Waking up with a swollen or bloated face is a surprisingly common experience. While it’s usually not a cause for alarm, persistent morning puffiness can be frustrating—especially when it affects your appearance or confidence before you’ve even had your first sip of coffee. The good news is that facial puffiness in the morning is often temporary and influenced by lifestyle habits, sleep posture, hydration, and underlying health factors. Understanding the root causes allows you to take targeted action and wake up looking more rested and refreshed.
What Causes Morning Facial Puffiness?
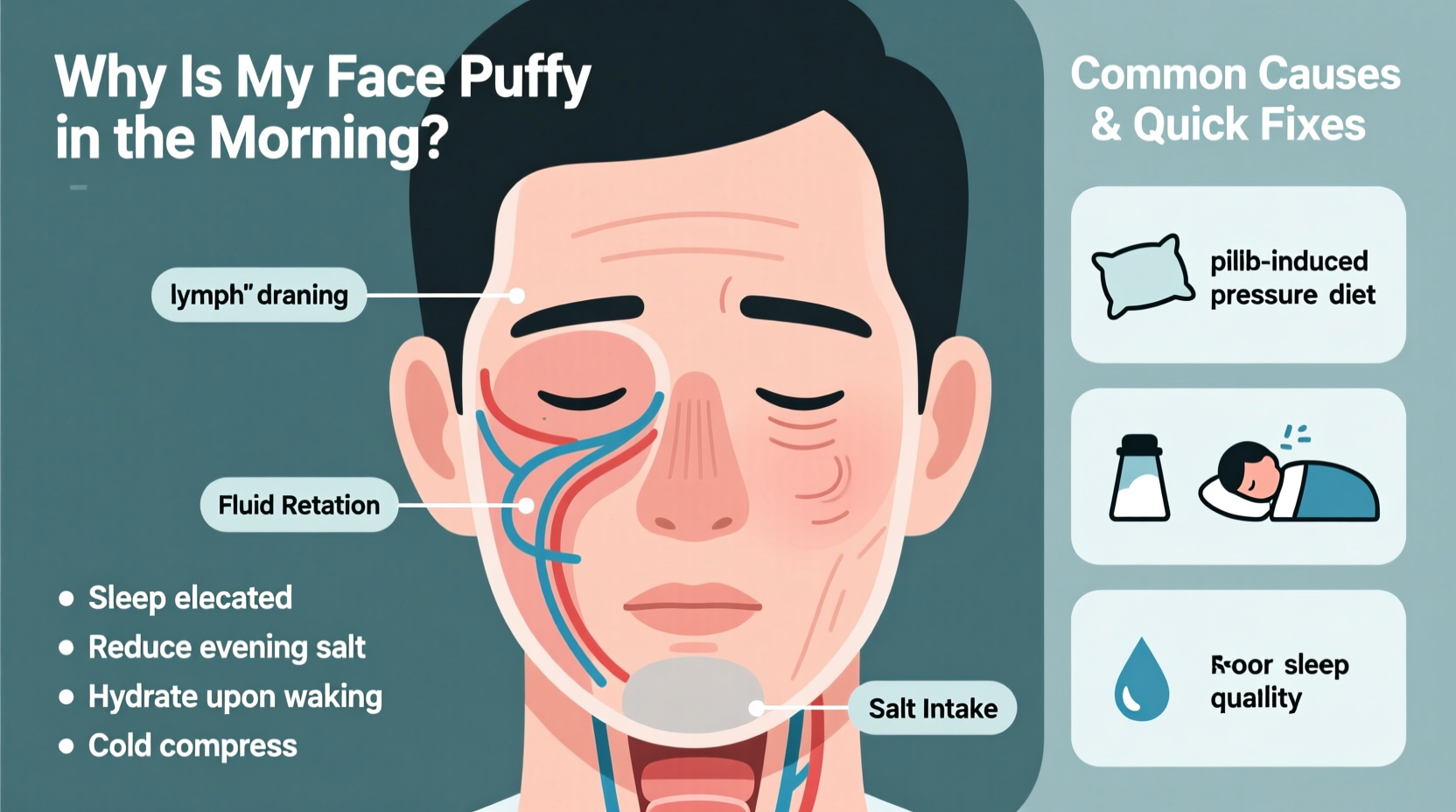
Facial swelling upon waking occurs primarily due to fluid accumulation in the soft tissues around the eyes, cheeks, and jawline. Gravity plays a key role: when you lie flat during sleep, fluids redistribute throughout the body and tend to pool in areas with looser skin, such as the face. But beyond gravity, several other factors contribute to this condition.
- Sleep position: Sleeping on your back helps minimize fluid buildup, while lying on your side or stomach increases pressure and encourages fluid retention in the facial area.
- Dietary sodium intake: Consuming high-sodium meals—especially late at night—can lead to water retention, making your face appear swollen by morning.
- Dehydration: Ironically, not drinking enough water prompts the body to hold onto existing fluids, contributing to puffiness.
- Allergies: Seasonal allergies or reactions to skincare products, dust mites, or laundry detergents can trigger inflammation and swelling.
- Alcohol consumption: Alcohol dehydrates the body and dilates blood vessels, increasing fluid leakage into surrounding tissues.
- Lack of sleep: Poor sleep quality disrupts hormonal balance and circulation, both of which influence fluid regulation.
- Aging and weakened skin support: As we age, the skin loses elasticity and underlying fat pads may shift, making puffiness more noticeable.
Common Medical Conditions Linked to Facial Swelling
While most cases of morning puffiness are benign and resolve within hours, some underlying medical issues may contribute to chronic or severe swelling. It's important to recognize when facial puffiness might signal something more serious.
Kidney dysfunction: Impaired kidney function reduces the body’s ability to filter excess fluid and sodium, leading to generalized edema—including facial swelling. Other symptoms include fatigue, changes in urination, and leg swelling.
Thyroid disorders: Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) can cause a condition called myxedema, where mucopolysaccharides accumulate in the skin, resulting in puffiness, particularly around the eyes and face.
Sinus infections: Inflammation of the sinuses can create pressure and swelling in the cheeks and under-eye area, often accompanied by congestion, headache, and postnasal drip.
Autoimmune conditions: Diseases like lupus or Sjögren’s syndrome may present with facial swelling among other systemic symptoms.
“Persistent facial puffiness, especially when combined with fatigue, dry skin, or weight gain, should prompt evaluation for thyroid or renal issues.” — Dr. Lena Patel, Internal Medicine Specialist
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical advice if your facial swelling:
- Lasts all day without improvement
- Is accompanied by shortness of breath or throat tightness (possible allergic reaction)
- Involves pain, redness, or warmth (signs of infection)
- Occurs alongside unexplained weight changes, fatigue, or hair loss
Quick Fixes to Reduce Morning Face Puffiness
You don’t have to endure a puffy face until midday. With a few strategic steps, you can significantly reduce or eliminate swelling within minutes. These methods work by stimulating circulation, encouraging lymphatic drainage, and constricting blood vessels to minimize fluid buildup.
1. Cold Therapy
Applying cold to the face causes vasoconstriction—narrowing of blood vessels—which reduces inflammation and swelling.
- Roll a chilled jade roller or metal spoon over your cheeks and under your eyes.
- Use a cold compress or splash your face with icy water.
- Store eye gels or facial tools in the refrigerator overnight for instant relief.
2. Gua Sha or Lymphatic Drainage Massage
Gentle upward strokes along the jawline, neck, and under the eyes encourage the lymphatic system to drain excess fluid.
Start at the center of the chin and move outward along the jaw to the lymph nodes near the ears. Then sweep down the sides of the neck to help flush trapped fluid.
3. Hydrate Immediately
Drinking a large glass of water upon waking signals your body to release retained fluids. Add a squeeze of lemon for mild diuretic effects and improved digestion.
4. Caffeinated Green Tea Bags
Cool used green tea bags in the fridge and place them over closed eyelids for 5–10 minutes. The caffeine helps constrict blood vessels, while antioxidants reduce inflammation.
5. Use a Depuffing Eye Cream
Look for ingredients like caffeine, niacinamide, peptides, or horse chestnut extract. These compounds stimulate microcirculation and strengthen capillaries.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Long-Term Prevention
To stop morning puffiness before it starts, consider modifying daily habits that contribute to fluid retention and poor circulation.
Reduce Sodium Intake
The average adult consumes far more sodium than recommended. Excess salt disrupts the body’s fluid balance. Aim for less than 2,300 mg per day (ideally closer to 1,500 mg).
Avoid processed foods, canned soups, salty snacks, and restaurant meals high in hidden sodium.
Limit Alcohol and Caffeine Before Bed
Both substances affect hydration and circulation. Alcohol is dehydrating and inflammatory; excessive caffeine can disrupt sleep and increase cortisol, which influences fluid balance.
Prioritize Sleep Quality
Consistent, high-quality sleep regulates hormones like cortisol and aldosterone, which control fluid retention. Aim for 7–9 hours per night and maintain a regular sleep schedule.
Sleep with Your Head Elevated
Using an adjustable bed or an extra pillow keeps your head above heart level, helping gravity drain fluids away from the face.
Stay Consistently Hydrated
Drink water steadily throughout the day rather than chugging large amounts at once. Herbal teas like dandelion or nettle act as natural diuretics and support kidney function.
Manage Allergies
If you suspect allergies are contributing to puffiness, identify triggers through elimination or testing. Switch to hypoallergenic laundry detergent, use dust-proof pillow covers, and keep windows closed during high pollen seasons.
| Habit | Impact on Facial Puffiness | Recommended Change |
|---|---|---|
| High-sodium dinner | Increases water retention | Choose low-sodium, whole-food meals |
| Alcohol before bed | Causes dehydration and inflammation | Avoid alcohol 3+ hours before sleep |
| Sleeping flat on your back | Promotes fluid pooling | Use a wedge pillow or elevate head |
| Inadequate daily water intake | Triggers fluid conservation | Drink 2–3 liters of water daily |
| Skincare product irritation | Leads to localized swelling | Switch to fragrance-free, non-comedogenic formulas |
Step-by-Step Morning Routine to Deflate Puffiness
Follow this five-minute protocol to visibly reduce facial swelling each morning:
- Hydrate (Day 1 Minute): Drink 8–12 oz of room-temperature water with lemon. This jumpstarts metabolism and rehydrates tissues.
- Rinse with Cool Water (Minute 2): Splash your face with cold water to activate vasoconstriction.
- Apply Cold Tools (Minutes 3–4): Use a refrigerated jade roller or spoons to massage the under-eye area and jawline using gentle upward motions.
- Apply Depuffing Serum or Cream (Minute 5): Dab on a lightweight eye gel containing caffeine or peptides. Avoid heavy creams that may trap fluid.
- Finish with Upward Facial Stretches: Tilt your head back, look at the ceiling, and open your mouth wide for 10 seconds. Repeat 3 times to engage neck muscles and promote drainage.
Mini Case Study: Sarah’s Transformation in Two Weeks
Sarah, a 34-year-old marketing executive, struggled with persistent morning puffiness that made her look tired despite getting seven hours of sleep. She frequently ate takeout dinners high in sodium and drank wine before bed. After consulting a dermatologist, she implemented several changes:
- Switched to home-cooked meals with minimal added salt
- Stopped drinking alcohol after 7 PM
- Began sleeping with her head elevated using a memory foam wedge
- Started a nightly skincare routine with a gentle cleanser and non-irritating moisturizer
- Added a morning ritual of cold water rinses and facial massage
Within two weeks, Sarah noticed a dramatic reduction in facial swelling. Her coworkers commented that she looked “more awake” and “less stressed.” Blood pressure and kidney tests came back normal, confirming the issue was lifestyle-related.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can drinking too much water cause facial puffiness?
No—paradoxically, not drinking enough water is more likely to cause puffiness. When dehydrated, your body holds onto fluids to compensate. Drinking adequate water supports kidney function and helps flush out excess sodium and toxins.
Why are my eyes puffier than the rest of my face?
The skin around the eyes is the thinnest on the body and has fewer supportive structures. This makes it more prone to visible swelling from fluid retention, allergies, or lack of sleep. Additionally, lying flat during sleep allows fluid to settle directly under the eyes.
Do anti-puffiness skincare products really work?
Yes, but results vary. Products containing caffeine, peptides, or niacinamide have clinical backing for improving microcirculation and strengthening capillary walls. However, they work best when paired with healthy habits—not as standalone solutions.
Final Checklist: Beat Morning Face Puffiness
- ✔️ Limit sodium intake, especially at dinner
- ✔️ Avoid alcohol and heavy meals before bedtime
- ✔️ Sleep with your head slightly elevated
- ✔️ Stay hydrated throughout the day
- ✔️ Use cold therapy and facial massage each morning
- ✔️ Switch to hypoallergenic skincare and laundry products
- ✔️ Monitor for signs of underlying medical conditions
Conclusion: Wake Up Refreshed, Not Puffy
Morning facial puffiness is more than just a cosmetic concern—it’s a signal from your body about hydration, diet, sleep quality, and overall health. While occasional swelling is normal, recurring puffiness deserves attention. By adjusting simple daily habits and understanding the science behind fluid retention, you can transform how your face looks and feels every morning.
Start tonight: put down the salty snack, skip the late-night cocktail, and prop up your pillow. Tomorrow, greet the mirror with brighter eyes and a smoother complexion. Small changes compound into lasting results—and you deserve to wake up feeling as good as you look.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?