A wireless mouse offers freedom from tangled cables and greater desk flexibility, but nothing disrupts productivity faster than a device that cuts out without warning. If your cursor freezes, skips, or disappears entirely—only to return moments later—you're not alone. Millions of users face random disconnections with their wireless mice, often mistaking the issue for hardware failure. In reality, most problems stem from correctable causes like interference, power issues, outdated drivers, or environmental factors. Understanding the root causes and applying systematic fixes can restore seamless control and eliminate frustration.
Common Causes of Wireless Mouse Disconnection
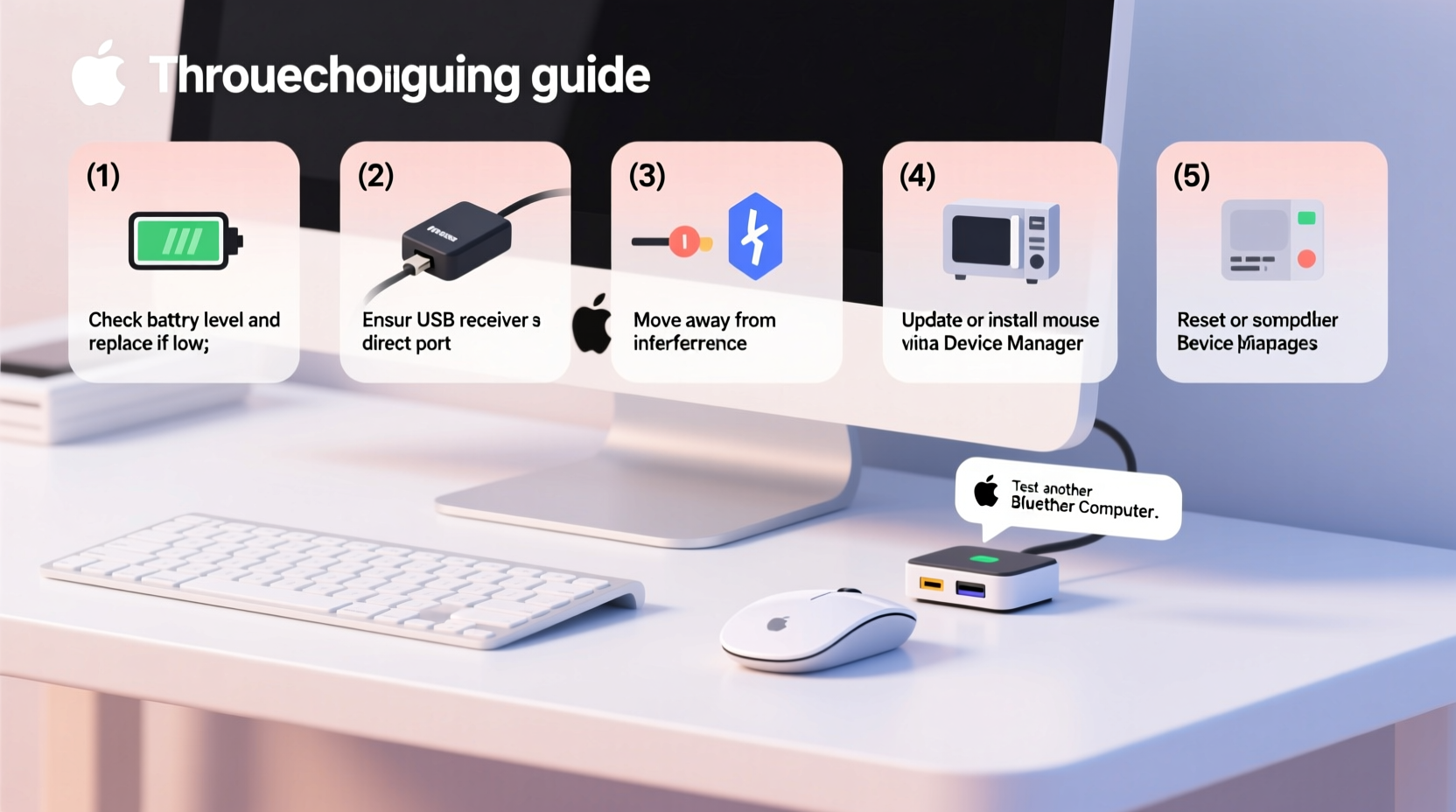
Before jumping into fixes, it’s essential to identify what might be causing the instability. Wireless mice rely on either Bluetooth or a USB dongle (typically using 2.4GHz radio frequency) to communicate with your computer. Any disruption in this signal can result in intermittent disconnection. The following are the most frequent culprits:
- Low battery power: As batteries drain, signal strength weakens, leading to erratic behavior.
- Radio frequency interference: Devices like cordless phones, microwaves, and even nearby Wi-Fi routers emit signals that can interfere with the 2.4GHz band.
- Dongle placement: A USB receiver placed behind a laptop or obstructed by metal components may lose line-of-sight, weakening the connection.
- Outdated or corrupted drivers: Missing updates or software conflicts can prevent consistent communication between the mouse and OS.
- USB port issues: Faulty, loose, or underpowered USB ports can interrupt power delivery and data transmission.
- Bluetooth congestion: In environments with multiple Bluetooth devices, pairing conflicts or bandwidth saturation may occur.
- Physical obstructions: Walls, metal surfaces, or even hands between the mouse and receiver can block the signal.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
Follow this structured approach to isolate and resolve the cause of your wireless mouse disconnections. Each step builds on the previous one, increasing in technical depth as needed.
- Replace or recharge the batteries. Even if the battery indicator shows remaining charge, weak cells can cause voltage drops under load. Use fresh alkaline batteries or fully charge the internal battery if applicable.
- Reposition the USB receiver. Plug the dongle directly into a front or side USB port. Avoid using extension cables or hubs. For desktops, consider a USB extender to place the receiver closer to the mouse.
- Eliminate sources of interference. Turn off nearby electronics such as speakers, smartphones, or microwave ovens temporarily to test if stability improves.
- Test on another computer. Connect the mouse to a different system to determine if the issue follows the device or remains with your machine.
- Update or reinstall mouse drivers. Go to Device Manager, locate your mouse under \"Mice and other pointing devices,\" right-click, and choose \"Update driver.\" If that fails, uninstall the device and restart to trigger automatic reinstallation.
- Check for operating system updates. Windows, macOS, and Linux distributions frequently release patches that improve peripheral compatibility.
- Clean the sensor lens. Dust or debris on the optical sensor can mimic disconnection symptoms. Gently wipe the bottom with a dry microfiber cloth.
- Reset the pairing (for Bluetooth models). Remove the device from Bluetooth settings, then pair it again from scratch.
Do’s and Don’ts When Using a Wireless Mouse
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Use high-quality, name-brand batteries | Don’t use old or mixed batteries in multi-cell devices |
| Place the USB receiver in an unobstructed location | Don’t plug the dongle into a rear PC port hidden behind metal casing |
| Keep firmware updated via manufacturer software (e.g., Logitech Options+, Dell Peripheral Manager) | Don’t ignore firmware update notifications |
| Limit concurrent wireless devices near the workspace | Don’t operate the mouse near strong electromagnetic sources |
| Store the mouse properly when not in use | Don’t leave it exposed to dust, moisture, or extreme temperatures |
Real-World Example: Fixing a Persistent Office Mouse Issue
Jamal, a financial analyst working from home, experienced daily disruptions with his wireless mouse during video calls and spreadsheet editing. The pointer would freeze for several seconds every 10–15 minutes. Initially assuming the mouse was faulty, he ordered a replacement—but the new one exhibited identical behavior. After ruling out battery issues and trying multiple USB ports, he noticed his Wi-Fi router sat just six inches from the USB receiver. Moving the router three feet away immediately resolved the problem. Further investigation revealed that both the router and mouse operated on overlapping 2.4GHz channels. By switching his router to a 5GHz network for primary use and reserving 2.4GHz only for legacy devices, Jamal eliminated all disconnections. This case underscores how environmental RF noise—not hardware defects—is often the true culprit.
“Over 60% of reported wireless peripheral failures are actually due to environmental interference or improper setup, not defective units.” — Dr. Lena Torres, Senior Hardware Engineer at Peripheral Systems Lab
Advanced Fixes and Optimization Tips
If basic troubleshooting doesn’t resolve the issue, deeper interventions may be necessary. These steps require slightly more technical awareness but are safe and effective when followed carefully.
Use a USB Extension Cable for Optimal Dongle Placement
The USB receiver needs clear line-of-sight to the mouse. On laptops, rear or side ports often place the dongle behind shielding materials. A short USB extension cable allows you to position the receiver in front of the laptop, significantly improving signal reception. Choose a shielded cable less than 1 meter long to avoid introducing new interference.
Switch from 2.4GHz to Bluetooth (or vice versa)
If your mouse supports both connection types, test which performs better in your environment. Some users find Bluetooth more stable in crowded RF zones, while others benefit from dedicated 2.4GHz channels. Toggle between modes using the switch on the mouse or through manufacturer software.
Disable Power-Saving Modes on USB Ports
Windows may turn off USB devices to save power, inadvertently cutting communication with your mouse.
To disable this:
- Open Device Manager.
- Expand “Universal Serial Bus controllers.”
- Right-click each “USB Root Hub” and select “Properties.”
- Go to the “Power Management” tab.
- Uncheck “Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power.”
- Repeat for all hubs.
Scan for RF Interference
Use a Wi-Fi analyzer app (like NetSpot or Acrylic Wi-Fi) to detect channel congestion. While these tools focus on networking, they reveal overall 2.4GHz activity. If channels 6–11 are saturated, your mouse signal may struggle. Although mice don’t let you manually change channels, reducing nearby traffic helps.
Preventive Maintenance Checklist
To maintain reliable performance over time, perform these actions regularly:
- ✅ Replace batteries before they reach critical levels
- ✅ Clean the mouse sensor weekly with a dry cloth
- ✅ Verify driver updates monthly via Device Manager or manufacturer software
- ✅ Re-pair Bluetooth mice every few months to clear cached errors
- ✅ Audit nearby electronics quarterly for new sources of interference
- ✅ Rotate spare batteries to extend lifespan and avoid leakage
- ✅ Store the mouse in a closed drawer when unused for extended periods
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a virus cause my wireless mouse to disconnect?
No, malware cannot directly disrupt the physical radio signal between your mouse and receiver. However, a heavily infected system may experience high CPU usage or driver corruption that indirectly affects input responsiveness. If disconnections coincide with system slowdowns or pop-ups, run a full antivirus scan.
Why does my mouse disconnect when I move it quickly?
This usually indicates low polling rate or signal lag. Most wireless mice default to 125Hz, meaning they report position 125 times per second. High-performance models offer 500Hz or 1000Hz. Check your mouse settings via manufacturer software and increase the polling rate if possible. Also ensure the surface is smooth and non-reflective for optimal tracking.
Is it better to use a wired mouse for reliability?
Wired mice inherently offer lower latency and immunity to RF interference. For mission-critical tasks like gaming, graphic design, or real-time trading, a wired connection provides unmatched consistency. However, modern high-end wireless mice (especially those using proprietary protocols like Logitech Lightspeed or Razer HyperSpeed) rival wired performance. The choice depends on your tolerance for occasional dropouts versus desire for clutter-free setup.
Final Thoughts and Action Plan
Random wireless mouse disconnections are rarely a sign of inevitable hardware failure. More often, they reflect overlooked environmental conditions, outdated software, or suboptimal setup practices. By methodically testing battery health, optimizing receiver placement, minimizing interference, and maintaining up-to-date drivers, you can achieve stable, uninterrupted performance. Remember that small adjustments—like moving a router or disabling USB power saving—can yield dramatic improvements. Don’t accept persistent glitches as normal; modern peripherals are designed for reliability when used correctly.
Start today: pick up your mouse, check the battery level, inspect the USB connection, and run through the troubleshooting checklist. Most issues can be resolved in under 30 minutes. Once fixed, implement preventive habits to avoid recurrence. Your workflow—and your patience—will thank you.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?