Nothing disrupts a smooth workflow like sending a print job only to find your printer labeled “offline.” Whether you're working from home, managing a small office, or handling last-minute school projects, a wireless printer that repeatedly disconnects can be both frustrating and costly in lost time. The good news is that most of these issues are fixable with the right approach. The root causes range from weak Wi-Fi signals and IP conflicts to outdated drivers and router settings. This guide breaks down the common reasons behind constant offline status and delivers actionable, step-by-step solutions to keep your printer reliably connected.
Understanding Why Printers Go Offline
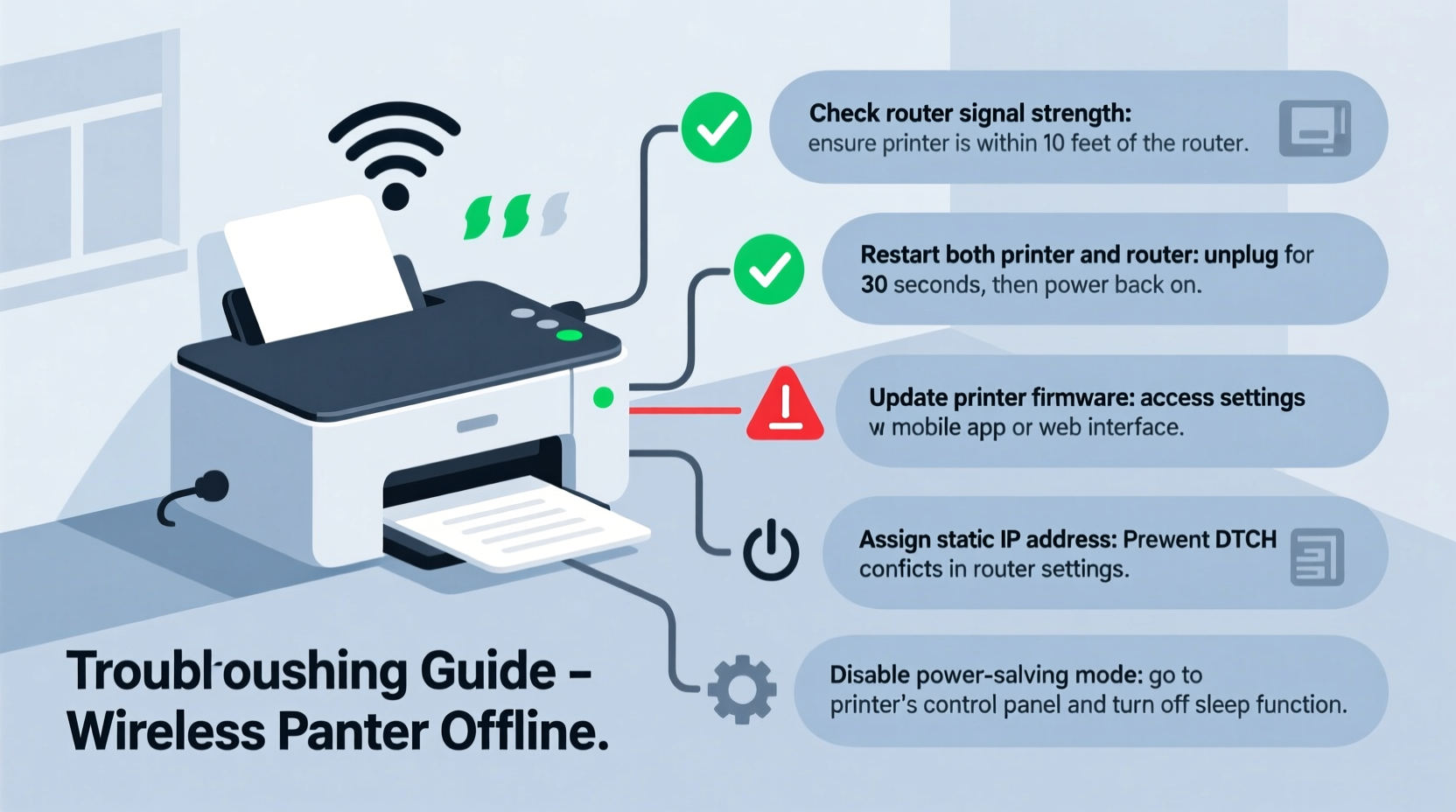
A printer showing as “offline” doesn’t necessarily mean it’s powered down or broken. In most cases, especially with wireless models, the issue lies in communication between your computer and the printer over the network. Windows and macOS often mislabel printers as offline due to connectivity hiccups, even when the device is fully functional.
Common triggers include:
- Weak or unstable Wi-Fi signal
- Printer not responding to network pings
- IP address changes (DHCP lease renewal)
- Outdated or corrupted printer drivers
- Power-saving modes disabling Wi-Fi
- Firewall or antivirus software blocking communication
- Router firmware bugs or interference from other devices
Printers rely on consistent two-way communication. If your computer fails to detect the printer—even momentarily—it may default to an “offline” state. Unlike wired connections, wireless setups are more prone to intermittent drops, making diagnosis essential.
Step-by-Step Guide to Restore Printer Connectivity
Follow this structured process to diagnose and resolve recurring offline issues. Start from the basics and move toward advanced fixes.
- Restart all devices – Power cycle your printer, computer, and router. Unplug each for 30 seconds, then reconnect. This clears temporary glitches and resets network handshakes.
- Verify Wi-Fi connection on the printer – Use the printer’s control panel to confirm it's connected to the correct network. Look for signal strength indicators.
- Check printer status in system settings – On Windows, go to Settings > Devices > Printers & scanners. On macOS, open System Settings > Printers & Scanners. Ensure the printer isn’t grayed out or marked “offline.”
- Set the printer as default – Right-click the printer and select “Set as default.” This forces the OS to prioritize it.
- Disable “Use Printer Offline” mode – In the print queue window, ensure this option is unchecked. Accidentally enabling it halts all jobs.
- Reconnect the printer to Wi-Fi – Remove and re-add the printer through your operating system using WPS, PIN, or manual setup.
- Update printer firmware – Visit the manufacturer’s website (HP, Epson, Canon, Brother, etc.) and download the latest firmware update tool.
- Install updated drivers – Download the full feature driver package directly from the manufacturer—do not rely solely on built-in OS drivers.
If the problem persists after these steps, dig deeper into network configuration and environmental factors.
Network Optimization for Stable Printing
Wireless printers depend heavily on your home or office network. Even minor interference can break the connection.
Improve Signal Strength
Place your printer within optimal range of the router—ideally no more than 30 feet away, with minimal obstructions. Avoid placing it near large metal objects, microwaves, cordless phones, or thick walls. These can degrade Wi-Fi performance.
Assign a Static IP Address
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) assigns temporary IP addresses. When your printer reboots, it may receive a new IP, causing computers to lose track of it.
To assign a static IP:
- Access your router’s admin page (usually via 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1).
- Log in with admin credentials.
- Navigate to DHCP settings or connected devices.
- Locate your printer by MAC address.
- Reserve a permanent IP address for it.
- Update the printer’s network settings to use this static IP manually (via control panel).
This ensures consistent identification across the network.
Switch to 2.4 GHz Band
Many modern routers broadcast dual bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. While 5 GHz offers faster speeds, it has shorter range and poorer wall penetration. Most printers only support 2.4 GHz. Confirm your printer is connected to the correct band—some routers merge them under one SSID, causing confusion.
Troubleshooting Checklist
Use this checklist to systematically eliminate common causes:
| Action | Status (✓/✗) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Printer powered on and displaying Wi-Fi icon | ||
| Printer connected to correct Wi-Fi network | Check via printer menu | |
| Computer and printer on same network | No guest or isolated networks | |
| “Use Printer Offline” disabled | In print queue settings | |
| Printer set as default | Ensures priority access | |
| Drivers updated from manufacturer site | Avoid generic OS drivers | |
| Firmware up to date | Check model-specific updater | |
| Static IP assigned via router | Prevents IP drift | |
| Firewall allows printer communication | Add exception if needed |
Go through each item methodically. Mark completed actions and note any anomalies. This helps identify patterns and saves time during future troubleshooting.
Real-World Example: Home Office Printer Issues
Sarah, a freelance graphic designer, relied on her HP OfficeJet Pro 9015e for client deliverables. Every few days, her printer would appear offline, forcing her to restart it multiple times. Deadlines were at risk, and client proofs delayed.
She first assumed it was a driver issue and reinstalled them repeatedly—but the problem returned within hours. After reading about IP instability, she checked her router and discovered her printer had a different IP each morning. She accessed her ASUS router settings, found the printer by MAC address, and reserved a static IP. Then, she manually configured the printer to use that address.
Next, she moved the printer from a back bedroom to her office, reducing distance from the router and removing a concrete wall from the signal path. Finally, she disabled the 5 GHz band temporarily during setup to ensure stable pairing on 2.4 GHz.
The result? No offline incidents in over three weeks. Her print jobs now complete reliably, and background syncing works seamlessly.
“Network stability is just as important as printer functionality. A well-configured router can prevent 80% of ‘offline’ errors.” — Marcus Lin, Network Infrastructure Consultant
Advanced Fixes and Prevention Tips
When basic steps don’t work, consider these advanced strategies:
Enable Bonjour or mDNS for macOS
Apple devices use Bonjour for device discovery. If disabled, your Mac might not detect the printer. Install Bonjour Print Services or ensure mDNS (Multicast DNS) is active on your network.
Adjust Power Management Settings
Some printers enter deep sleep after inactivity, dropping off the network entirely. Access the printer’s power settings and:
- Extend sleep timer
- Disable “Airplane Mode” or “Wi-Fi Off” in idle
- Turn off “Instant-On” if it interferes with connectivity
Use WPS Instead of Manual Setup
WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) simplifies pairing. Press the WPS button on your router, then initiate WPS on the printer within two minutes. This reduces configuration errors.
Limit Connected Devices
Overcrowded networks strain bandwidth and cause packet loss. Disconnect unused smart devices or set up a guest network for IoT gadgets to free up resources for critical devices like printers.
Upgrade Router Firmware
Old router firmware may lack proper QoS (Quality of Service) rules or contain bugs affecting peripheral detection. Check your ISP or router manufacturer for updates.
FAQ: Common Questions About Printer Offline Issues
Why does my printer go offline when I haven’t used it for a while?
Most wireless printers enter power-saving mode after periods of inactivity. During this state, Wi-Fi may shut down completely, making the device undetectable. Adjusting sleep settings or assigning a static IP helps maintain network presence.
Can antivirus software block my printer?
Yes. Some security suites include network monitoring features that flag printer communication as suspicious. Temporarily disable the firewall to test. If printing works, add an exception for your printer’s IP or executable (e.g., HP Smart, Epson Connect).
Is USB better than wireless for reliability?
For single-computer setups, USB offers unmatched reliability—no network dependency, instant detection, and consistent performance. However, it sacrifices convenience and multi-device access. For shared environments, a well-tuned wireless setup is still preferable.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Printing Experience
A printer that constantly goes offline isn’t a lost cause—it’s a solvable technical challenge. By understanding the interplay between your network, operating system, and printer firmware, you gain the power to create a stable, frustration-free printing environment. Start with simple resets, verify network alignment, lock in a static IP, and update all software components. Small adjustments often yield dramatic improvements.
Don’t accept repeated disconnections as normal. With the right knowledge, you can transform an unreliable device into a dependable tool that supports your productivity, not hinders it.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?