A clogged ear is more than just an annoyance—it can affect balance, hearing, and overall comfort. Whether it’s a sensation of fullness, muffled sound, or pressure, the feeling of a blocked ear often prompts immediate concern. While many cases resolve on their own, understanding the underlying causes and knowing which remedies are safe and effective can make all the difference in finding quick relief.
Common Causes of a Clogged Ear
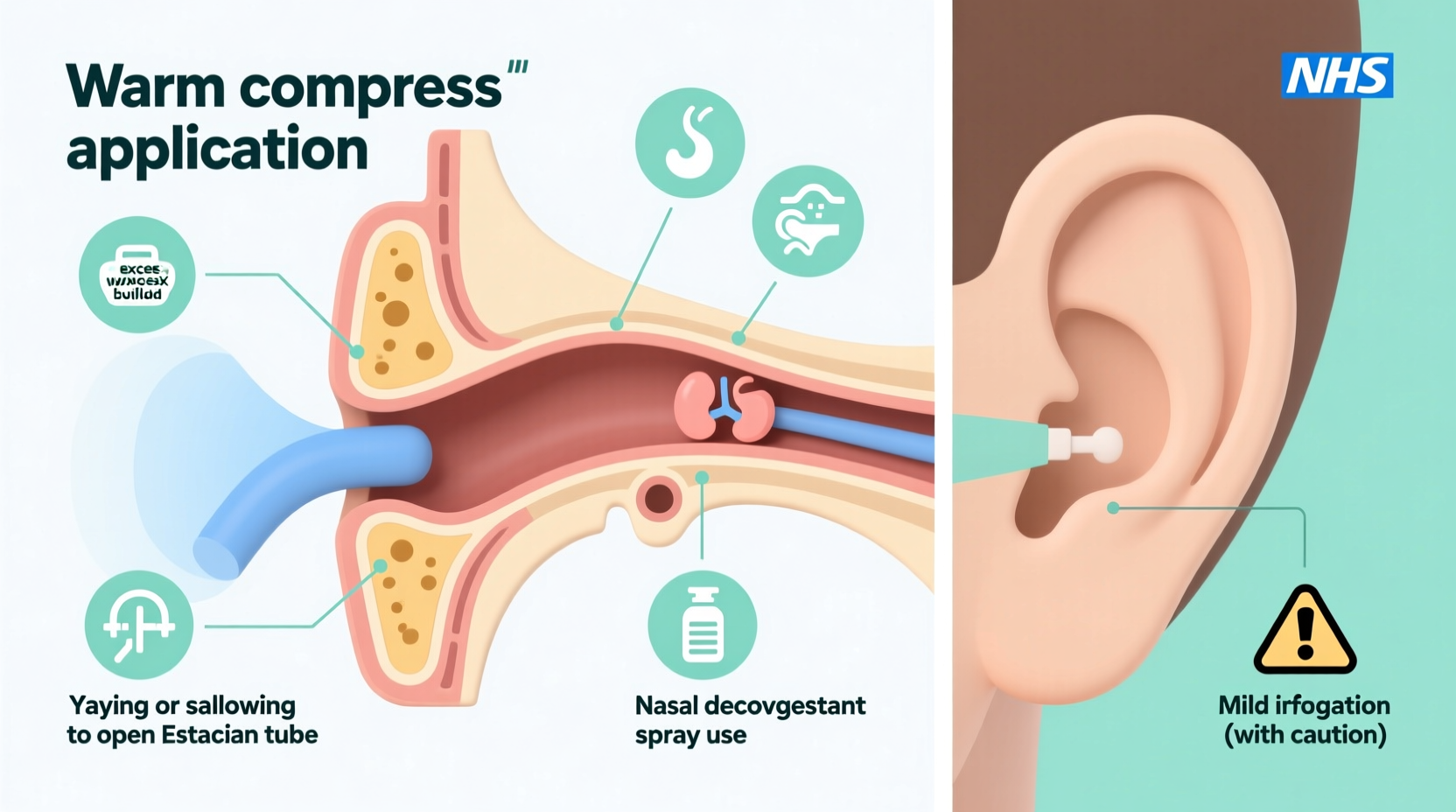
A blocked ear isn't a condition in itself but rather a symptom of various underlying issues. Identifying the root cause is essential for choosing the right treatment approach.
- Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: The Eustachian tube connects your middle ear to the back of your throat. When it becomes inflamed or blocked—often due to colds, allergies, or sinus infections—it can’t equalize pressure, leading to that familiar “plugged” sensation.
- Earwax Buildup (Cerumen Impaction): Earwax naturally protects the ear canal, but excessive accumulation can block sound and create discomfort. This is one of the most frequent reasons for ear fullness.
- Altitude Changes: Rapid changes in altitude during flying or mountain driving can cause temporary ear blockage as air pressure shifts faster than the Eustachian tube can adjust.
- Swimmer’s Ear (Otitis Externa): Water trapped in the ear canal fosters bacterial growth, causing swelling, pain, and a blocked feeling.
- Ear Infections: Middle ear infections (otitis media) often come with fluid buildup behind the eardrum, creating pressure and muffled hearing, especially in children.
- Foreign Objects: Especially in children, small objects inserted into the ear can physically block the canal.
Safe and Effective Home Remedies
Many clogged ears respond well to simple, at-home treatments. However, it's crucial to assess symptoms first. If you experience severe pain, drainage, dizziness, or sudden hearing loss, seek medical help immediately.
For Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
To help open the Eustachian tubes and relieve pressure:
- Swallowing or yawning: These actions activate muscles that open the tubes.
- Chewing gum or sucking on candy: Increases swallowing frequency, aiding pressure equalization.
- Valsalva maneuver: Gently pinch your nose, close your mouth, and blow softly until you hear a pop. Do not use force—this can damage the eardrum.
For Earwax Blockage
If wax is the culprit, softening it first can lead to natural expulsion.
- Apply a few drops of warm (not hot) olive oil, mineral oil, or over-the-counter ear drops twice daily for 3–5 days.
- After softening, tilt your head and flush the ear gently with lukewarm water using a bulb syringe.
- Dry the outer ear thoroughly afterward.
“Never insert objects like bobby pins or Q-tips into the ear canal. You risk perforating the eardrum or pushing wax further in.” — Dr. Linda Chen, Otolaryngologist
When to See a Doctor
While home care works for mild cases, certain red flags require professional evaluation:
| Symptom | Home Care OK? | See a Doctor? |
|---|---|---|
| Mild fullness after a flight | Yes | No |
| Pain, fever, or fluid drainage | No | Yes – possible infection |
| Hearing loss lasting over 48 hours | No | Yes – could indicate serious blockage |
| Dizziness or vertigo | No | Yes – may signal inner ear issue |
| Recent head injury | No | Immediate medical attention needed |
Doctors may perform ear irrigation, prescribe antibiotic ear drops, or use specialized tools to remove impacted wax. In chronic cases, they might recommend pressure-equalizing tubes or allergy management.
Prevention and Long-Term Relief Tips
Preventing recurrent ear blockages involves consistent habits and awareness of triggers.
Step-by-Step Prevention Plan
- Manage Allergies: Treat seasonal allergies with antihistamines or nasal sprays to reduce Eustachian tube inflammation.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration thins mucus and ear secretions, helping the Eustachian tube function better.
- Use Decongestants Wisely: Short-term use during colds or flights can reduce swelling, but avoid prolonged use due to rebound congestion.
- Clean Ears Safely: Wipe only the outer ear with a damp cloth. Let the ear’s natural cleaning process handle the inside.
- Equalize Pressure Early: Begin swallowing or chewing before takeoff and descent during flights.
Real Example: Air Travel and Ear Discomfort
Sarah, a frequent flyer, often experienced painful ear pressure during landings. After repeated discomfort, she consulted an ENT specialist who diagnosed chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction exacerbated by undiagnosed allergies. With a regimen of nasal corticosteroids before flights and consistent use of the Valsalva maneuver, her symptoms improved dramatically within weeks. She now prepares for every flight with preventive measures and rarely experiences clogging.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can stress cause a clogged ear feeling?
Stress doesn’t directly block the ear, but it can contribute to muscle tension around the jaw and neck, which may affect ear pressure perception. Additionally, stress weakens immunity, increasing susceptibility to colds and sinus issues that indirectly lead to ear fullness.
Is it safe to use hydrogen peroxide for earwax?
In diluted form (typically mixed with water), hydrogen peroxide is commonly used in ear drops to break down wax. However, it should not be used if you have a perforated eardrum, ear tubes, or active infection. Always consult a doctor if unsure.
How long does a clogged ear last?
Mild cases from altitude or minor congestion may resolve in minutes to hours. Earwax blockages can take days to clear with treatment. Infections or persistent Eustachian dysfunction may last weeks without proper care. If symptoms persist beyond 7–10 days, see a healthcare provider.
Conclusion: Take Action for Clearer Hearing and Comfort
A clogged ear is a common but manageable issue when approached with knowledge and caution. From understanding whether the cause is wax, pressure, or infection to applying safe remedies and knowing when to seek help, taking informed steps ensures faster recovery and prevents complications. Don’t ignore persistent symptoms—early intervention protects your hearing and quality of life.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?