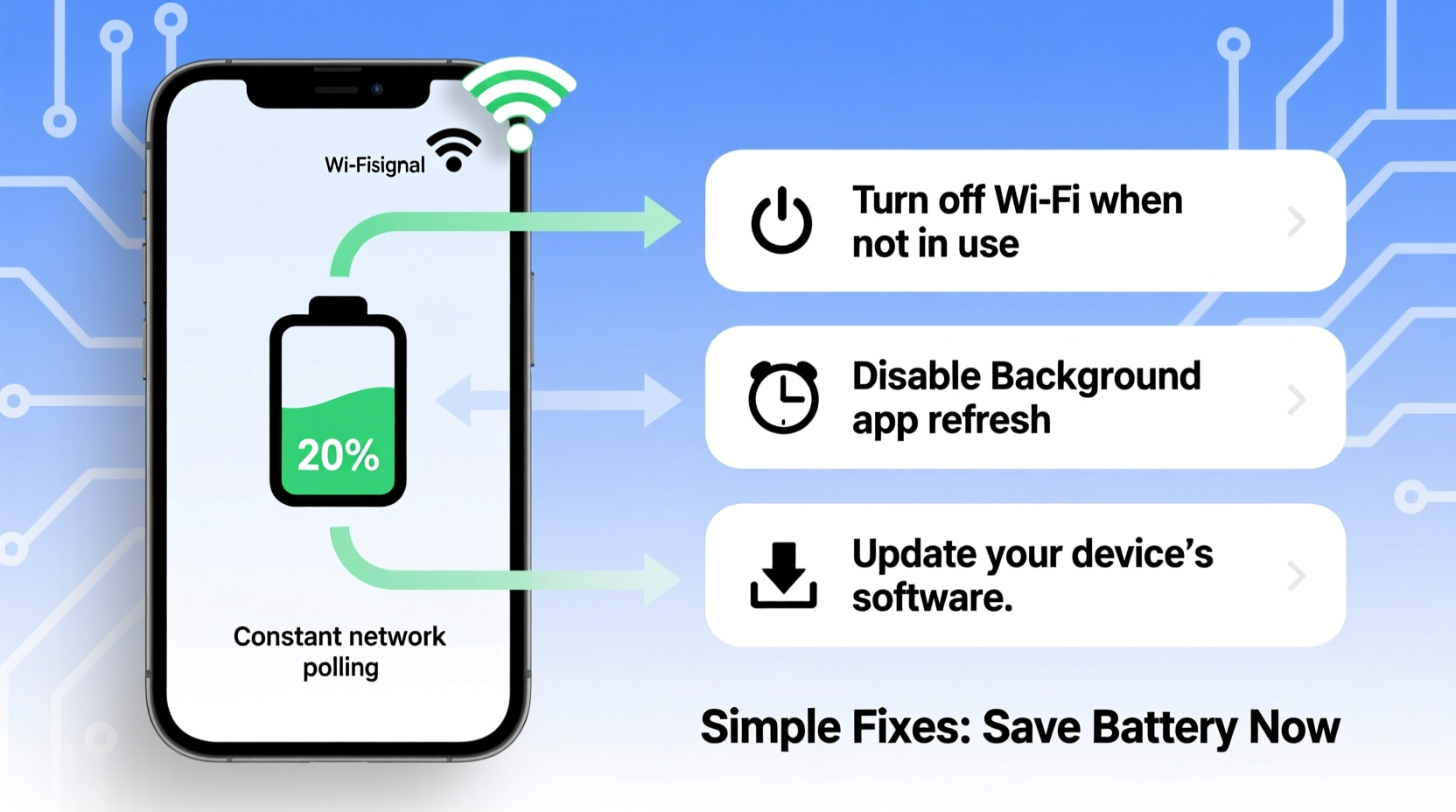
Wi-Fi is generally more energy-efficient than cellular data, especially for streaming or downloading large files. However, under certain conditions, Wi-Fi can consume more power than expected. The key lies in how your phone manages the connection and what happens once it's online.
One primary reason is signal strength. When your phone connects to a distant or obstructed Wi-Fi router, it boosts its radio output to maintain a stable link. This increased effort draws more power, similar to how shouting across a room tires you out faster than speaking at arm’s length. In environments with thick walls, interference from appliances, or crowded networks (like in apartments or offices), your phone may constantly struggle to stay connected.
Another major contributor is background activity. Once connected to Wi-Fi, apps often sync automatically — email clients check for new messages, social media apps refresh feeds, cloud backups run, and software updates download. While convenient, this surge in background processing increases CPU usage and screen wake cycles, accelerating battery drain.
Additionally, some phones default to aggressive Wi-Fi scanning, even when already connected. This feature, designed to switch seamlessly between networks, forces the device to continuously search for stronger signals, consuming extra power. Android and iOS both include settings to manage this, but they’re often left on by default.
“Wi-Fi itself isn’t the problem — it’s how the phone uses it. Poor signal management and uncontrolled background syncing are the real culprits behind unexpected battery loss.” — Dr. Alan Reeves, Mobile Systems Engineer, MIT Media Lab
Common Causes of Excessive Wi-Fi Battery Drain
To effectively address the issue, it helps to identify which specific factor is affecting your device. Below are the most frequent causes:
- Weak Wi-Fi signal: Forces the phone to work harder to transmit and receive data.
- Background app refresh: Apps like Facebook, Instagram, Gmail, and Dropbox sync frequently over Wi-Fi.
- Automatic network switching: Phones that scan for other networks while connected waste power.
- Outdated router firmware: Older routers may not support modern power-saving protocols like Wi-Fi Power Save Mode.
- Too many connected devices: Network congestion slows speeds and increases transmission time, prolonging radio use.
- Auto-join settings: Connecting to every available network exposes your phone to unstable or malicious hotspots.
Step-by-Step Guide to Reduce Wi-Fi Battery Drain
Follow this practical sequence to diagnose and resolve excessive battery consumption linked to Wi-Fi:
- Check Wi-Fi signal strength
Go to your phone’s Wi-Fi settings and look at the signal bars. If it’s below half, consider moving closer to the router or resetting the router. - Limit background app refresh
- iOS: Settings > General > Background App Refresh > Turn off for non-essential apps.
- Android: Settings > Apps > [App Name] > Mobile Data & Wi-Fi > Background data > Disable.
- Disable Wi-Fi scanning
Prevents your phone from constantly hunting for networks:- Android: Settings > Location > Scanning > Wi-Fi scanning > Off.
- iOS: Settings > Privacy > Location Services > System Services > Networking & Analytics > Off.
- Forget unreliable networks
Remove saved networks that are weak or rarely used to prevent automatic reconnection attempts. - Update router firmware
Log into your router’s admin panel (usually via 192.168.1.1) and check for firmware updates. Modern firmware improves compatibility and power efficiency. - Use Wi-Fi scheduler (Android)
Install apps like \"Tasker\" or use built-in digital wellbeing tools to turn Wi-Fi off during sleep hours. - Enable Low Data Mode (iOS) or Data Saver (Android)
These modes reduce background traffic and auto-play features on Wi-Fi.
Do’s and Don’ts: Managing Wi-Fi and Battery Life
| Do | Don’t |
|---|---|
| Keep your phone within reasonable range of the router. | Leave Wi-Fi on in areas with no usable networks. |
| Turn off background refresh for heavy apps like social media. | Assume all Wi-Fi networks are battery-friendly. |
| Use airplane mode in very low-signal zones if not expecting calls. | Ignore system updates — they often include battery optimizations. |
| Restart your phone weekly to clear memory and reset connections. | Connect to public Wi-Fi unnecessarily — security risks aside, poor signal hurts battery. |
Mini Case Study: Sarah’s Weekend Battery Mystery
Sarah, a freelance graphic designer, noticed her iPhone drained completely by midday during weekends, despite charging overnight. She wasn’t doing anything unusual — just browsing, answering emails, and watching videos at home. Curious, she checked her battery usage stats and found Safari and Mail were topping the list, even though she hadn’t actively used them much.
After reviewing her settings, she discovered that “Background App Refresh” was enabled for nearly all apps, and her home Wi-Fi had weakened due to a recent router firmware glitch. Although the internet still worked, the signal strength had dropped significantly behind her desk. Her phone was working overtime to maintain the connection while apps silently refreshed in the background.
She moved the router to a central location, updated its firmware, and disabled background refresh for non-critical apps. The next weekend, her battery lasted until 8 PM — a full 6 hours longer than before. The fix didn’t require new hardware or technical expertise, just awareness and small adjustments.
Expert Tips for Long-Term Battery Health
Beyond immediate fixes, adopting sustainable habits ensures your phone remains efficient over time. Consider these advanced strategies:
- Set up dual-band routing: If your router supports 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, prioritize 5 GHz for mobile devices. It’s faster and often less congested, reducing transmission time and power use.
- Use Quality of Service (QoS) settings: On advanced routers, limit bandwidth-heavy devices during peak usage times to prevent network strain.
- Monitor battery health: Both iOS and Android now provide battery health metrics. Replace the battery if capacity drops below 80% — degraded batteries drain faster regardless of usage.
- Turn off Wi-Fi when sleeping: Use automation tools (e.g., Shortcuts on iOS or Bixby Routines on Samsung) to disable Wi-Fi at night unless needed for updates.
FAQ: Common Questions About Wi-Fi and Battery Drain
Does keeping Wi-Fi on always drain the battery?
No — if you're near a strong network and have background activity under control, Wi-Fi typically saves battery compared to cellular data. The drain occurs mainly with weak signals or excessive syncing.
Should I turn off Wi-Fi when not at home?
Yes, especially in areas with spotty coverage. Constant scanning for saved networks consumes power. Alternatively, enable auto-off features or use location-based rules to disable Wi-Fi when away.
Can a router affect my phone’s battery life?
Absolutely. An outdated or poorly positioned router forces devices to boost transmission power. Modern routers with WPA3, beamforming, and MU-MIMO technology improve efficiency and reduce strain on connected devices.
Battery Optimization Checklist
Use this checklist weekly to ensure your phone isn't wasting power on Wi-Fi:
- ✅ Check Wi-Fi signal strength at common locations (desk, bedroom, kitchen).
- ✅ Review battery usage stats in Settings.
- ✅ Disable background refresh for high-drain apps.
- ✅ Forget unused or weak Wi-Fi networks.
- ✅ Disable Wi-Fi scanning in Location settings.
- ✅ Restart your phone to reset network processes.
- ✅ Update phone OS and router firmware monthly.
- ✅ Consider automating Wi-Fi toggles based on time or location.
Final Thoughts: Take Control of Your Phone’s Power Use
Your phone’s battery life isn’t solely determined by the size of the battery or age of the device — it’s shaped by how you use connectivity features like Wi-Fi. What seems like a minor convenience, such as automatic syncing or seamless network switching, can accumulate into significant power loss over time. The solution isn’t to abandon Wi-Fi but to use it wisely.
By auditing your settings, optimizing your environment, and understanding the interplay between signal quality and app behavior, you can enjoy fast, reliable internet without sacrificing battery. These changes don’t require technical mastery — just awareness and consistency. Start today by checking one setting, then build from there. Small actions compound into long-term gains.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?