If you've ever settled in for a movie night only to be interrupted by endless spinning wheels and frozen screens, you're not alone. Buffering during peak viewing hours—typically between 7 PM and 10 PM—is one of the most common frustrations among smart TV users. While it may seem like your internet provider or streaming service is at fault, the truth is more nuanced. The issue stems from network congestion, hardware limitations, and suboptimal setup choices that can all be addressed with the right knowledge.
Understanding why buffering happens—and what you can do about it immediately—can transform your streaming experience from frustrating to seamless. This guide breaks down the technical causes behind peak-hour lag and provides actionable steps to reduce or eliminate buffering, starting tonight.
Why Peak Hours Cause Streaming Delays
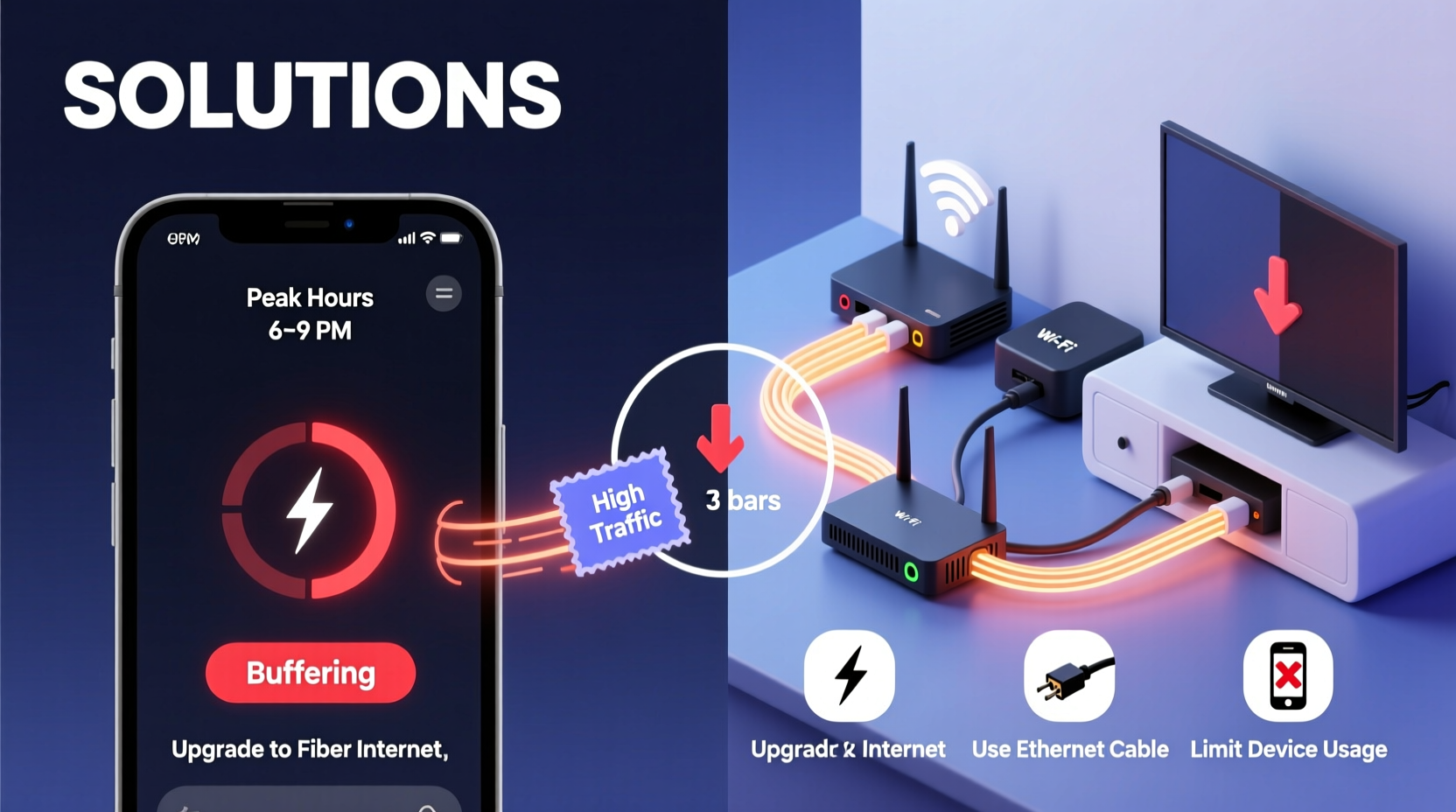
Peak hours refer to the time of day when the highest number of people are using the internet simultaneously. In most households, this coincides with evening entertainment: families watching Netflix, kids gaming online, and smartphones downloading updates. During this window, local networks and internet service providers (ISPs) experience heavy traffic, leading to reduced bandwidth availability per user.
Your ISP allocates bandwidth across its network based on demand. When thousands of users in your neighborhood stream high-definition content at once, the available bandwidth gets stretched thin. This doesn't mean your plan has changed—it means shared infrastructure is under pressure. Think of it like rush hour on a highway: even if your car is capable of going fast, traffic slows everyone down.
Streaming services like Netflix, Hulu, or Disney+ require consistent data flow. For HD video, you need at least 5 Mbps; for 4K, 25 Mbps or more. If your effective speed drops below these thresholds due to congestion, the video player starts buffering to preload content while it waits for stable delivery.
Common Causes of Buffering Beyond Network Congestion
While peak-time congestion plays a major role, several other factors contribute to poor streaming performance:
- Wi-Fi signal interference: Walls, appliances, and neighboring networks can weaken your Wi-Fi signal, especially if your router is far from your TV.
- Outdated router firmware: Older routers may not handle modern streaming demands efficiently, particularly with multiple devices connected.
- Device limitations: Budget smart TVs or older streaming sticks may struggle with decoding high-bitrate streams, even with good internet.
- Background device usage: Phones, tablets, and computers downloading updates or syncing in the background consume bandwidth without your awareness.
- Server-side throttling: Some ISPs engage in throttling—intentionally slowing certain types of traffic, including video streaming—during high-demand periods.
Each of these issues compounds the problem, making it essential to evaluate both your internal home network and external internet conditions.
Step-by-Step Guide to Improve Streaming Instantly
You don’t need to upgrade your internet plan or buy new equipment to fix buffering. Many improvements can be made within minutes. Follow this sequence for immediate results:
- Restart your router and modem. Unplug both devices for 30 seconds, then power them back on. This clears temporary glitches and refreshes your IP connection.
- Move closer to your router or use an Ethernet cable. Wi-Fi strength degrades over distance. If possible, connect your TV directly via Ethernet for maximum stability.
- Reduce active devices on your network. Pause downloads, disconnect unused phones/tablets, and stop cloud backups until after prime time.
- Lower the streaming resolution temporarily. On most platforms, you can manually adjust video quality settings to reduce bandwidth usage.
- Reboot your streaming device. Whether it’s a Roku, Fire Stick, Apple TV, or built-in smart system, restarting clears memory and resets connections.
- Check for firmware updates on your router and TV. Manufacturers often release performance patches that improve connectivity.
These steps address the most frequent culprits behind sudden slowdowns. Implement them before considering costly upgrades.
Do’s and Don’ts of Home Streaming Optimization
| Do | Don’t |
|---|---|
| Use wired Ethernet whenever possible for critical devices like TVs and game consoles. | Rely solely on Wi-Fi extenders unless professionally configured—they often create more problems than they solve. |
| Place your router centrally, elevated, and away from metal objects or microwaves. | Hide your router in a cabinet or basement corner where signals get blocked. |
| Set Quality of Service (QoS) rules on your router to prioritize streaming devices. | Allow automatic software updates to run during peak viewing hours. |
| Upgrade to a dual-band or tri-band mesh Wi-Fi system if coverage is poor. | Assume higher Mbps always equals better streaming—latency and jitter matter just as much. |
| Monitor bandwidth usage through your router’s admin panel or apps like GlassWire. | Ignore recurring buffering—if it happens nightly, there's a fixable root cause. |
Real Example: How One Household Fixed Nightly Buffering
The Patel family in Austin, Texas, experienced constant buffering every evening on their 4K Samsung TV, despite having a 100 Mbps internet plan. They assumed they needed to upgrade, but decided to troubleshoot first.
After running a speed test at 8 PM, they found their actual download speed was only 18 Mbps—far below their plan’s promise. Upon checking their network, they discovered two laptops were downloading Windows updates, a tablet was backing up to iCloud, and their security cameras were uploading footage—all during peak time.
They took three actions: scheduled automatic updates for early morning, enabled QoS on their router to prioritize the TV, and connected the TV via Ethernet instead of Wi-Fi. Within one evening, buffering disappeared. Their effective streaming bandwidth jumped to 75 Mbps during peak hours, enough for smooth 4K playback.
This case illustrates that bandwidth isn’t just about your plan—it’s about how it’s used and delivered.
Expert Insight: What Industry Professionals Say
“Most buffering issues aren’t caused by slow internet plans, but by inefficient network management. A well-configured home network with proper device prioritization can outperform a faster but disorganized setup.” — Daniel Reeves, Senior Network Engineer at Broadband Insights Group
Reeves emphasizes that consumers often overlook router settings and device placement. “People focus on speed numbers advertised by ISPs,” he says, “but real-world performance depends on signal quality, interference, and concurrent usage.”
Tips for Long-Term Streaming Stability
For sustained improvement beyond quick fixes, consider these strategic upgrades:
- Invest in a mesh Wi-Fi system: Systems like Google Nest Wi-Fi or Eero provide seamless coverage and intelligent load balancing across devices.
- Enable DNS optimization: Switching to faster DNS servers like Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) or Google (8.8.8.8) can reduce latency in content lookup.
- Use a dedicated streaming device: Devices like Apple TV 4K or NVIDIA Shield offer superior processing power and smoother app performance compared to built-in smart TV systems.
- Contact your ISP about throttling: Ask if they throttle video traffic and whether an \"unlimited\" or \"gaming-optimized\" tier is available.
- Upgrade your plan strategically: If you consistently stream 4K on multiple devices, consider upgrading to 200 Mbps or higher—but only after optimizing your current setup.
FAQ: Common Questions About TV Buffering
Is buffering always due to slow internet?
No. While insufficient bandwidth is a common cause, buffering can also result from Wi-Fi interference, outdated hardware, server issues on the streaming platform, or too many connected devices consuming data simultaneously.
Can my neighbor’s internet affect mine?
Indirectly, yes. If you share the same ISP node or cable network segment, heavy usage by nearby homes can reduce available bandwidth during peak times—a phenomenon known as \"neighborhood congestion.\"
Will switching to 5 GHz Wi-Fi help reduce buffering?
Yes, in most cases. The 5 GHz band offers faster speeds and less interference than 2.4 GHz, though it has shorter range. Use 5 GHz for devices close to the router, like your living room TV.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Streaming Experience
Buffering during peak hours doesn’t have to be an inevitable part of modern life. With a clear understanding of network dynamics and a few targeted adjustments, you can dramatically improve your streaming reliability—often without spending a dime. From reconnecting your TV via Ethernet to managing background device usage, the solutions are practical and accessible.
Start tonight. Run a speed test, reboot your equipment, and apply the checklist above. Small changes compound into big improvements. Once you’ve optimized your setup, enjoy uninterrupted movies, shows, and live events exactly when you want them.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?