If you’ve ever launched a game only to be greeted by endless loading screens or lag spikes, while your phone breezes through 4K video streams, you’re not alone. Many gamers experience frustratingly slow internet speeds on their consoles despite having strong Wi-Fi on smartphones. The disconnect isn’t just in your head—it’s rooted in technical differences between devices, network behavior, and signal handling. Understanding these factors is the first step toward reclaiming smooth gameplay and reducing latency.
Understanding the Core Differences Between Devices
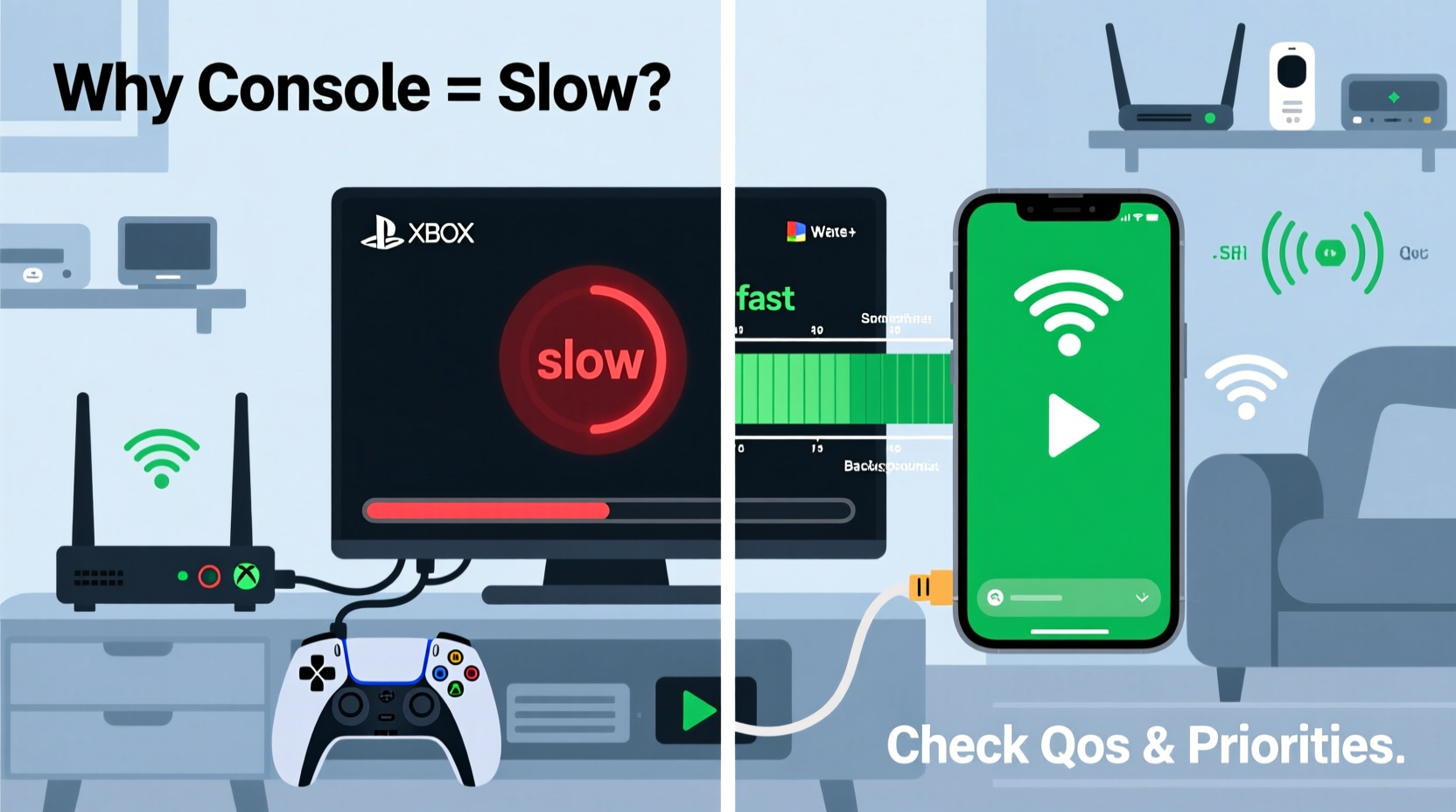
Your phone and gaming console may connect to the same router, but they are fundamentally different in how they use and respond to your network. Modern smartphones are engineered for mobility and efficiency, often equipped with advanced Wi-Fi chipsets optimized for quick data bursts, background syncing, and adaptive frequency switching. Gaming consoles, on the other hand, demand sustained high-bandwidth connections for downloads, voice chat, and real-time multiplayer interactions.
One key difference lies in **Wi-Fi standards**. Most recent phones support Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), which improves speed, reduces congestion, and enhances performance in crowded networks. Older or mid-tier consoles—like the PlayStation 4 or Xbox One—only support up to Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) or even older protocols. Even newer consoles like the PS5 and Xbox Series X include Wi-Fi 6, but their placement and antenna design can limit real-world performance compared to sleeker, more agile phones.
Another factor is **network prioritization**. Smartphones dynamically shift between Wi-Fi and cellular data, often choosing the fastest available option without user input. Consoles, however, lock into a single connection and lack intelligent failover mechanisms. If your console connects via a weak Wi-Fi signal, it won’t automatically switch—even if a better option exists.
Common Causes of Slow Console Internet Speeds
The disparity in performance usually stems from one or more of the following issues:
- Distance and physical obstructions: Walls, furniture, and appliances weaken Wi-Fi signals. Consoles are often placed in entertainment centers behind cabinets, which block radio waves.
- Interference from other devices: Microwaves, cordless phones, and Bluetooth gadgets emit electromagnetic noise that disrupts the 2.4 GHz band—commonly used by consoles.
- Network congestion: Multiple devices streaming, downloading, or updating simultaneously can saturate bandwidth, especially during peak hours.
- DNS bottlenecks: Default DNS settings may route traffic inefficiently, increasing latency.
- Firmware or software lags: Outdated console OS versions or router firmware can degrade network responsiveness.
Phones typically mitigate these issues through better antenna positioning, dual-band support, and aggressive power management. They also tend to reconnect faster after signal drops, whereas consoles may maintain a “connected” status even when throughput is poor.
Signal Strength vs. Real-World Performance
It’s possible for your console to show full Wi-Fi bars while still suffering from poor performance. Signal strength indicators reflect radio power, not actual data throughput. A strong signal doesn’t guarantee low latency or high bandwidth—especially if the channel is congested or interference is present.
“Many users assume full bars mean optimal performance, but in reality, signal quality, channel overlap, and packet loss matter far more than bar count.” — David Lin, Network Infrastructure Engineer at NetGrade Labs
Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnose and Fix Console Lag
Follow this structured approach to identify and resolve the root cause of slow internet on your console:
- Test your current speeds: Run a speed test directly on your console (via settings menu). Compare results with a test on your phone using the same network.
- Check connection type: Determine whether your console uses Wi-Fi or Ethernet. Wired connections almost always outperform wireless ones.
- Reboot your equipment: Power cycle your console, router, and modem. This clears temporary glitches and resets IP assignments.
- Move closer to the router: Temporarily relocate your console near the router to rule out distance-related degradation.
- Switch Wi-Fi bands: If your router supports dual-band (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz), connect your console to the less congested 5 GHz band for higher speeds and lower latency.
- Update firmware: Check for updates on both your console and router. Manufacturers often release patches that improve network stability.
- Change DNS settings: Replace default DNS with faster alternatives like Google DNS (8.8.8.8 / 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare (1.1.1.1).
- Limit background activity: Pause downloads, cloud backups, and automatic updates on other devices during gameplay.
- Use Quality of Service (QoS) settings: Log into your router’s admin panel and prioritize your console’s traffic to reduce lag.
- Test with Ethernet: Connect your console directly to the router via an Ethernet cable. If speeds improve significantly, your Wi-Fi setup needs optimization.
Comparison: Phone vs. Console Network Behavior
| Factor | Smartphone | Gaming Console |
|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi Standards Supported | Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 6E (on newer models) | Varies; PS4 = Wi-Fi 5, PS5/Xbox Series X = Wi-Fi 6 |
| Antenna Sensitivity | High (multiple internal antennas) | Moderate (limited by enclosure design) |
| Band Switching | Automatic (2.4 GHz ↔ 5 GHz ↔ cellular) | Manual or static once connected |
| Traffic Prioritization | OS manages app priorities efficiently | Limited; all games treated equally unless QoS enabled |
| Background Data Usage | Aggressive syncing, push notifications | Mainly system updates and cloud saves |
| Latency Tolerance | Higher (designed for variable conditions) | Lower (real-time interaction demands consistency) |
This table highlights why phones often appear “faster”—they’re built for adaptability, while consoles require stable, high-throughput environments to perform optimally.
Real Example: Fixing John’s Lagging PS5
John, a dedicated Call of Duty player, noticed his PS5 frequently dropped frames during matches, despite his phone streaming Netflix in 4K without buffering. His router was in the hallway, and the console sat inside a closed media cabinet 20 feet away. Initial speed tests showed 85 Mbps on his iPhone and only 18 Mbps on the PS5.
He followed the diagnostic steps: moved the console out of the cabinet, switched to the 5 GHz band, and updated his router firmware. Speeds improved to 62 Mbps. Still not ideal, he then connected via Ethernet and achieved 92 Mbps with ping reduced from 110ms to 28ms. The difference in gameplay was immediate—no more rubberbanding or delayed gunfire.
John’s case illustrates how environmental and configuration factors outweigh raw internet plans. His ISP provided ample bandwidth, but poor deployment limited his console’s access to it.
Essential Checklist for Optimal Console Performance
Use this checklist to ensure your console gets the best possible connection:
- ✅ Reboot router and modem weekly
- ✅ Position console within line-of-sight of the router
- ✅ Connect to the 5 GHz Wi-Fi band if supported
- ✅ Disable unused devices on the network during gaming
- ✅ Set custom DNS (e.g., 1.1.1.1 or 8.8.8.8)
- ✅ Enable QoS and assign highest priority to your console
- ✅ Use Ethernet whenever feasible
- ✅ Update console system software regularly
- ✅ Limit automatic downloads to off-peak hours
- ✅ Consider a Wi-Fi extender or mesh system for large homes
Frequently Asked Questions
Can my phone really have faster internet than my console on the same network?
Yes. Phones often have superior Wi-Fi reception due to better antenna design and adaptive connectivity. They may also use cellular data in the background, giving the impression of faster performance. Additionally, mobile apps are optimized for low-latency bursts, whereas consoles require continuous high-speed throughput.
Why does my console say “connected” but still lag?
A “connected” status only means the device has joined the network, not that it’s receiving usable bandwidth. Issues like packet loss, high ping, or throttling due to congestion can occur even with a stable connection. Always run a speed and latency test within your console’s network settings to verify actual performance.
Is Wi-Fi 6 necessary for gaming?
While not strictly necessary, Wi-Fi 6 offers significant advantages: lower latency, better handling of multiple devices, and improved efficiency in dense environments. If you live in a multi-device household or experience frequent interference, upgrading to a Wi-Fi 6-compatible router and using a modern console that supports it can make a noticeable difference.
Expert Recommendations for Long-Term Stability
For sustained improvements, experts recommend investing in infrastructure rather than relying solely on tweaks. A mesh Wi-Fi system like Google Nest Wi-Fi Pro, Eero Pro 6E, or ASUS ZenWiFi can eliminate dead zones and provide seamless roaming. These systems use intelligent routing to direct traffic where it’s needed most.
Additionally, enabling **MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple Input, Multiple Output)** allows your router to communicate with multiple devices simultaneously instead of sequentially, reducing wait times. Beamforming technology focuses signals toward active devices, improving range and reliability for consoles located farther from the router.
“Gamers should treat their network like any other critical component—just as important as graphics settings or controller sensitivity. A subpar connection undermines even the most powerful hardware.” — Sarah Nguyen, Lead Network Architect at GameNet Solutions
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Gaming Experience
The frustration of slow internet on your console while your phone flies through data is common—but entirely fixable. By understanding the technical disparities between devices and systematically addressing signal quality, interference, and network configuration, you can achieve the responsive, high-speed connection your games deserve. Don’t accept lag as inevitable. Use the tools, tips, and strategies outlined here to diagnose, optimize, and future-proof your setup.









 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4
Comments
No comments yet. Why don't you start the discussion?